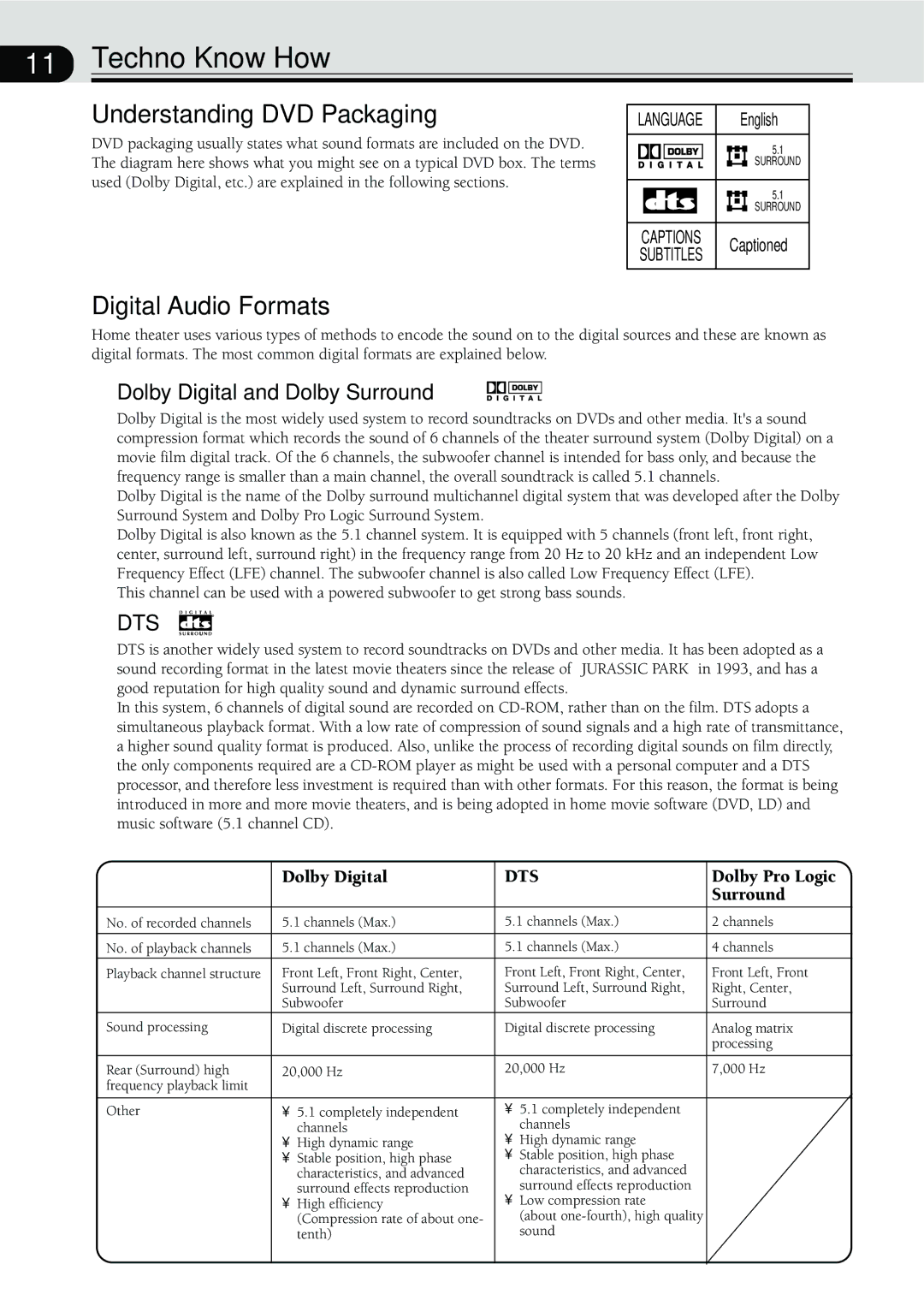
VSX-C300-S, VSX-C300 specifications
The Pioneer VSX-C300 and VSX-C300-S are compact, versatile audio receivers that cater to both casual listeners and home theater enthusiasts. Designed with modern technology and user-friendly features, these models deliver impressive sound quality in a sleek and stylish package.One of the standout features of both the VSX-C300 and VSX-C300-S is their 5.1 channel surround sound capability. This allows users to enjoy a rich audio experience, whether watching movies or listening to music. The receivers support various audio formats, including Dolby Digital and DTS, ensuring comprehensive compatibility with a wide range of media.
Both models are equipped with Advanced Direct Energy HD Amplification technology, which minimizes energy waste while maximizing output quality. This technology not only reduces power consumption but also enhances audio clarity, providing a dynamic listening experience. Additionally, the receivers feature 100 watts per channel, which ensures sufficient power for driving speakers while maintaining low distortion levels.
Integrated into the VSX-C300 and VSX-C300-S is a multitude of connectivity options. These receivers include HDMI inputs, which support high-definition video and audio, along with analog inputs for legacy devices. The availability of digital optical and coaxial inputs further enhances flexibility, offering users multiple ways to connect their media sources.
The user interface is intuitive, featuring a clear display and an easy-to-navigate remote control. Both receivers also support basic networking capabilities, allowing users to access music streaming services. This feature is particularly appealing in today's digital age, where convenience and access to a vast library of music are paramount.
Pioneer places a strong emphasis on ease of use, and both receivers reflect that ethos. Automatic speaker calibration simplifies the setup process, ensuring that users achieve optimal sound quality tailored to their room's acoustics. The included MCACC (Multi-Channel Acoustic Calibration System) automatically adjusts settings to create an immersive sound environment.
In summary, the Pioneer VSX-C300 and VSX-C300-S combine stylish design with advanced audio technology. Their 5.1 channel surround sound, Advanced Direct Energy HD Amplification, multiple connectivity options, and user-friendly features make these receivers an excellent choice for anyone looking to enhance their audio experience. Whether for movie nights or enjoying music, these receivers are a solid investment for quality sound.