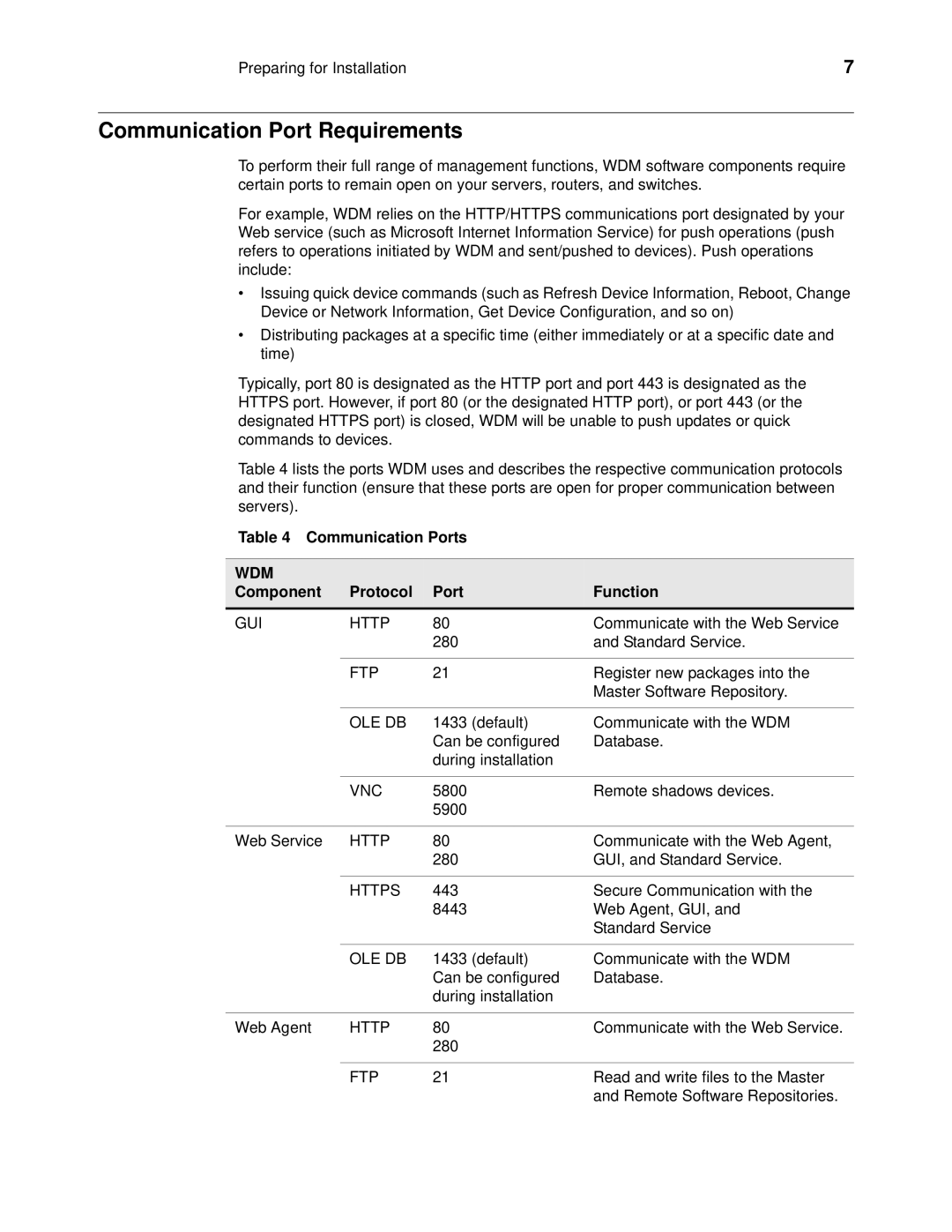
wyse devise manager release 4.9 specifications
Wyse Technology, a prominent provider of cloud client computing solutions, has made significant strides in enhancing device management capabilities with the release of Wyse Device Manager (WDM) version 4.9. This latest iteration introduces a plethora of features designed to optimize the management of Wyse thin clients, making it an indispensable tool for IT administrators.One of the standout features of WDM 4.9 is its improved user interface, which streamlines navigation and provides a more intuitive experience. The revamped dashboard allows administrators to gain insights into the status of devices at a glance. This user-friendly design not only enhances usability but also reduces the learning curve for new users.
WDM 4.9 also emphasizes automation and efficiency. Enhanced scheduling capabilities enable IT teams to automate routine tasks, such as software updates and device configurations. This automation minimizes manual intervention, reducing the potential for errors and freeing up IT resources for other critical tasks.
The release also brings advanced reporting features, providing detailed analytics and insights into device performance. IT administrators can generate comprehensive reports on various metrics, including device usage, health statuses, and compliance with company policies. This data-driven approach allows organizations to make informed decisions regarding their IT infrastructure.
Security is a significant focus in WDM 4.9, with improved features that ensure the integrity of managed devices. Enhanced security protocols and compliance measures help safeguard sensitive data, making it an essential tool for organizations prioritizing data protection. The integration of advanced encryption methods adds an additional layer of security, ensuring that communication between devices and the management console remains confidential.
Moreover, WDM 4.9 supports a diverse range of Wyse thin clients, making it flexible for various deployment environments. Compatibility with both Windows and Linux operating systems broadens its applicability, allowing organizations to choose the best devices for their needs.
Finally, Wyse Device Manager 4.9 integrates seamlessly with popular cloud services, enhancing its capabilities and allowing for a more cohesive IT ecosystem. This integration simplifies workflows and enables a centralized management approach, making it easier for organizations to manage their devices effectively.
In conclusion, Wyse Device Manager 4.9 equips organizations with the tools they need to efficiently manage their thin client environments. With a focus on user experience, automation, security, and compatibility, this latest release reaffirms Wyse Technology's commitment to providing leading-edge solutions in cloud computing and device management.