Automation– and Drive Technology- SCE
2.NOTES FOR DATA BLOCKS
Data Blocks (DBs) can be used by your program to save data in the CPU. Your hard disk contains up to 8 KBytes ( 8192 Bytes ) space.
There are two types of data blocks. Global DBs, where all OBs, FBs and FCs read all saved data or can even write in the DB and local instance DBs, which are assigned a particular FB.
In the DBs, different data types (e.g. BOOL or WORD ) can be saved in arbitrary order. This structuring of a DB follows through input in a table with the tool
LAD, STL,FBD - S7 Block Programming .
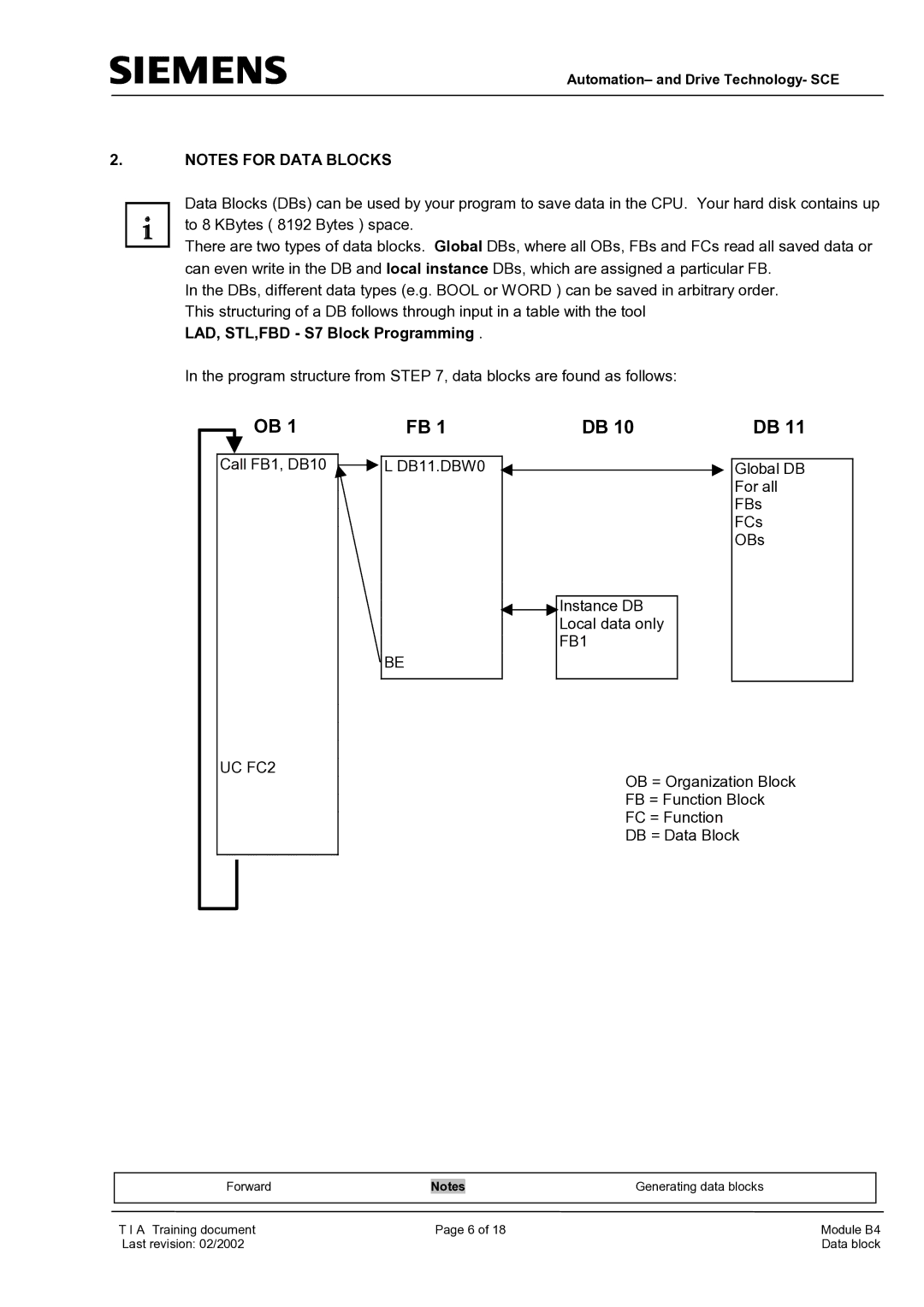
In the program structure from STEP 7, data blocks are found as follows:
| OB 1 |
|
|
|
| FB 1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Call FB1, DB10 |
|
| L DB11.DBW0 | |||
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
BE
UC FC2
DB 10 |
| DB 11 |
|
|
|
Global DB
For all
FBs
FCs
OBs
Instance DB
Local data only
FB1
OB = Organization Block
FB = Function Block
FC = Function
DB = Data Block
|
|
|
|
|
Forward | Notes |
| Generating data blocks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
T I A Training document | Page 6 of 18 | Module B4 | ||
Last revision: 02/2002 |
|
| Data block | |