1.25" eyepiece adapter. The other eyepiece can be placed in the eyepiece rack until it is needed.
The basic assembly of your SkyQuest IntelliScope Dobsonian is now complete. It should appear as shown in Figure 1. The dust cap on the front of the telescope tube should always remain in place when the telescope is not in use. It is also a good idea to store eyepieces in an eyepiece case and to replace the cover caps on the focuser and finder scope when the telescope is idle.
3.Aligning (Collimating) the Optical System
To get the sharpest images, your telescope’s optical sys- tem must be in precise alignment. The process of aligning the primary and secondary mirrors with each other and with the mechanical axis of the telescope is called collimating. Collimating is relatively easy to do and can be done in day- light or at night.
Because the primary mirror is shipped separately from the optical tube, the telescope’s optics must be collimated before it can be used. Most of the adjustments will be to the tilt of the primary mirror, as the secondary mirror has been
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() drawtube
drawtube
Reflection of primary mirror clip
b.
a.
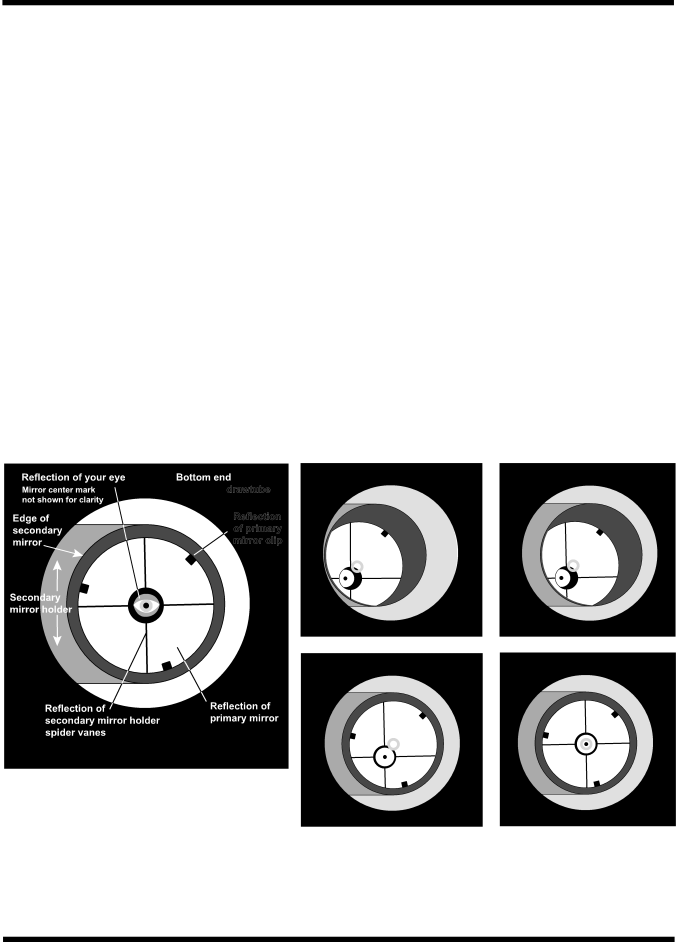
To check collimation, remove the eyepiece and look down the focuser drawtube. You should see the secondary mirror cen- tered in the drawtube, as well as the reflection of the primary mirror centered in the secondary mirror, and the reflection of the secondary mirror (and your eye) centered in the reflection of the primary mirror, as depicted in Figure 21a. If anything is
The Collimation Cap and Mirror Center Mark
Your SkyQuest XT12 IntelliScope comes with a collimation cap. This is a simple cap that fits on the focuser drawtube like a dust cap, but has a hole in the center and a reflective inner surface. The cap helps center your eye so that collimating is easier to perform. Figures 21b through 21e assume you have the collimation cap in place.
As an additional aid in collimating, the primary mirror of the SkyQuest XT12 IntelliScope has a tiny adhesive ring marking its exact center. This center ring will not affect the images you see when observing with the telescope in any way (since it lies directly in the shadow of the secondary mirror), but will greatly facilitate collimating when using the supplied collima- tion cap or other, more sophisticated collimation devices such as the Orion LaserMate Laser Collimator.
c.
d.e.
Figure 21. Collimating the optics. (a) When the mirrors are properly aligned, the view down the focuser drawtube should look like this. (b) With the collimation cap in place, if the optics are out of alignment, the view might look something like this. (c) Here, the secondary mirror is centered under the focuser, but it needs to be adjusted (tilted) so that the entire primary mirror is visible. (d) The secondary mirror is correctly aligned, but the primary mirror still needs adjustment. When the primary mirror is correctly aligned, the “dot” will be centered, as in (e).
10