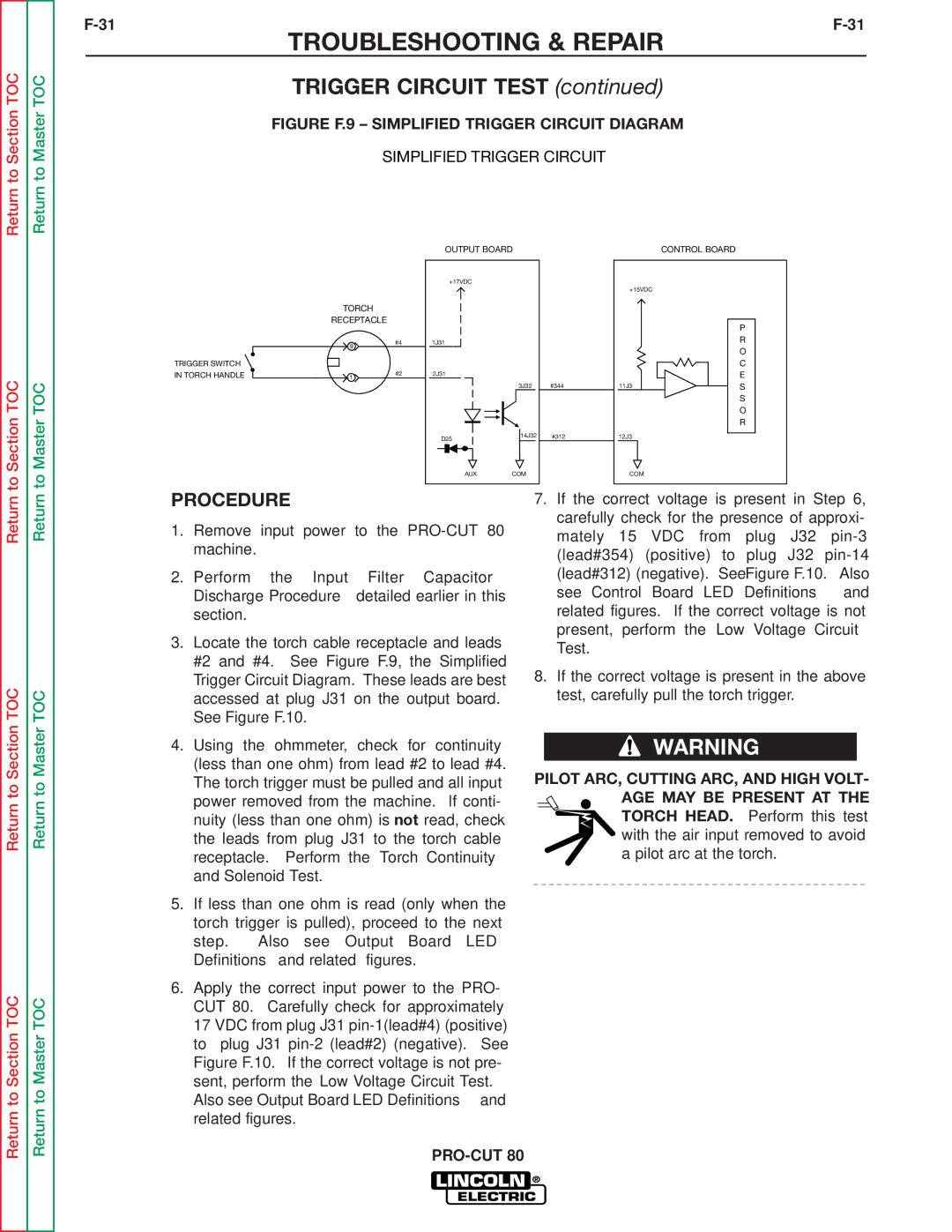
