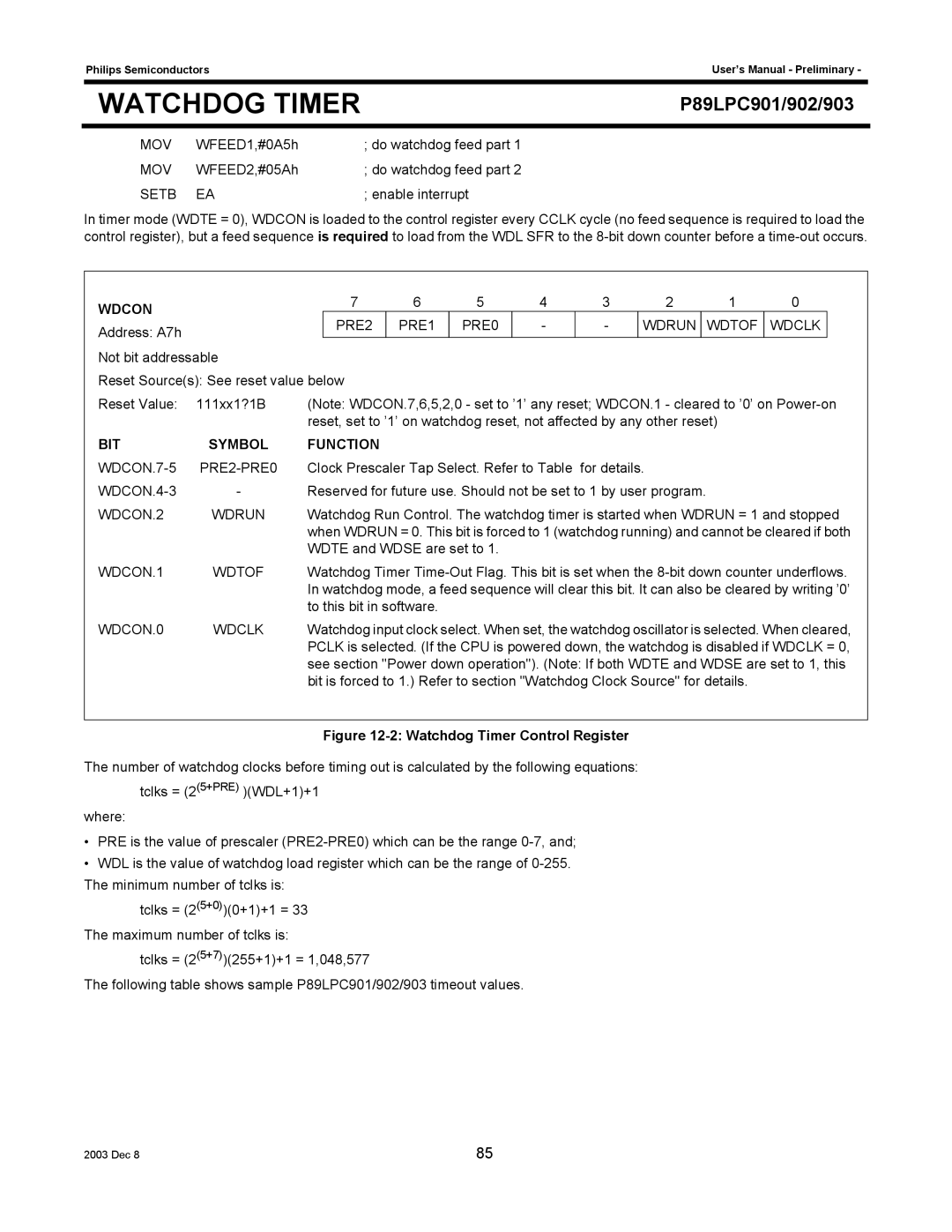
P89LPC903, P89LPC902, P89LPC901 specifications
The Philips P89LPC901, P89LPC902, and P89LPC903 are a series of 8-bit microcontrollers designed for embedded system applications. These models, which belong to the LPC900 series, are notable for their affordability and versatility, making them an attractive choice for both hobbyists and professional developers.One of the core features of the P89LPC901, P89LPC902, and P89LPC903 microcontrollers is their powerful 8-bit architecture. Operating at clock speeds up to 20 MHz, they deliver efficient performance suited for a range of tasks. Each model includes a comprehensive instruction set that supports various data manipulation and arithmetic functions, enabling extensive programming capabilities.
These microcontrollers come with built-in memory, with configurations that vary among the three models. The P89LPC901 typically features 4 KB of Flash memory and 256 bytes of RAM, while the P89LPC902 and P89LPC903 offer enhanced memory options. This Flash memory allows for reprogrammability, making it easier to update and modify applications as needed.
Another significant characteristic of the LPC900 series is their integrated peripherals. These models are equipped with a variety of I/O ports, allowing for easy interfacing with other devices and components. The P89LPC901 supports up to 32 I/O pins, while the P89LPC902 and P89LPC903 provide additional features such as analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), timers, and serial communication interfaces. This broad range of peripherals empowers developers to design complex applications without needing extra hardware.
Power consumption is also a key consideration for microcontroller applications. The P89LPC901, P89LPC902, and P89LPC903 are designed with low power consumption in mind, making them ideal for battery-operated devices and energy-efficient projects. They can operate in various power modes, allowing for greater flexibility in deployment.
In terms of technology, these microcontrollers utilize advanced CMOS technology, ensuring high reliability and durability. Their design offers a robust solution for numerous applications, including consumer electronics, industrial controls, and automation systems.
In summary, the Philips P89LPC901, P89LPC902, and P89LPC903 microcontrollers present an attractive combination of performance, integrated peripherals, low power consumption, and versatility. Their features cater to a wide array of applications, keeping them relevant in a rapidly evolving technology landscape. For hobbyists and professionals alike, these microcontrollers represent a reliable foundation for embedded system development.