SBFTF10xx-10x
Operation -- Continued
Product Features -- Continued
Distance Extension
The SBFTF10xx-10x media converter segments 10Base-T copper Ethernet and/or 100Base-TX copper fast Ethernet and 100Base-FX fiber fast Ethernet collision domains.
In a half-duplexEthernet or fast Ethernet environment, the SBFTF10xx-10x media converter extends network distances by segmenting collision domains so that the 5-Segment Rule (see page 10) or the 512-Bit Rule (see pages 9 and 10) applies separately to each collision domain.
In a full-duplexEthernet or fast Ethernet environment, the SBFTF10xx-10x media converter extends network distances to the physical cable limitations imposed by the selected copper and fiber cables (see pages 1 and 2).
Congestion Reduction
The SBFTF10xx-10x media converter does not forward collision signals or error packets from one collision domain to another, improving baseline network performance. In addition, the media converter filters packets destined for local devices, also reducing network congestion.
Optional Accessories (sold separately)
Part Number Description
SPS-1872-SAOptional External Power Supply; 18-72VDC Stand-Alone Output: 12.6VDC, 1.0 A
SPS-1872-PSOptional External Power Supply; 18-72VDC Piggy-back; Output: 12.6VDC, 1.0 A
E-MCR-0412-Slot Media Converter Rack (includes universal internal power supply) 17 x 15 x 5 in. (432 x 381 x 127 mm)
WMBL Optional Wall Mount Brackets; Length: 4.7in. (119mm)
WMBV Optional Vertical Mount Bracket; Length: 5.0 in. (127 mm)
WMBD Optional DIN Rail Mount Bracket; Length: 5.0 in. (127 mm)
WMBD-FOptional DIN Rail Mount Bracket (flat); Length: 3.3in. (84 mm)
Half-Duplex Network
512-Bit Rule - 100Base-TX or 100Base-FX
Use the 512-Bit Rule to calculate the 100Base-TX or 100Base-FX half-duplex collision domain.
In a half-duplex network, the maximum cable lengths are determined by the round trip delay limitations of each fast Ethernet collision domain. (A collision domain is the longest path between any two terminal devices, e.g. a terminal, switch, or router.)
The 512-Bit Rule determines the maximum length of cable permitted by calculating the round-trip delay in bit-times (BT) of a particular collision domain. If the result is less than or equal to 512 BT, the path is good.
To calculate the round-trip delay for a collision domain:
| 1. | Find the collision domain, i.e. the longest | | |
| | path between any two terminal devices | Class I hub | 140 BT |
| | (e.g., terminal, switch, and/or router). | Class II hub | 92 BT |
| 2. | Calculate the round-trip delay in bit- | terminal/router | 50 BT |
| | times for each length of cable. | 1 meter TP cable | 1.11 BT |
| | 1 meter fiber cable | 1 BT |
| 4. | Determine the bit-time values for each |
| Fast Ethernet switch | 50 BT |
| 3. | device (see table to the right). | SBFTF10xx-10x | 50 BT |
| Add the bit-time values for each length of | | |
cable and the bit-times for each device.
NOTE: The 512-Bit Rule applies separately to each collision domain.
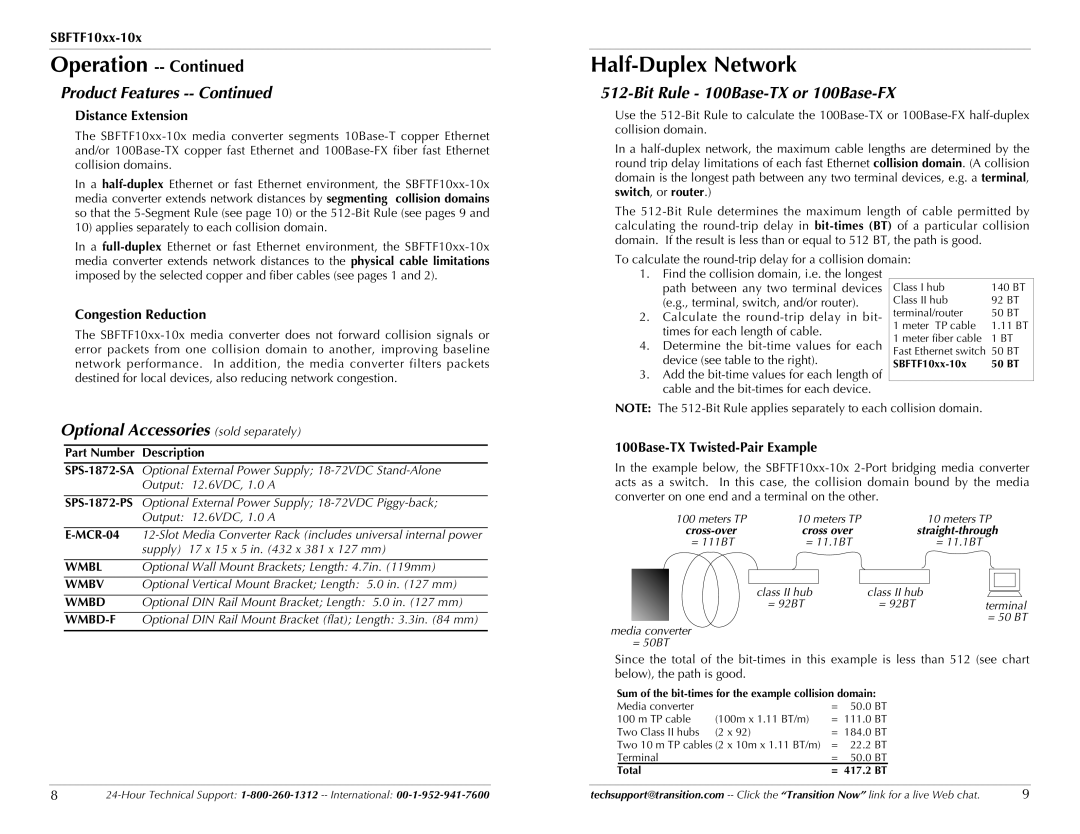
100Base-TX Twisted-Pair Example
In the example below, the SBFTF10xx-10x 2-Port bridging media converter acts as a switch. In this case, the collision domain bound by the media converter on one end and a terminal on the other.
100 meters TP | 10 meters TP | | 10 meters TP |
cross-over | cross over | straight-through |
= 111BT | = 11.1BT | | | = 11.1BT |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| class II hub | class II hub | | |
| = 92BT | = 92BT | | terminal |
| | | | | | = 50 BT |
media converter
= 50BT
Since the total of the bit-times in this example is less than 512 (see chart below), the path is good.
Sum of the bit-times for the example collision domain:
Media converter | | = | 50.0 | BT |
100 m TP cable | (100m x 1.11 BT/m) | = | 111.0 | BT |
Two Class II hubs | (2 x 92) | = | 184.0 | BT |
Two 10 m TP cables (2 x 10m x 1.11 BT/m) | = | 22.2 | BT |
Terminal | | = | 50.0 | BT |
Total | | = | 417.2 | BT |