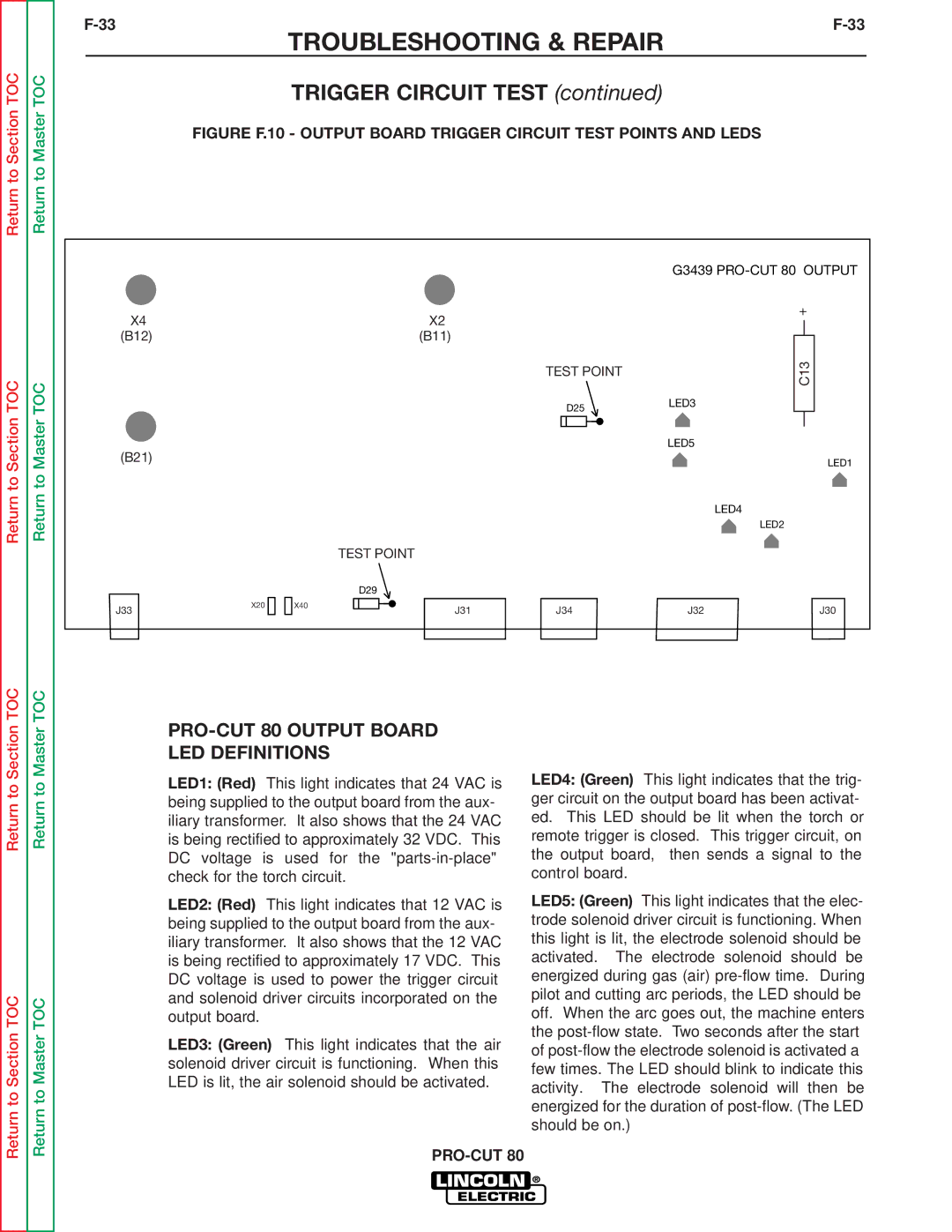
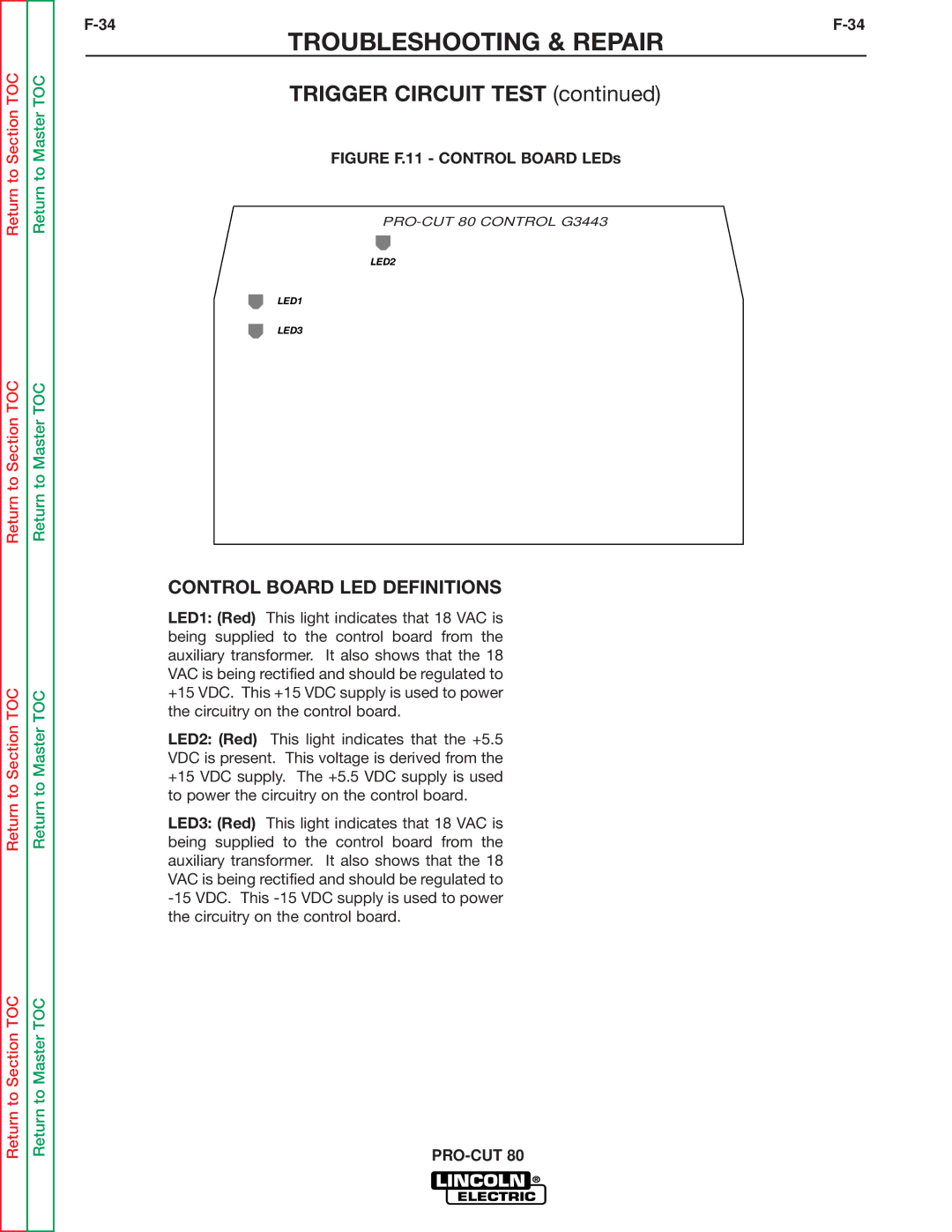
