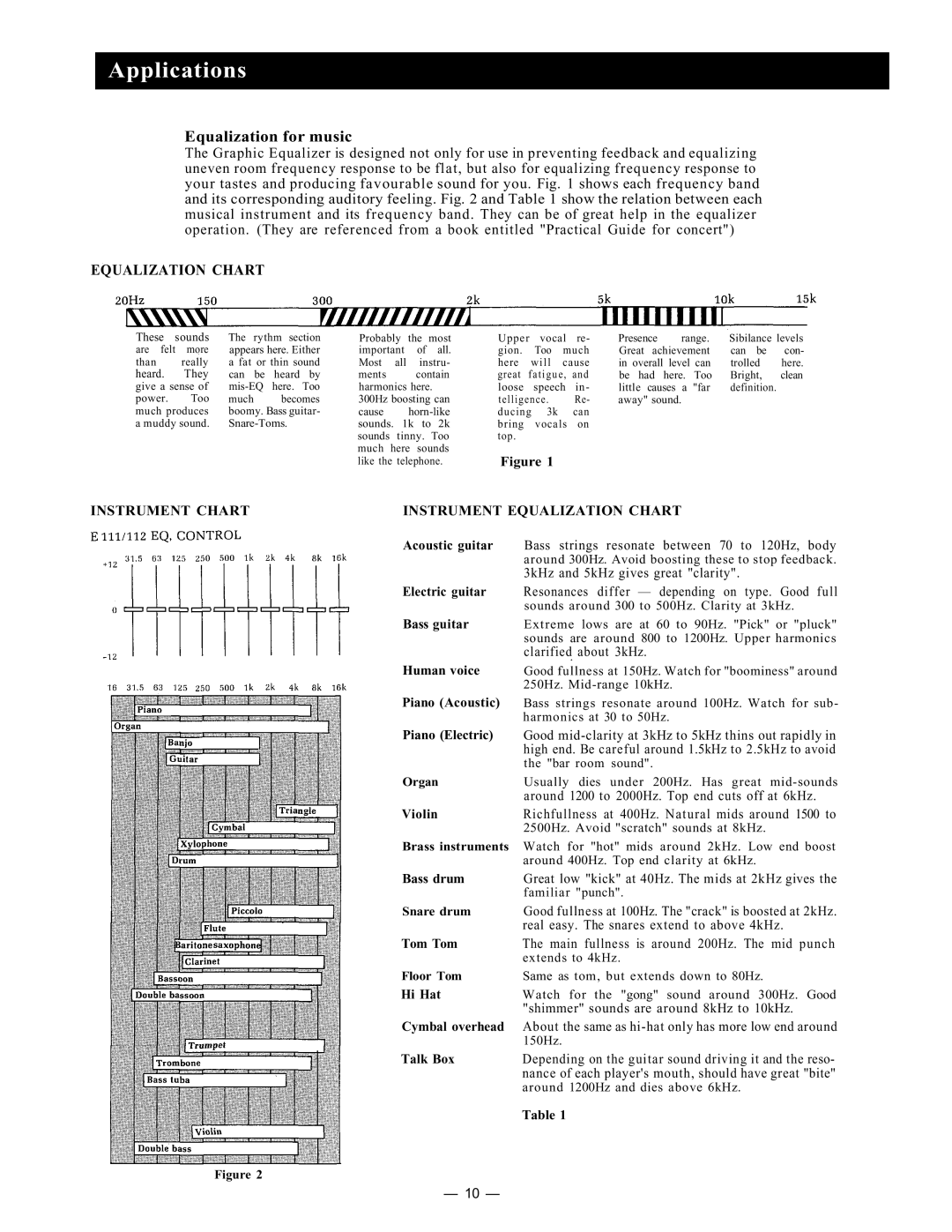
E111 specifications
The Viking Electronics E111 is a versatile and reliable entry phone designed to enhance security and communication in various settings, including schools, businesses, and residential buildings. This product stands out for its robust construction and user-friendly features, catering to users seeking both durability and functionality.One of the main features of the E111 is its high-quality communication capabilities. It is equipped with a built-in speaker and microphone, allowing for clear two-way audio communication between the entry point and the designated answering location. This is particularly beneficial in situations where immediate interaction is necessary, such as for visitor access or emergency notifications.
The E111 utilizes advanced technology to ensure reliability and ease of use. It incorporates a touch-tone keypad, making it easy for users to dial specific numbers without requiring extensive training. The keypad's design is user-friendly, featuring large buttons that are easy to see and press, even in low-light conditions.
Another notable characteristic of the Viking E111 is its robust construction. The unit is housed in a rugged, weather-resistant enclosure that can withstand harsh environmental conditions. This makes it suitable for outdoor installations where exposure to moisture and temperature fluctuations is a concern. The durable design ensures that the E111 will provide reliable service over time.
In terms of installation, the E111 is designed for straightforward integration into existing systems. It offers multiple mounting options, which can accommodate various installation preferences and locations. The unit can be connected to a standard telephone line or integrated into a larger intercom system, offering flexibility to suit the specific needs of any facility.
Moreover, the E111 features adjustable volume controls, allowing users to customize audio levels for optimal clarity. This adaptability is especially useful in environments with varying noise levels, ensuring effective communication regardless of surrounding distractions.
Overall, the Viking Electronics E111 entry phone is an ideal solution for enhancing security and communication at entry points. Its combination of advanced technology, user-friendly features, and robust construction makes it a popular choice for a variety of applications. Whether it is used in a commercial building, a school, or a residential setting, the E111 delivers reliable performance and ease of use for both residents and visitors alike.