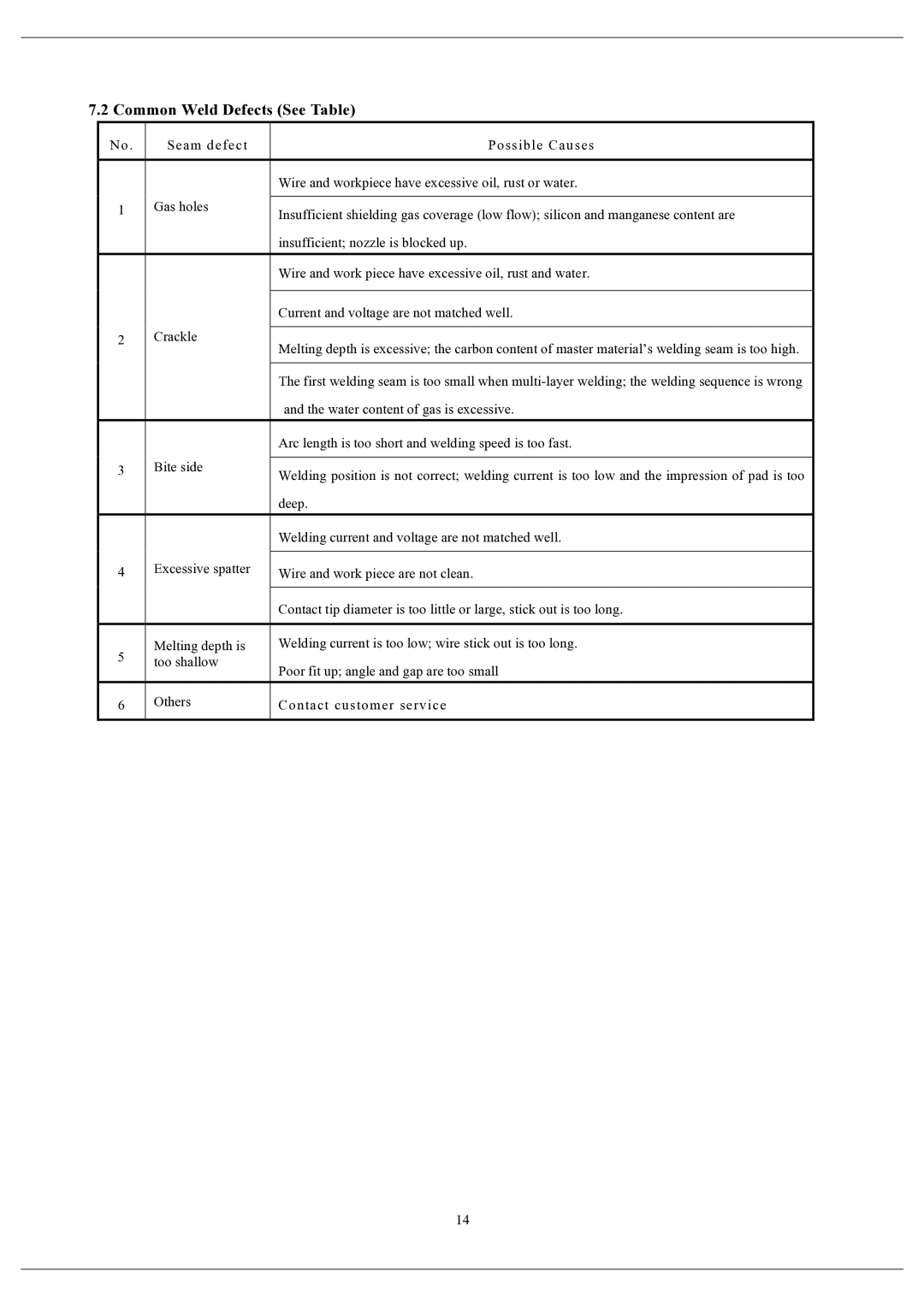
7.2 Common Weld Defects (See Table)
No. | Seam defect | Possible Causes | |
|
|
| |
|
| Wire and workpiece have excessive oil, rust or water. | |
1 | Gas holes |
| |
Insufficient shielding gas coverage (low flow); silicon and manganese content are | |||
|
| ||
|
| insufficient; nozzle is blocked up. | |
|
|
| |
|
| Wire and work piece have excessive oil, rust and water. | |
|
|
| |
|
| Current and voltage are not matched well. | |
2 | Crackle |
| |
Melting depth is excessive; the carbon content of master material’s welding seam is too high. | |||
|
| ||
|
|
| |
|
| The first welding seam is too small when | |
|
| and the water content of gas is excessive. | |
|
|
| |
|
| Arc length is too short and welding speed is too fast. | |
3 | Bite side |
| |
Welding position is not correct; welding current is too low and the impression of pad is too | |||
|
| ||
|
| deep. | |
|
|
| |
|
| Welding current and voltage are not matched well. | |
4 | Excessive spatter |
| |
Wire and work piece are not clean. | |||
|
|
| |
|
| Contact tip diameter is too little or large, stick out is too long. | |
|
|
| |
5 | Melting depth is | Welding current is too low; wire stick out is too long. | |
too shallow | Poor fit up; angle and gap are too small | ||
| |||
|
| ||
|
|
| |
6 | Others | Contact customer service | |
|
|
|
14