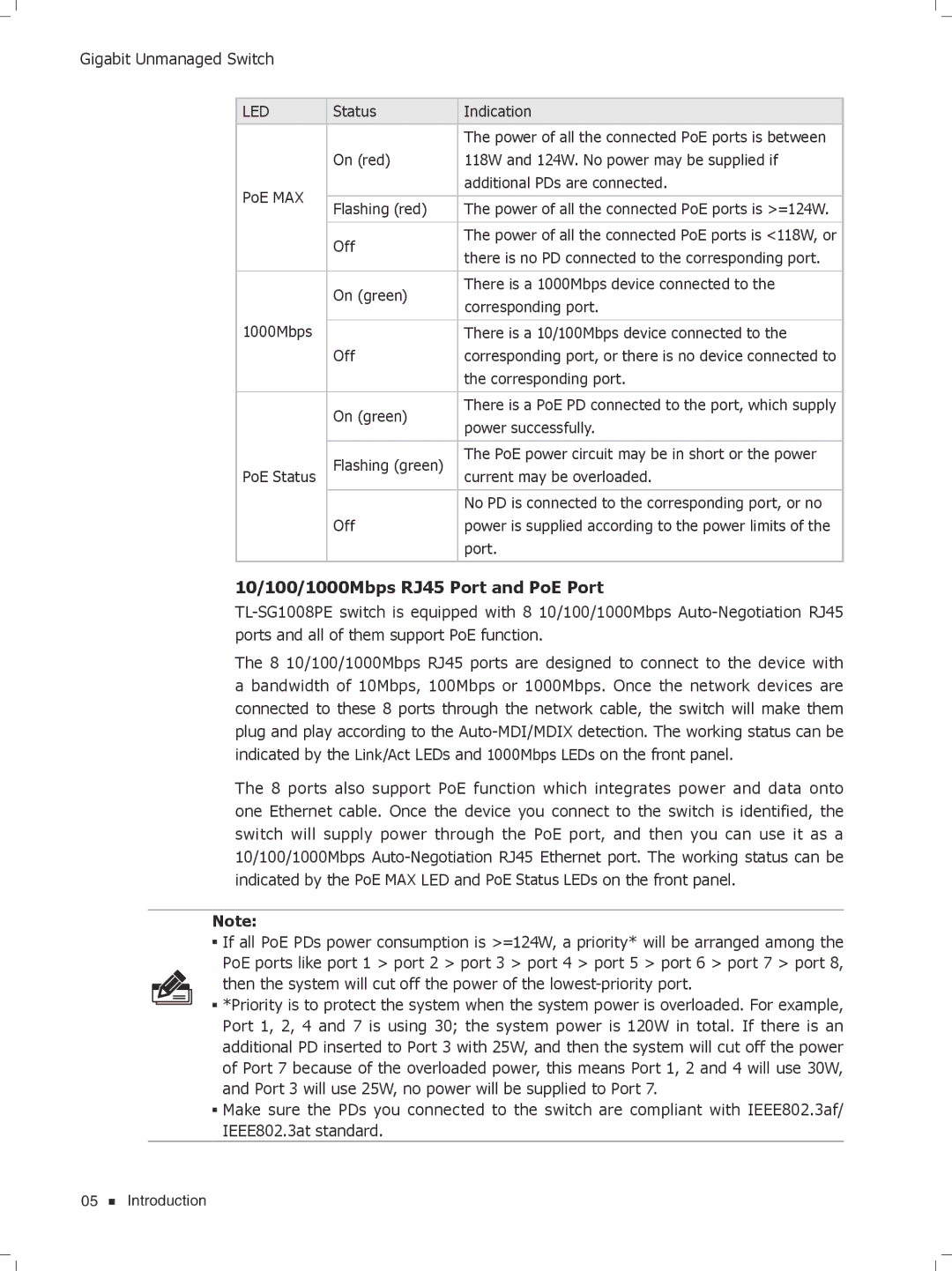
TL-SG1024D, TL-SG1016D, TL-SG1008PE, TL-SG1016, TL-SG1008 specifications
TP-Link has earned a reputation for delivering reliable and high-performance networking solutions, and its series of Gigabit switches is no exception. Among its offerings, the TL-SG1016, TL-SG1048, TL-SG1024, TL-SG1008, and TL-SG1016D stand out for their robust features, advanced technologies, and versatility in meeting the needs of various network environments.The TL-SG1016 is a 16-port Gigabit Ethernet switch designed for small to medium-sized businesses. It boasts a user-friendly design, enabling easy plug-and-play setup without the need for configuration. With a wide range of supported operating systems, this switch is compatible with various devices, ensuring seamless integration into existing networks. It supports auto-negotiation, delivering optimal port speed and duplex mode, thus enhancing overall performance.
For those requiring additional port density, the TL-SG1048 offers 48 ports while retaining the same high performance. It’s ideal for larger networks, providing ample connectivity for devices and users. The switch features Layer 2 technology, ensuring efficient data forwarding and enhanced traffic management. Its fanless design contributes to silent operation, making it suitable for office environments where noise levels must be kept to a minimum.
The TL-SG1024, with its 24-port configuration, strikes a balance between size and performance, making it perfect for growing networks. Much like its siblings, it utilizes Gigabit Ethernet to facilitate high-speed data transfers. An essential characteristic of this switch is its energy efficiency—compliance with IEEE 802.3az standards allows it to save power during low-traffic periods, contributing to lower operational costs.
The TL-SG1008 is an 8-port switch designed for small offices or home use. Despite its compact size, it delivers Gigabit speeds across all ports, ensuring that bandwidth-intensive applications run smoothly. It also features a plug-and-play setup for straightforward installation and ease of use.
Finally, the TL-SG1016D is a cost-effective 16-port switch tailored for small office needs. It includes features like auto-MDI/MDIX, which eliminates the need for crossover cables, allowing for versatility in connections. The switch’s metal casing ensures durability, while its power-saving technology minimizes energy consumption.
These TP-Link switches effectively combine performance, energy efficiency, and user-friendly features, making them suitable for diverse networking needs in both commercial and residential environments. Their reliability and excellent performance make them a preferred choice for users looking to enhance their network infrastructure.