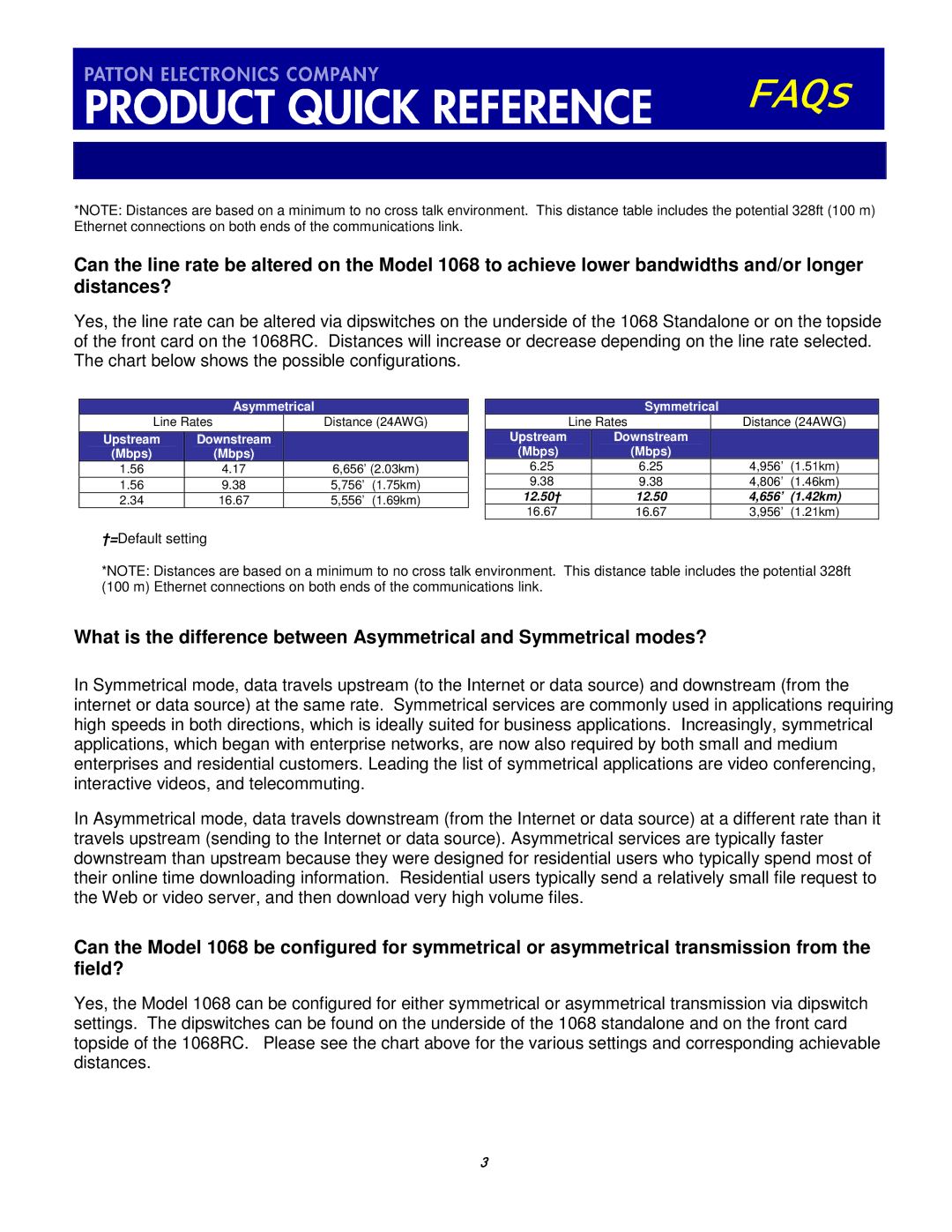
1068 VDSL specifications
Patton Electronic's 1068 VDSL is a high-performance device specifically designed to meet the demands of modern telecommunications environments. Utilizing very-high-bit-rate digital subscriber line (VDSL) technology, the 1068 model excels in providing efficient data transmission over existing copper telephone lines, significantly enhancing broadband service delivery.One of the standout features of the Patton 1068 VDSL is its exceptional data rates. The device can achieve upstream speeds of up to 100 Mbps and downstream speeds that can also reach similar levels under optimal conditions. This makes it ideal for service providers looking to offer high-speed internet access to residential and business customers, particularly in areas where fiber deployment is challenging or cost-prohibitive.
The 1068 VDSL incorporates advanced PAM-16 modulation technology, which enables it to transmit more bits per symbol. This results in greater efficiency and maximizes the use of available bandwidth. Furthermore, the device supports both ADSL and VDSL protocols, allowing for versatile operation across different network configurations.
One of the key characteristics of the Patton 1068 is its ease of installation and management. It features a user-friendly web-based interface that simplifies configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting tasks. This allows service providers to reduce deployment time and operational costs while ensuring an optimal user experience.
The 1068 VDSL also boasts enhanced reach capabilities, achieving transmission distances of up to 1,500 meters under optimal conditions. This extended range makes it particularly advantageous for connecting remote locations that might be far from a central office.
In terms of reliability, this device is equipped with robust error correction techniques and quality of service (QoS) features, ensuring stable and uninterrupted connectivity. It supports a variety of service-level agreements (SLAs) to accommodate diverse customer needs.
In conclusion, the Patton Electronic 1068 VDSL is a versatile and powerful solution for addressing the growing demand for high-speed internet services. Its combination of high data rates, extended reach, easy management, and reliable performance makes it an attractive option for telecommunications providers seeking to enhance their offerings and improve customer satisfaction. With its ability to leverage existing infrastructure, the 1068 VDSL represents a significant advancement in broadband technology, helping to bridge the digital divide in underserved areas.