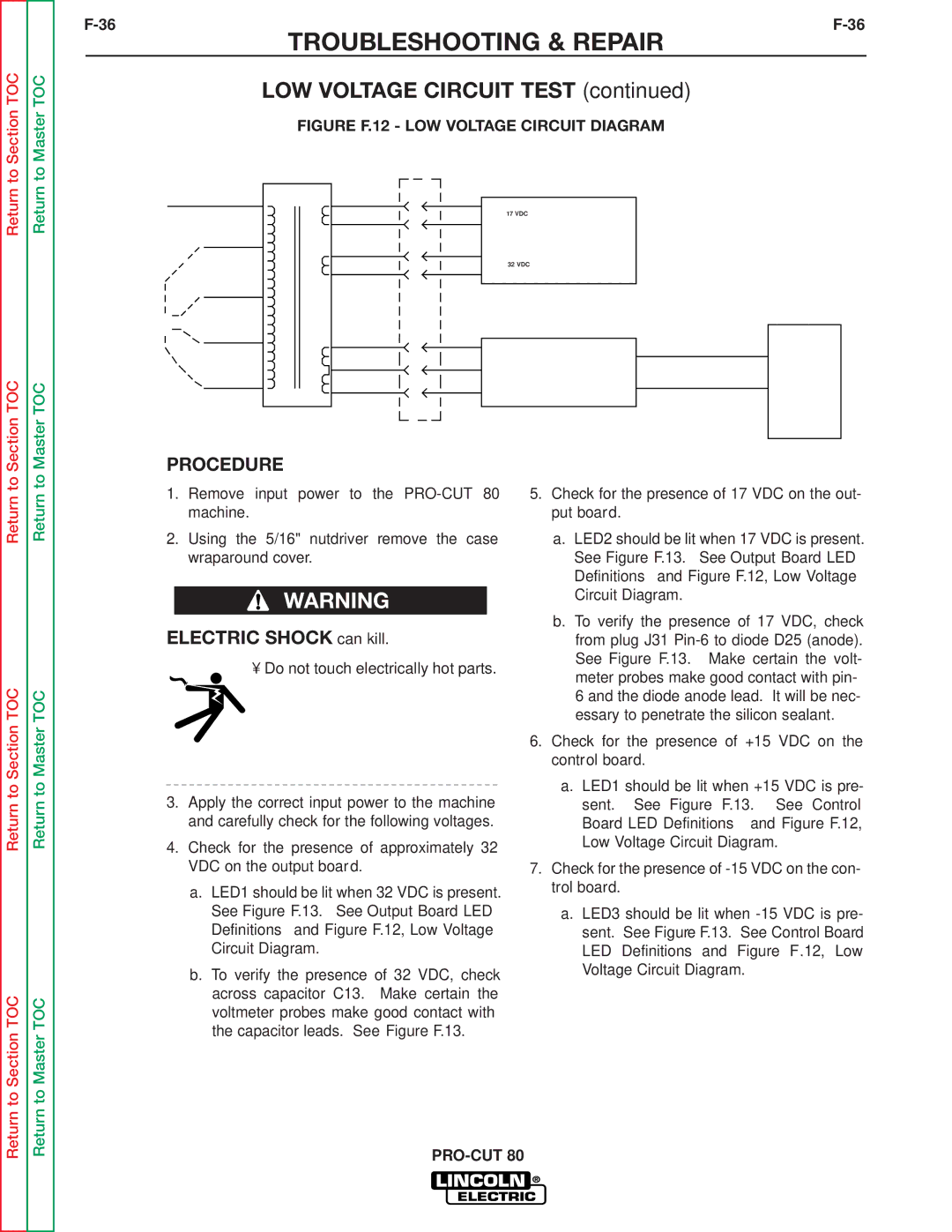
