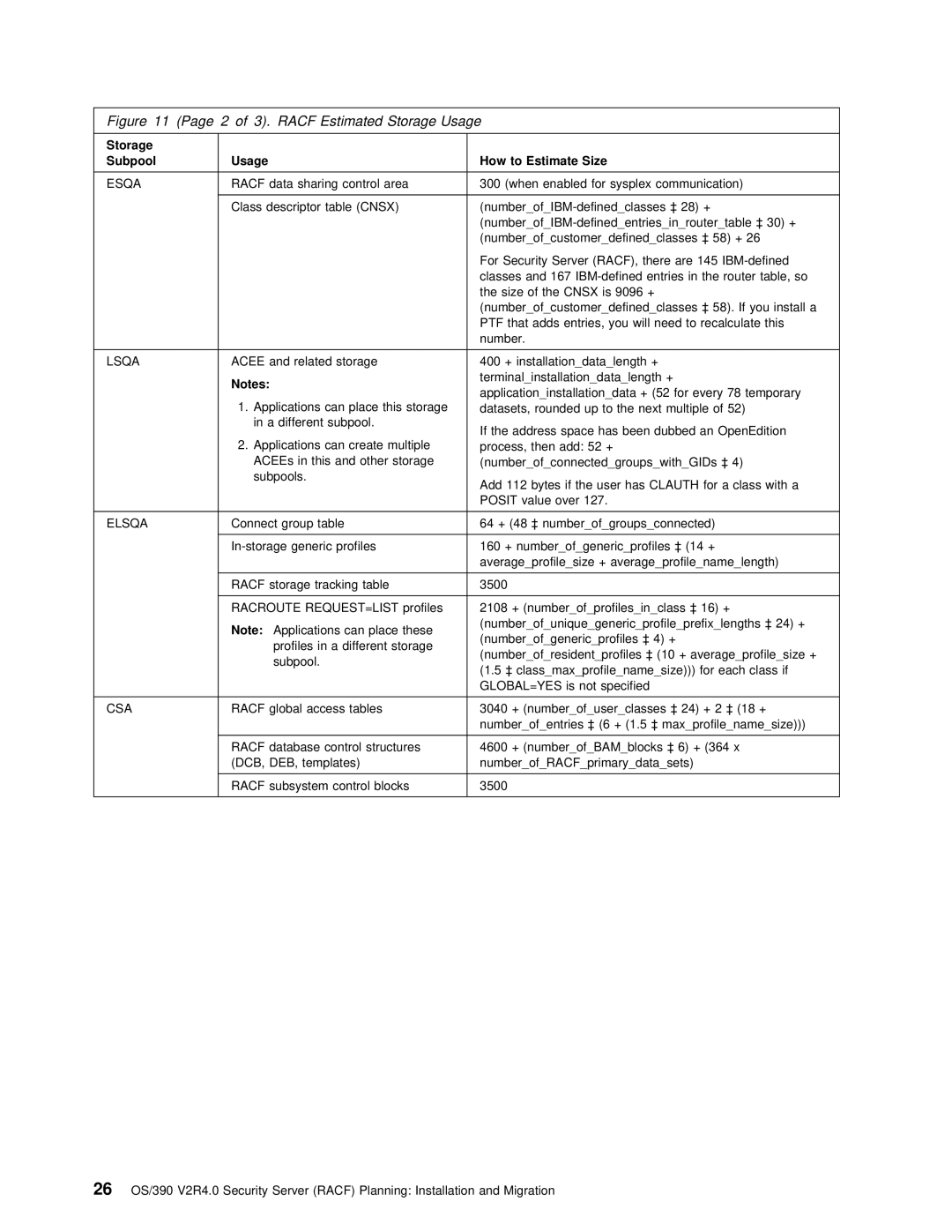
OS/390 specifications
IBM OS/390, a versatile operating system, was a cornerstone in enterprise environments and played a pivotal role in mainframe computing. Released in the mid-1990s, OS/390 combined the strengths of IBM's MVS (Multiple Virtual Storage) with new features and enhancements, targeting scalability, reliability, and performance in demanding business applications.One of the key features of OS/390 was its robust support for multiple users and processes. The system allowed thousands of concurrent users to access applications and data, ensuring high availability and minimizing downtime—a critical requirement for many large organizations. This scalability was supported through various enhancements in memory management and processor scheduling, enabling optimal resource allocation across diverse workloads.
OS/390 was known for its superior workload management capabilities. The Workload Manager (WLM) component allowed administrators to define service policies, specifying how system resources would be allocated according to the priority of tasks. This ensured that critical business processes received the necessary resources while less critical tasks were managed more flexibly.
Another significant characteristic of OS/390 was its commitment to security. The operating system provided comprehensive security features, including user authentication, data encryption, and auditing capabilities. This focus on security was vital for organizations handling sensitive data, ensuring compliance with regulations and safeguarding against unauthorized access.
OS/390 also supported advanced technologies that facilitated integration and development. The system included features like the IBM CICS (Customer Information Control System) for transaction processing and IMS (Information Management System) for database management. These technologies allowed organizations to build robust, high-performance applications tailored to specific business needs.
The ease of network integration was another strength of OS/390. With the advent of the Internet and global connectivity, OS/390 systems could easily interface with various network protocols, enabling businesses to operate in a connected world. This inclusion paved the way for many organizations to expand their capabilities and offer new services, driving digital transformation.
In conclusion, IBM OS/390 represented a significant advancement in mainframe technology, combining scalability, security, and robust workload management. Its rich feature set and support for critical enterprise applications solidified its role as a vital component of many organizations' IT infrastructures, ensuring they could meet their operational challenges head-on while supporting future growth. As technology continues to evolve, the legacy of OS/390 remains influential in the realm of computing.