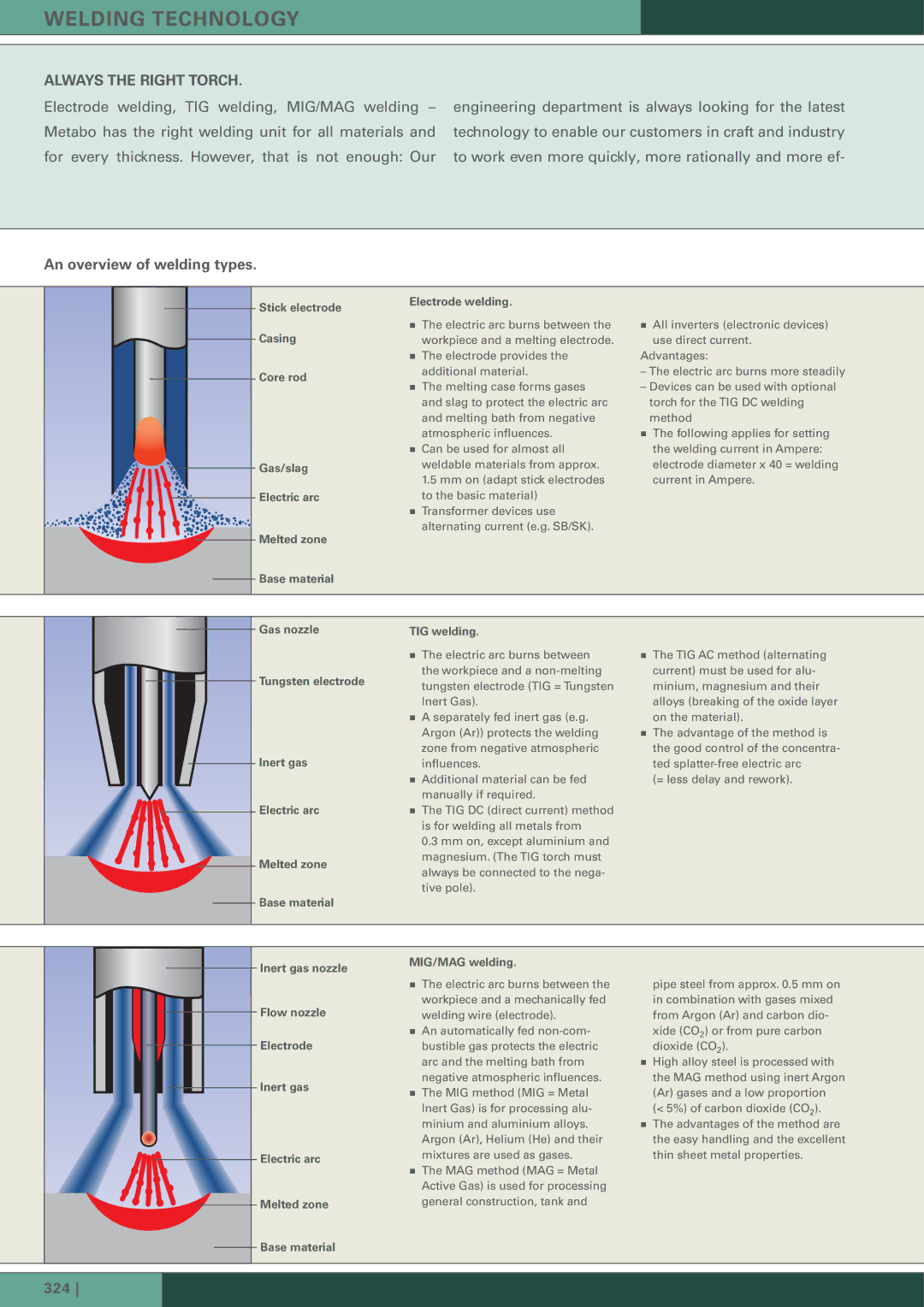
Welding Technology specifications
Metabo Welding Technology has established itself as a leader in the welding and cutting industry, providing innovative solutions tailored for professional welders and metalworkers. Known for their high-quality tools and advanced engineering, Metabo's welding technology is designed for durability, efficiency, and precision.One of the main features of Metabo's welding technology is its versatility. The company offers a wide range of welding machines, including MIG, TIG, and MMA (manual metal arc) welding, allowing users to perform various tasks with a single tool. This versatility enables welders to tackle projects in different settings, from automotive repairs to metal fabrication and welding workshops.
Metabo welding machines also incorporate advanced inverter technology, which enhances performance and efficiency. This technology enables the machines to deliver consistent arc stability, even in difficult conditions. It leads to smoother welding processes, reduces the risk of defects, and enhances overall productivity. The lightweight nature of inverter machines makes them portable, offering ease of use for professionals on the go.
Another noteworthy aspect of Metabo's welding technology is its user-centric design. Many machines come equipped with ergonomic handles and intuitive controls, allowing for long hours of comfortable operation. The interfaces are designed to provide clear visibility of settings, ensuring that users can adjust parameters without complicated navigation.
Safety is paramount in Metabo's welding solutions. Features such as thermal overload protection, which prevents overheating, and anti-stick mechanisms, which prevent the electrode from sticking to the workpiece, showcase the brand's commitment to user safety. These features help to mitigate common risks associated with welding, making the experience safer for operators.
Additionally, Metabo focuses on energy efficiency in its welding machines. With reduced energy consumption, users can benefit from lower operational costs while contributing to eco-friendly practices. This aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainability in various industries today.
In summary, Metabo Welding Technology stands out for its innovative and versatile range of welding machines, advanced inverter technology, ergonomic designs, safety features, and energy efficiency. With a commitment to quality and performance, Metabo continues to be a trusted choice for professionals demanding reliability and excellence in welding.