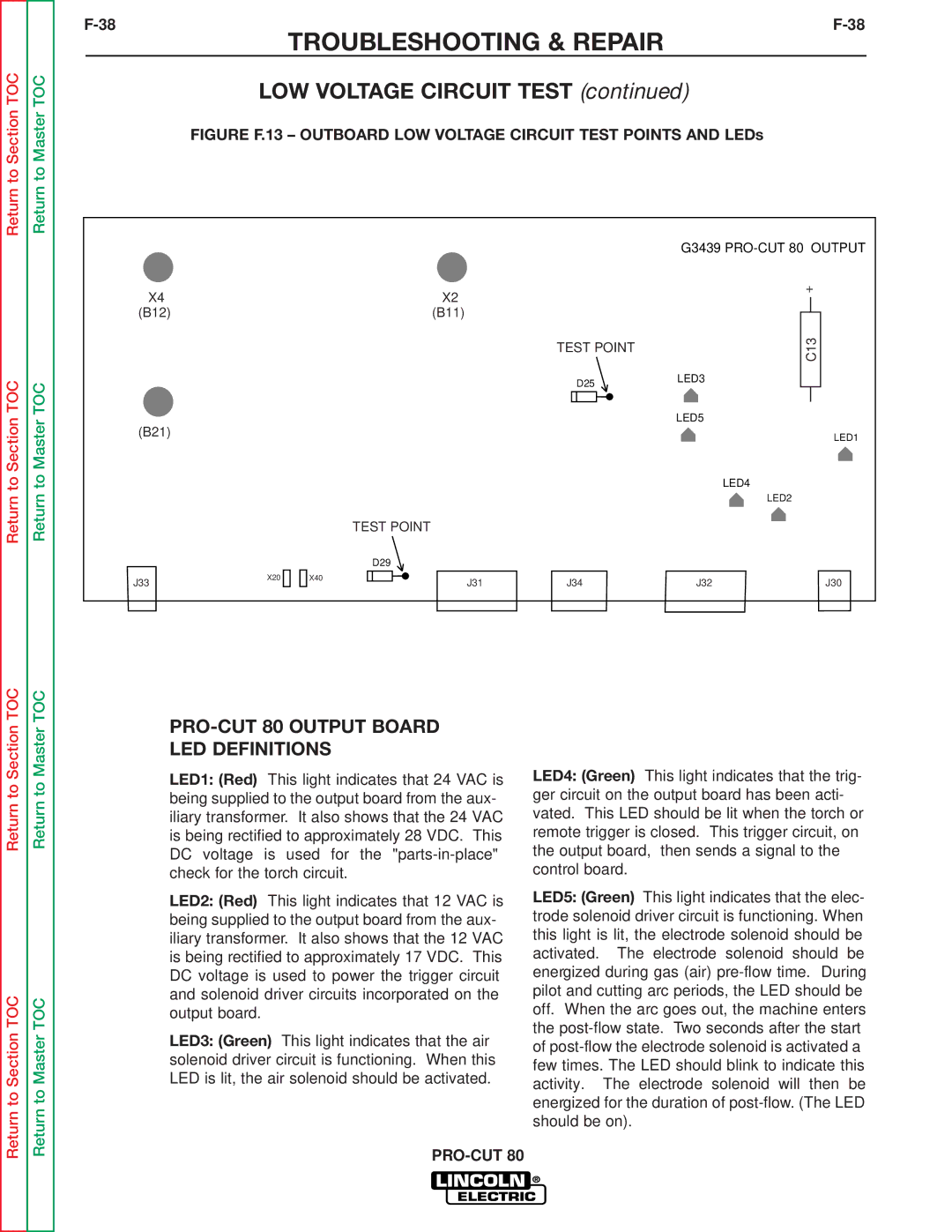
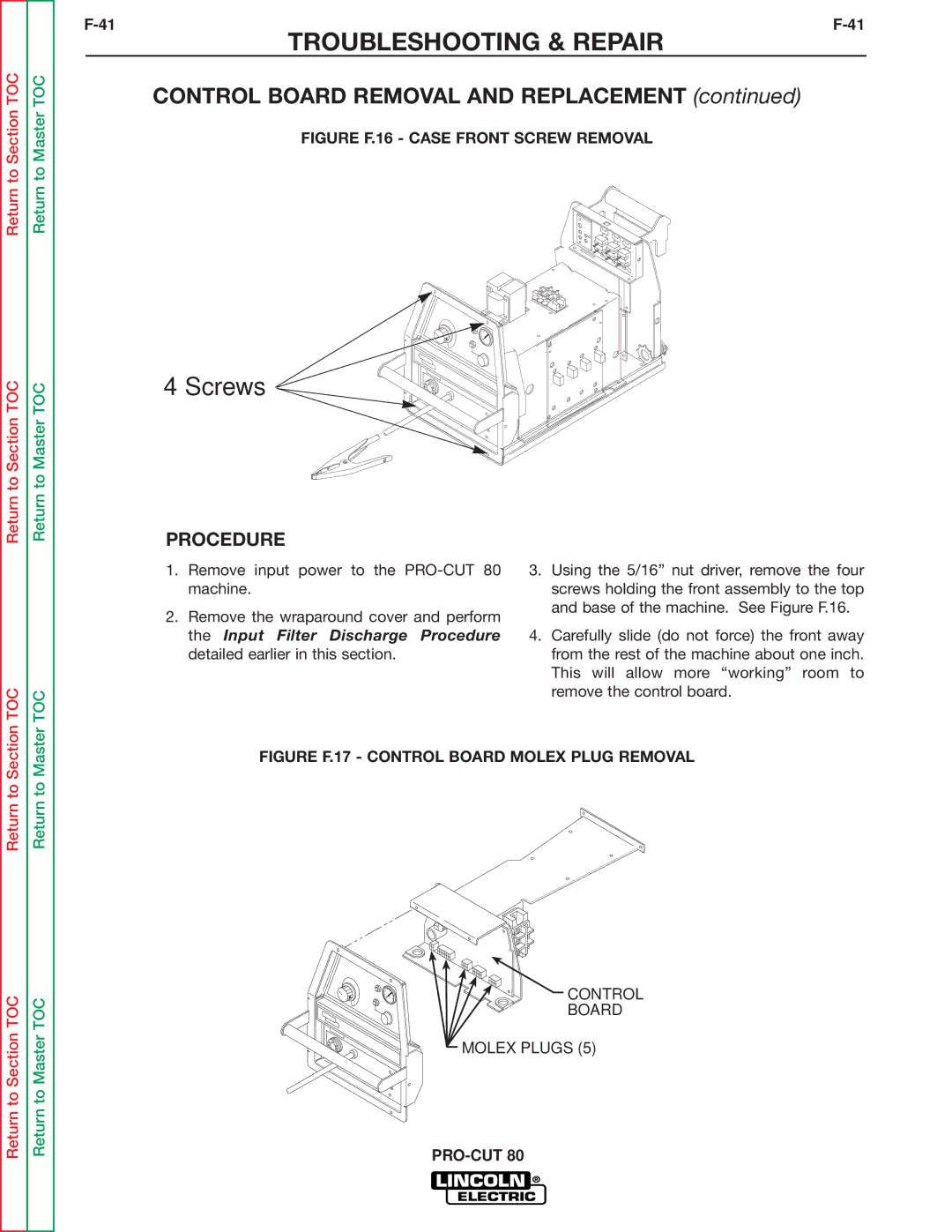
