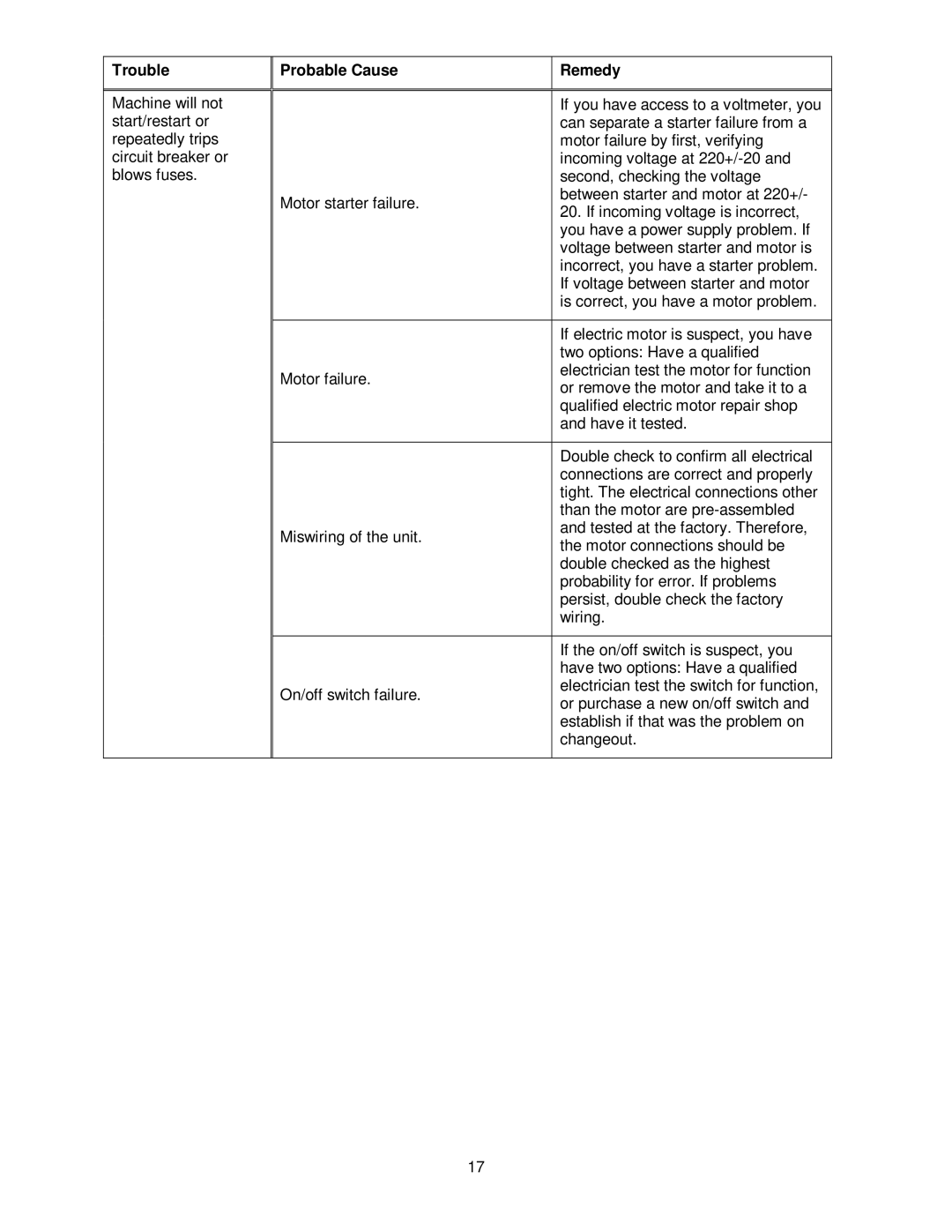
Trouble
Machine will not start/restart or repeatedly trips circuit breaker or blows fuses.
Probable Cause | Remedy | |
|
| |
| If you have access to a voltmeter, you | |
| can separate a starter failure from a | |
| motor failure by first, verifying | |
| incoming voltage at | |
| second, checking the voltage | |
Motor starter failure. | between starter and motor at 220+/- | |
20. If incoming voltage is incorrect, | ||
| ||
| you have a power supply problem. If | |
| voltage between starter and motor is | |
| incorrect, you have a starter problem. | |
| If voltage between starter and motor | |
| is correct, you have a motor problem. | |
|
| |
| If electric motor is suspect, you have | |
| two options: Have a qualified | |
Motor failure. | electrician test the motor for function | |
or remove the motor and take it to a | ||
| ||
| qualified electric motor repair shop | |
| and have it tested. | |
|
| |
| Double check to confirm all electrical | |
| connections are correct and properly | |
| tight. The electrical connections other | |
| than the motor are | |
Miswiring of the unit. | and tested at the factory. Therefore, | |
the motor connections should be | ||
| ||
| double checked as the highest | |
| probability for error. If problems | |
| persist, double check the factory | |
| wiring. | |
|
| |
| If the on/off switch is suspect, you | |
| have two options: Have a qualified | |
On/off switch failure. | electrician test the switch for function, | |
or purchase a new on/off switch and | ||
| ||
| establish if that was the problem on | |
| changeout. | |
|
|
17