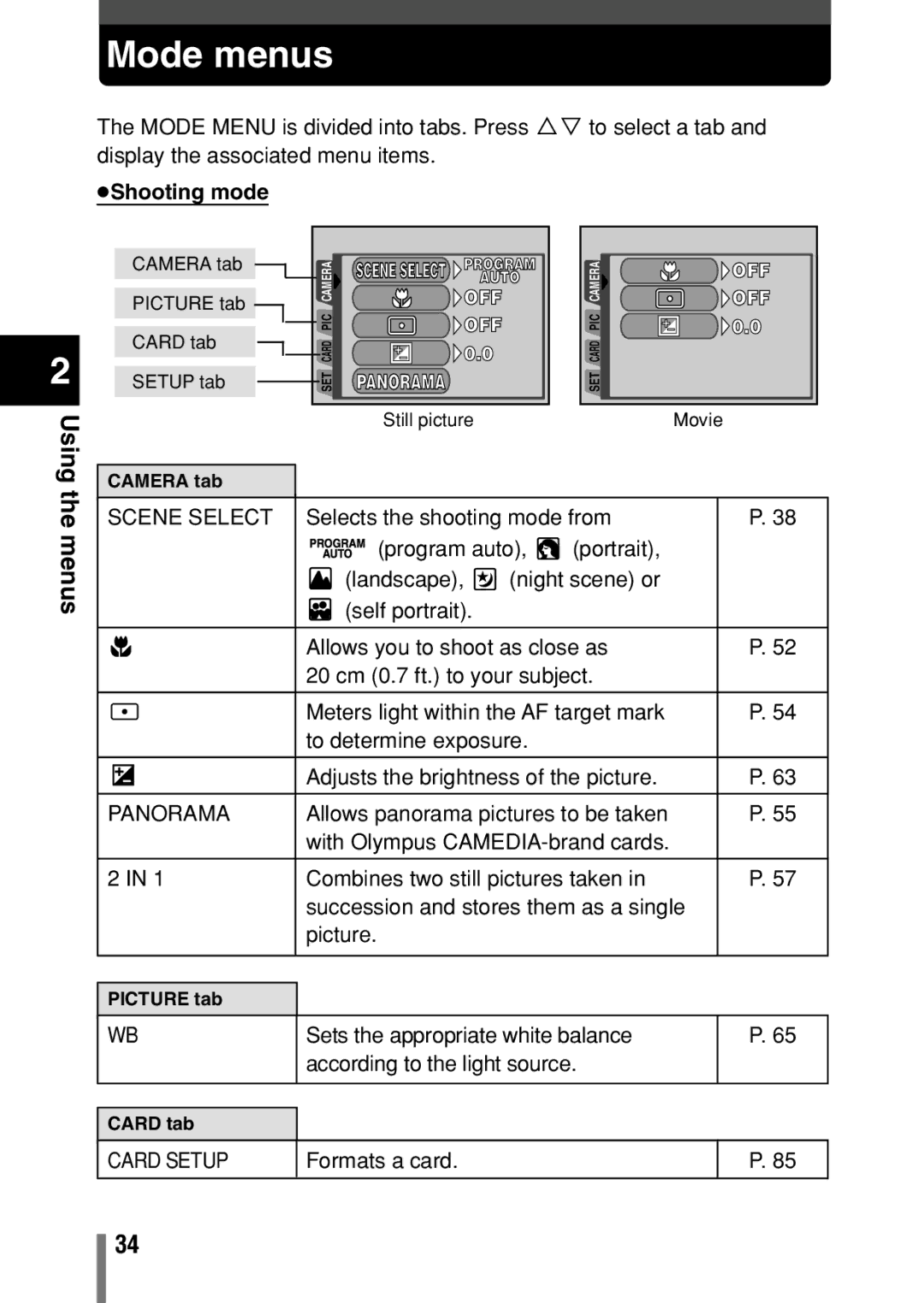
C-150, D390, D-390 specifications
The Olympus D-390, D390, and C-150 are compact digital cameras that made a significant impact in the early 2000s, introducing users to the world of digital photography with ease and efficiency. These models were designed for both beginners and more experienced users, providing a range of features that enabled high-quality image capture while remaining simple to operate.One of the standout features of the Olympus D-390 is its 3.2-megapixel image sensor. This resolution was quite impressive for its time, allowing users to take clear and detailed photos suitable for prints and sharing. The D-390 was equipped with a 3x optical zoom lens, enabling users to capture subjects both near and far without sacrificing image quality. This versatility made the camera a popular choice for various photography scenarios, whether it be landscapes, portraits, or spontaneous moments.
The camera's design emphasized user-friendliness, boasting a simple interface that made it accessible for users of all skill levels. The D-390 featured automatic exposure adjustments, allowing users to focus on framing their shot rather than fiddle with technical settings. Additionally, the camera supported a range of shooting modes, including portrait, landscape, and night scene, to help users get the best results in different lighting conditions.
Another key characteristic of the Olympus D-390 and similar models like the C-150 was their compact size and lightweight design. Weighing just a few ounces, they were ideal for users looking for a camera that could easily be carried in a pocket or purse. This portability encouraged spontaneous photography, as users could have their camera ready to capture unexpected moments.
The C-150 variant provided several enhanced features, including improved image quality due to advanced processing technologies. The inclusion of various scene modes allowed for greater customization of shooting preferences, catering to the specific needs of each photographic scenario. Furthermore, the C-150’s compatibility with xD-Picture Cards provided expandable storage, allowing users to store more images without worrying about running out of space.
In summary, the Olympus D-390, D390, and C-150 were pivotal models in the transition from film to digital photography. Their user-friendly design, impressive specifications for the time, and portability made them popular choices among amateur photographers. These cameras laid the foundation for the advanced digital cameras we see today, demonstrating Olympus's commitment to innovation and quality in the photography market.