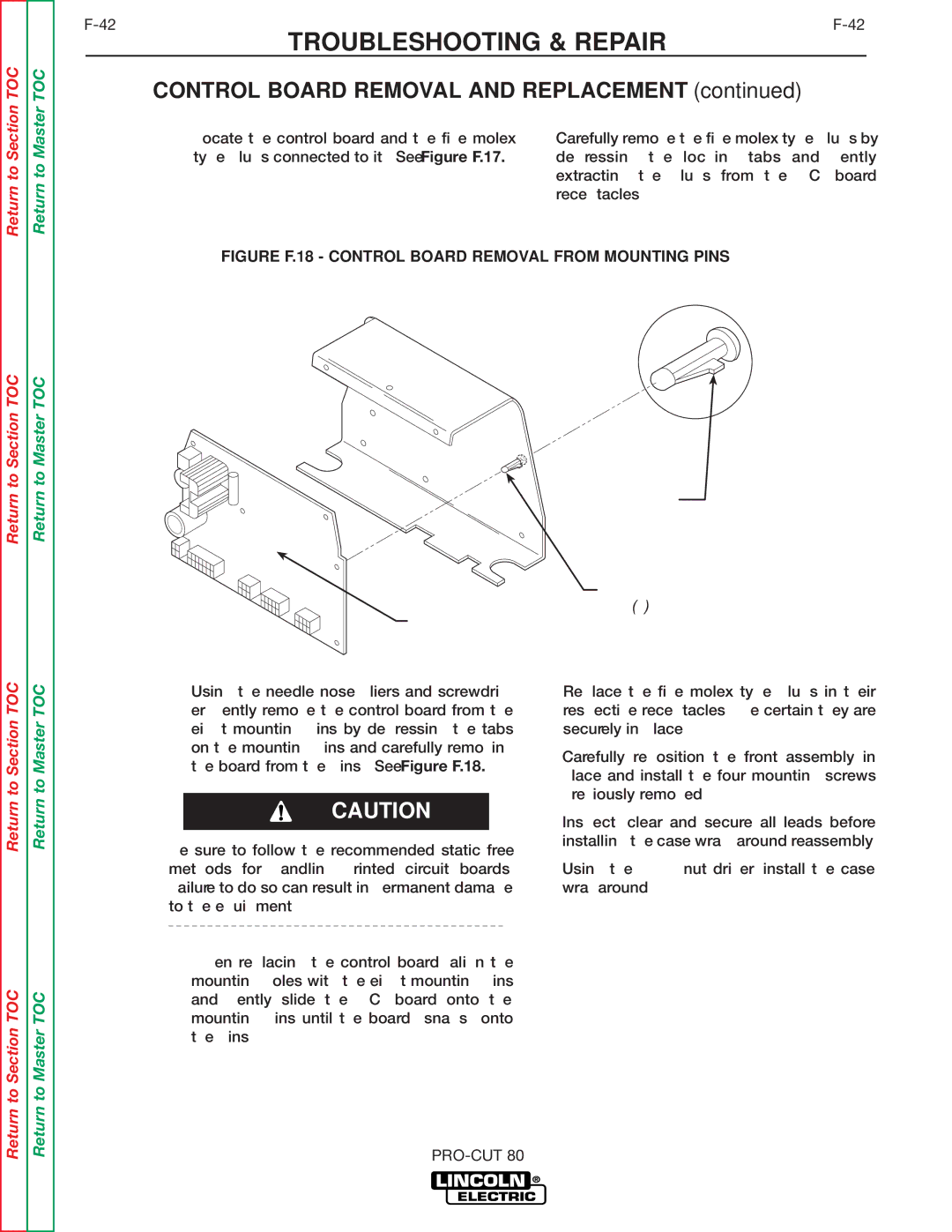
