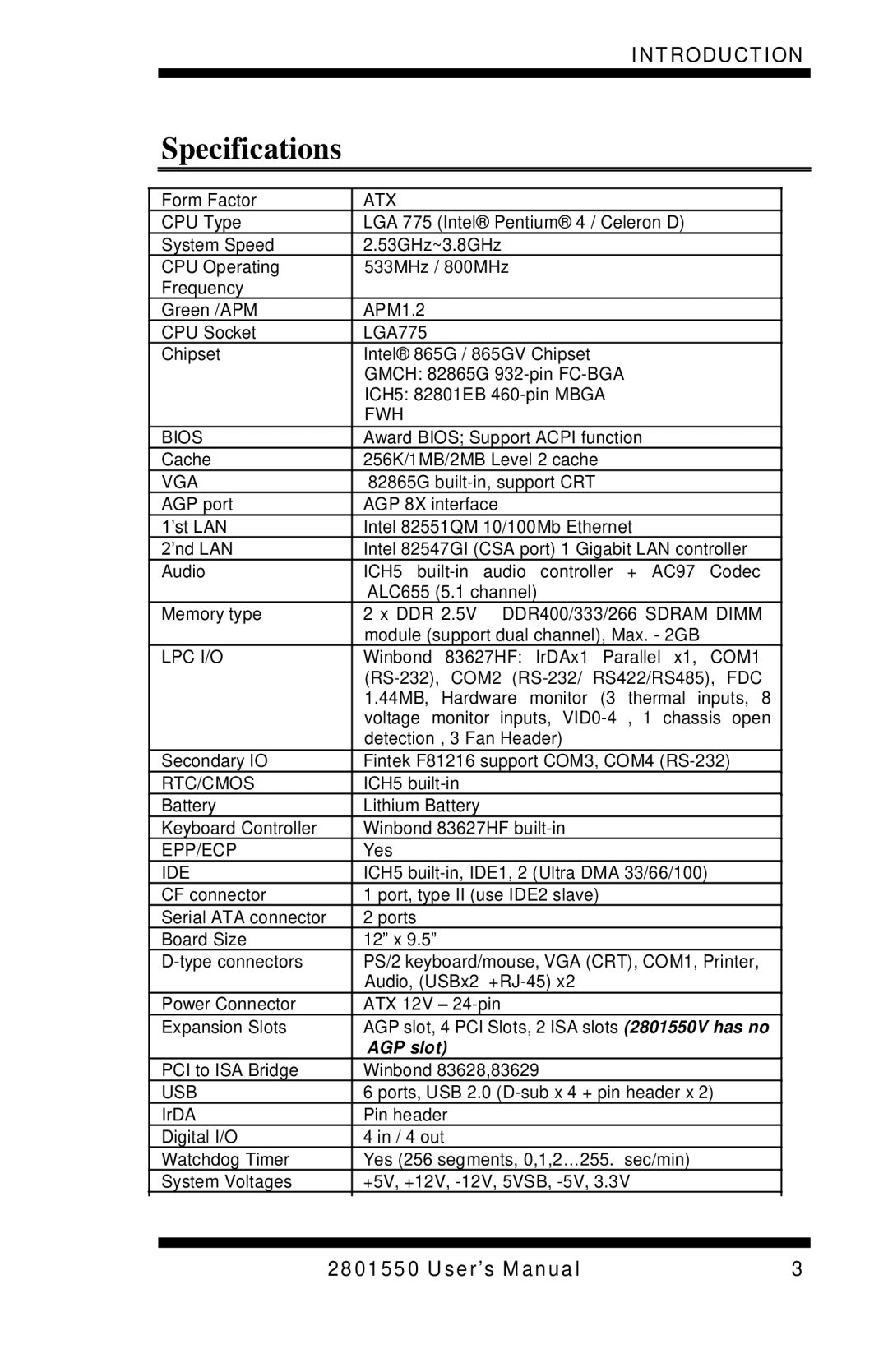
LGA775 specifications
The Intel LGA775, also known as Socket T, was a significant advancement in CPU socket design when it was introduced in 2004, primarily tailored for Intel's Pentium 4, Pentium D, Core 2 Duo, and Xeon processors. This socket provided a robust platform for users seeking performance improvements over previous socket designs, specifically the LGA 478.One of the standout features of LGA775 is its physical layout. The socket utilizes a Land Grid Array configuration, comprising 775 pins on the motherboard that create an electrical connection with the chip. This design enhances the physical stability of the connection, reducing the likelihood of damage during component installation.
LGA775 supports a range of Intel technologies such as Dual-Core processing, which significantly improved multitasking and performance in demanding applications by integrating two cores within a single processor. This advancement laid the groundwork for more efficient computing, catering to both casual and professional users alike.
Another key technology associated with the LGA775 platform is the Enhanced Speedstep Technology (EIST), which allowed processors to adjust their voltage and frequency dynamically. This not only optimized performance but also contributed to energy efficiency, making it a more environmentally friendly choice for users.
The socket supports various front-side bus (FSB) speeds, ranging from 800 MHz to 1600 MHz, enabling higher data transfer rates between the CPU and RAM. This performance characteristic is critical for applications that require substantial memory throughput, such as video editing and gaming.
Moreover, LGA775 was compatible with a variety of chipsets that enhanced its capabilities, such as those featuring Intel's own Express Chipsets. These chipsets included integrated graphics, USB 2.0 support, and improved storage interfaces like SATA, which streamlined data management and boosted overall system performance.
Over the years, LGA775 has become a popular choice for budget and mid-range desktops, particularly because of its versatility and broad compatibility with different processor generations. Even with the advent of newer sockets, LGA775 remains a memorable part of Intel's legacy, representing a crucial stepping stone towards modern multi-core architectures.
In summary, Intel's LGA775 socket brought about comprehensive advancements in design, performance, and power management, making it a noteworthy component in the history of computing. Its influence continues to be felt, as it set the standards for subsequent socket designs that prioritize efficiency and performance.