Manually Configuring your Modem
Statistics | (Superframes represent the highest level of data |
| presentation. |
| Each superframe contains regular ADSL frames, |
| one of which is used to provide superframe |
| synchronization, identifying the start of a |
| superframe. Some of the remaining frames are |
| also used for special functions.) |
|
|
Received | Number of interleaved superframes received. |
Superframes |
|
Interleaved |
|
|
|
Transmitted | Number of interleaved superframes transmitted. |
Superframes |
|
Interleaved |
|
|
|
Received | Number of fast superframes received. |
Superframes |
|
Fast |
|
|
|
Transmitted | Number of fast superframes transmitted. |
Superframes |
|
Fast |
|
|
|
Manually Configuring your Modem
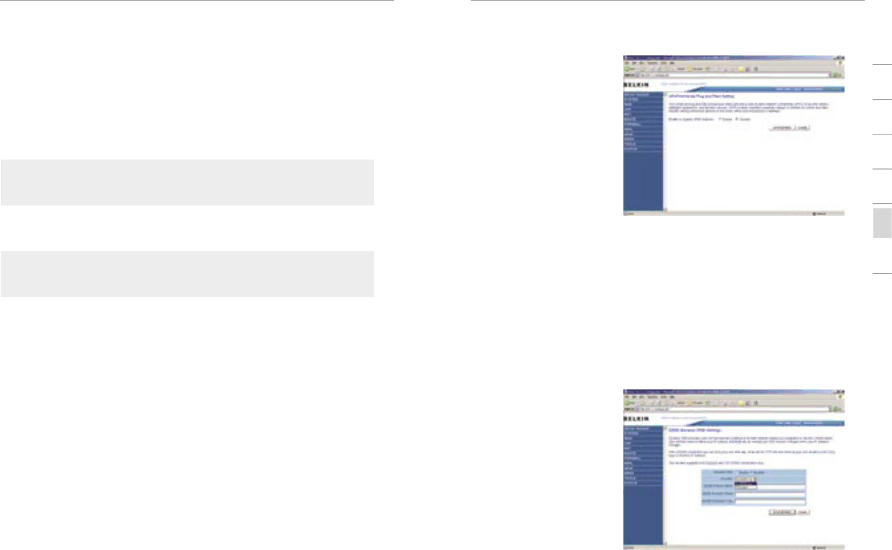
UPnP
UPnP (Universal
to be configured in a specific way to operate properly. This usually requires opening TCP and UDP ports, and in
some instances, setting trigger ports. An application that is UPnP compliant has the ability to communicate with the Modem, basically “telling” the Modem which way it needs the firewall configured. The Modem ships with the UPnP feature disabled. If you are using any applications that are
DDNS
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name Server) provides a way to tie a domain name to the Modems WAN IP. DDNS allows your domain name to follow your IP Address automatically by having your DNS records changed when your IP Address changes.
With a DDNS connection you can host your own web site, email server, FTP site and more at your
own location even if you have a dynamic IP Address.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
section
50 | 51 |