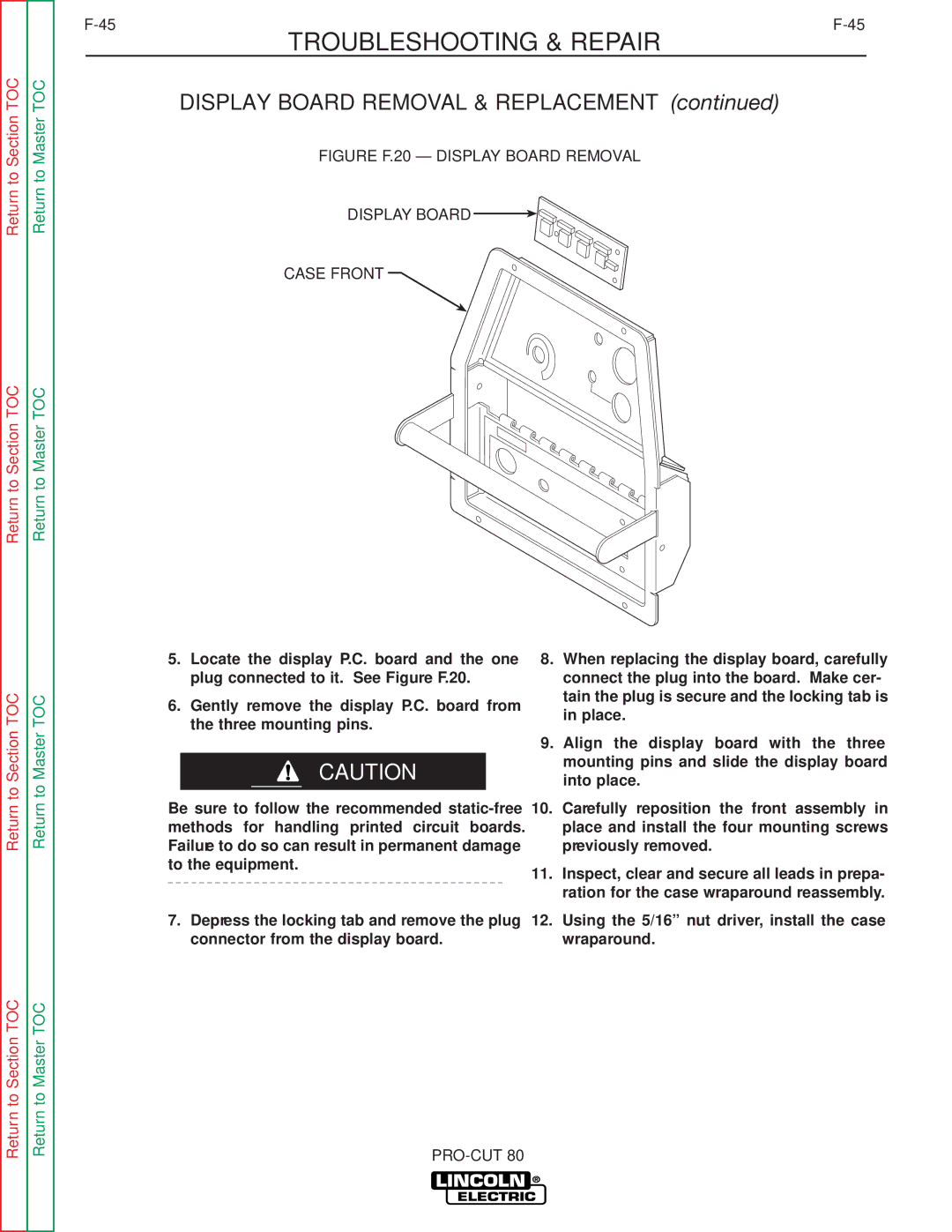
