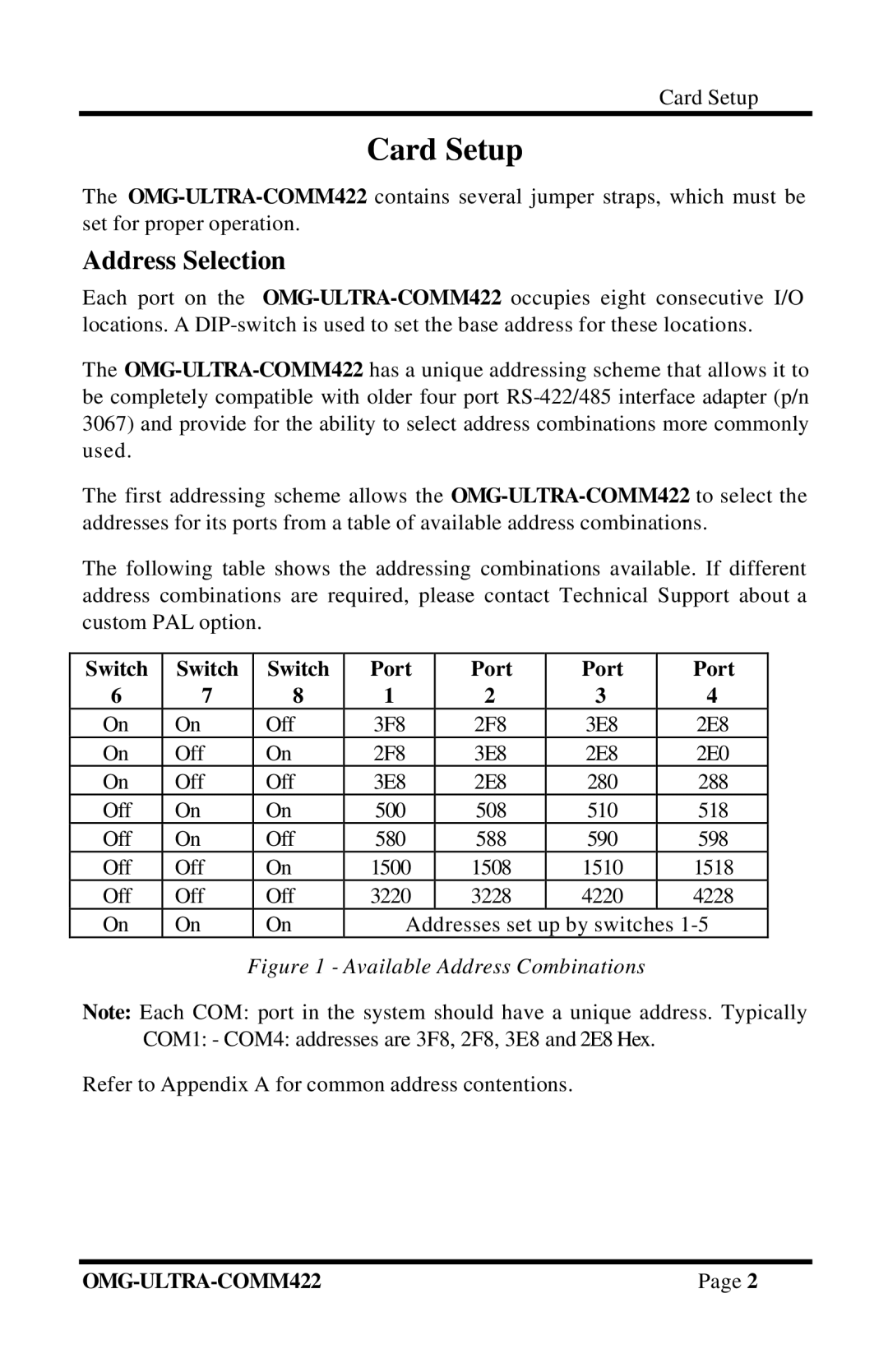
RS-422/485 specifications
Omega Engineering is a renowned leader in the field of measurement and control technologies, particularly in the realm of data communication for industrial automation. The RS-422 and RS-485 protocols are part of Omega's robust offering, designed to facilitate reliable and efficient data transmission over relatively long distances. These protocols are widely used in various applications ranging from industrial machinery to building automation systems.One of the main features of RS-422 is its ability to support long-distance communication, allowing data to be transmitted up to 4,000 feet (approximately 1,200 meters) at speeds of up to 10 Mbps. This is achieved through the use of differential signaling, which provides improved noise immunity compared to single-ended signaling systems. RS-422 employs a single transmitter and multiple receivers, making it ideal for point-to-multipoint configurations.
On the other hand, RS-485 extends the capabilities of RS-422 by allowing multiple devices to be connected on the same bus. It supports up to 32 devices, which can be either transmitters or receivers, making it exceptionally versatile for networking applications. RS-485 can communicate effectively over distances up to 4,000 feet and at speeds of 10 Mbps as well. This makes it an attractive option for applications where several devices need to communicate with a central controller.
An essential characteristic of both protocols is their resilience to electromagnetic interference, which is often a concern in industrial environments. The differential signaling used in RS-422 and RS-485 reduces noise susceptibility, ensuring data integrity even in challenging conditions. Additionally, these protocols function effectively in half-duplex or full-duplex modes, providing flexibility based on application requirements.
Moreover, Omega Engineering’s implementations of RS-422 and RS-485 comply with established standards, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices. This interoperability is crucial for seamless integration into existing systems and enhancing overall productivity.
In summary, Omega Engineering's RS-422 and RS-485 technologies offer robust, reliable, and versatile solutions for data communication in industrial settings. With features such as long-distance communication, multiple device connections, and exceptional noise immunity, these protocols continue to serve as foundational technologies in various automation and control applications. As industries evolve, Omega Engineering remains committed to advancing these technologies to meet the growing demands of modern data communication.