DMZ Firewall Solution for the Express Router
The purpose of this setup is to prohibit any direct data transmission between the Internet and the secure network. All data must go through proxy servers on the DMZ.
We recommend that you set up the DMZ on the LAN2 (10 Mbps) port and your secure network on the LAN1 (100/10 Mbps) port.
This document provides two DMZ solutions when connecting to the Internet, one using a single external IP address and the other using a number of IP addresses (at least four IP addresses are needed, including network identification and broadcast address).
Note: Solutions using dynamic address assignment by the ISP are not supported.
1.4IP Filters in the Express Router
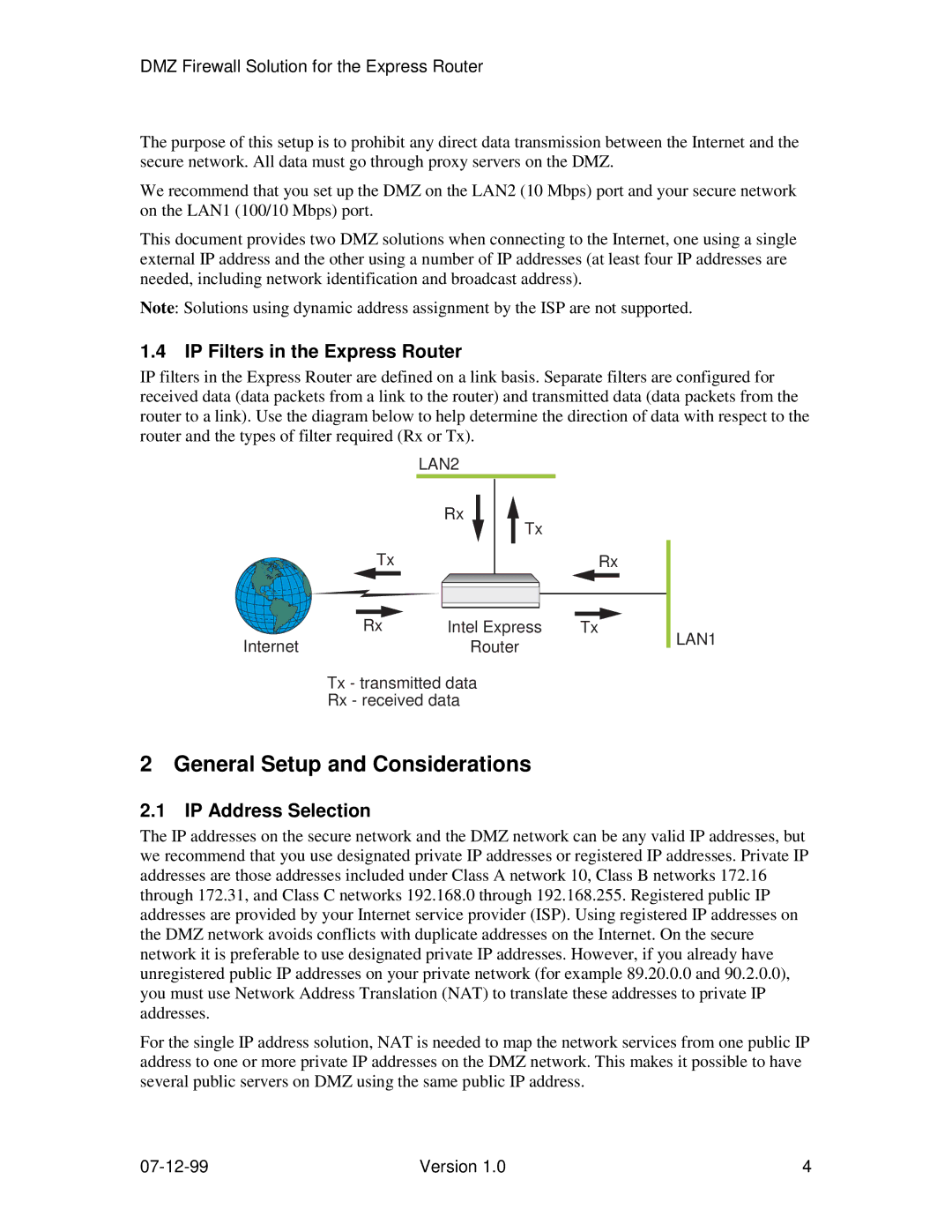
IP filters in the Express Router are defined on a link basis. Separate filters are configured for received data (data packets from a link to the router) and transmitted data (data packets from the router to a link). Use the diagram below to help determine the direction of data with respect to the router and the types of filter required (Rx or Tx).
| LAN2 |
| Rx |
| Tx |
Tx | Rx |
Rx | Intel Express | Tx |
InternetRouter
Tx - transmitted data
Rx - received data
2 General Setup and Considerations
2.1IP Address Selection
LAN1
The IP addresses on the secure network and the DMZ network can be any valid IP addresses, but we recommend that you use designated private IP addresses or registered IP addresses. Private IP addresses are those addresses included under Class A network 10, Class B networks 172.16 through 172.31, and Class C networks 192.168.0 through 192.168.255. Registered public IP addresses are provided by your Internet service provider (ISP). Using registered IP addresses on the DMZ network avoids conflicts with duplicate addresses on the Internet. On the secure network it is preferable to use designated private IP addresses. However, if you already have unregistered public IP addresses on your private network (for example 89.20.0.0 and 90.2.0.0), you must use Network Address Translation (NAT) to translate these addresses to private IP addresses.
For the single IP address solution, NAT is needed to map the network services from one public IP address to one or more private IP addresses on the DMZ network. This makes it possible to have several public servers on DMZ using the same public IP address.
Version 1.0 | 4 |