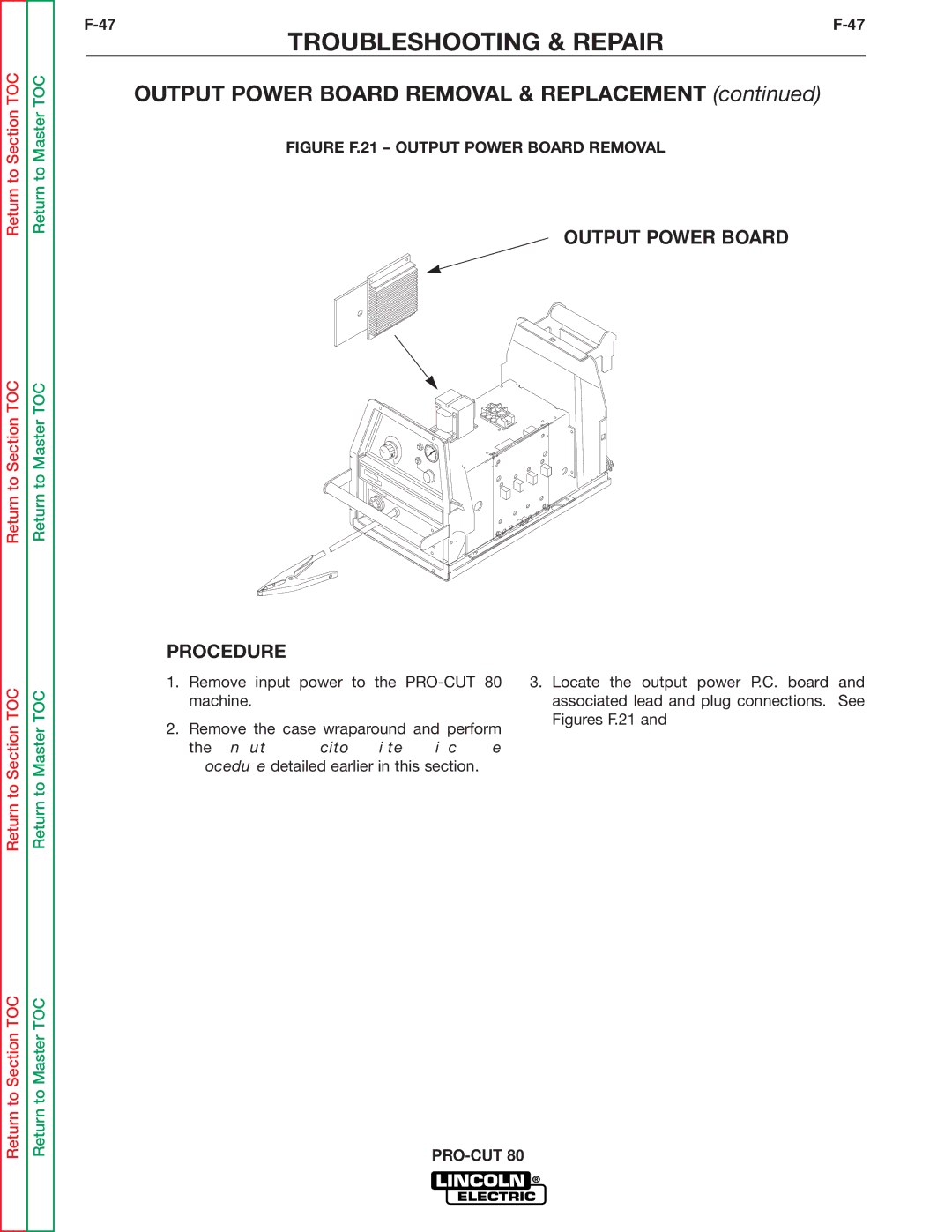
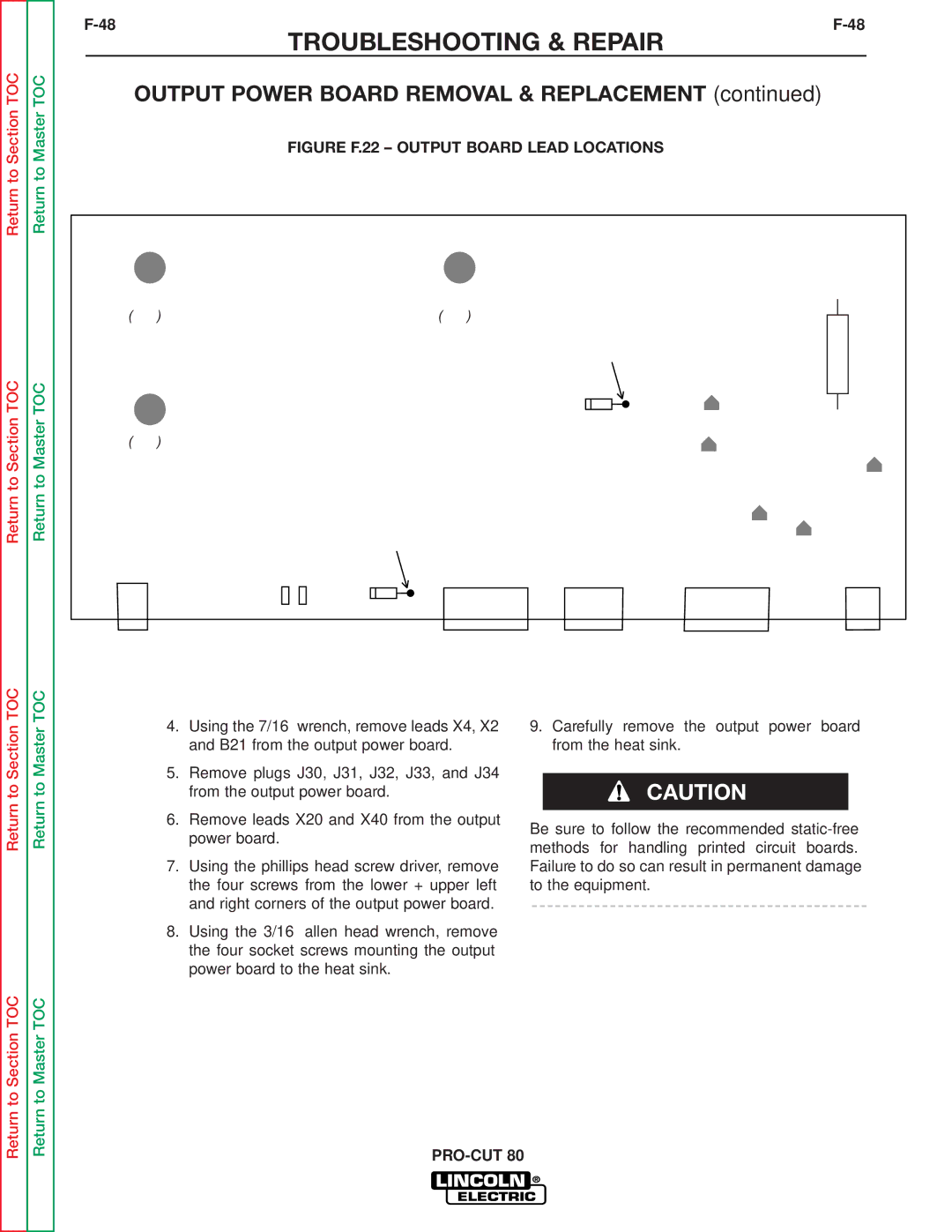
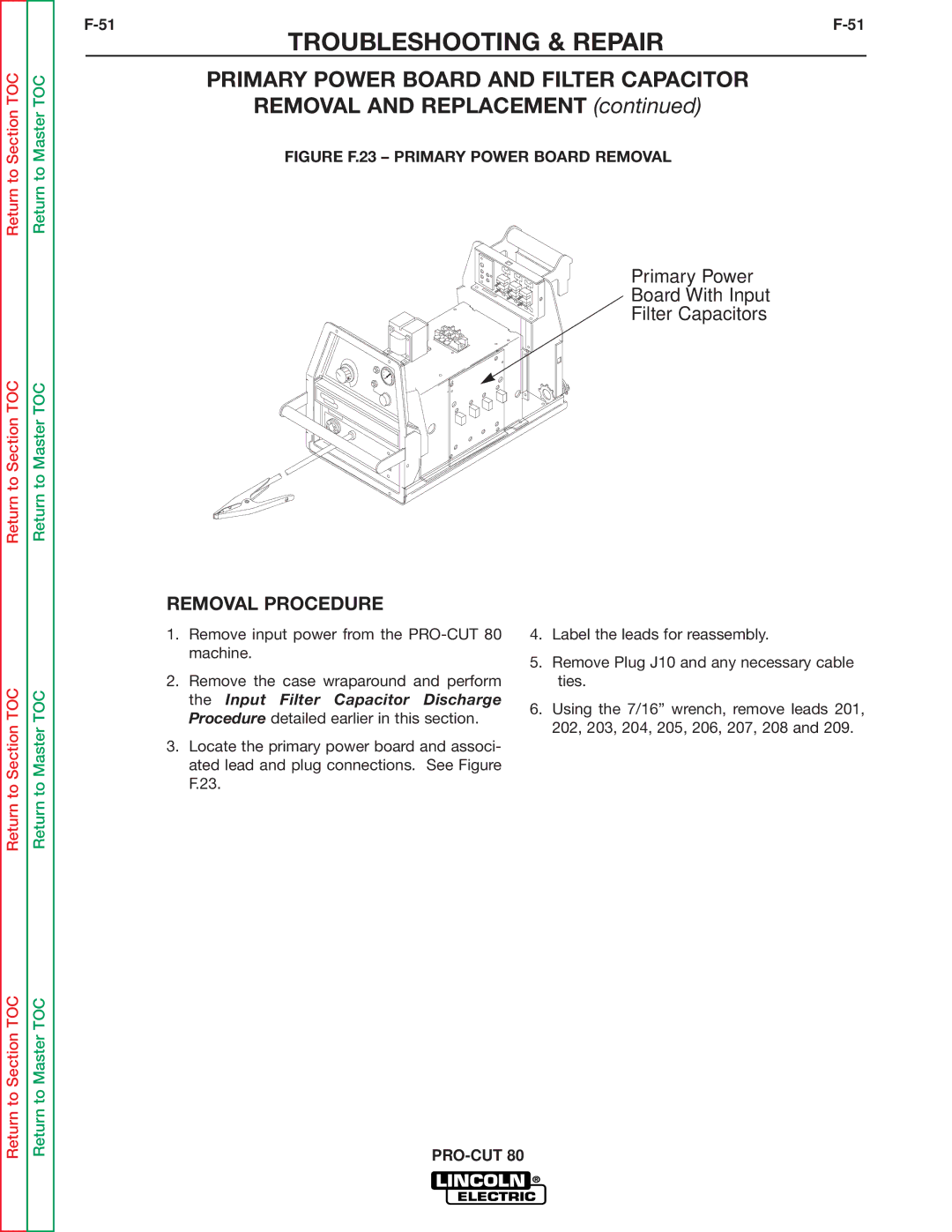
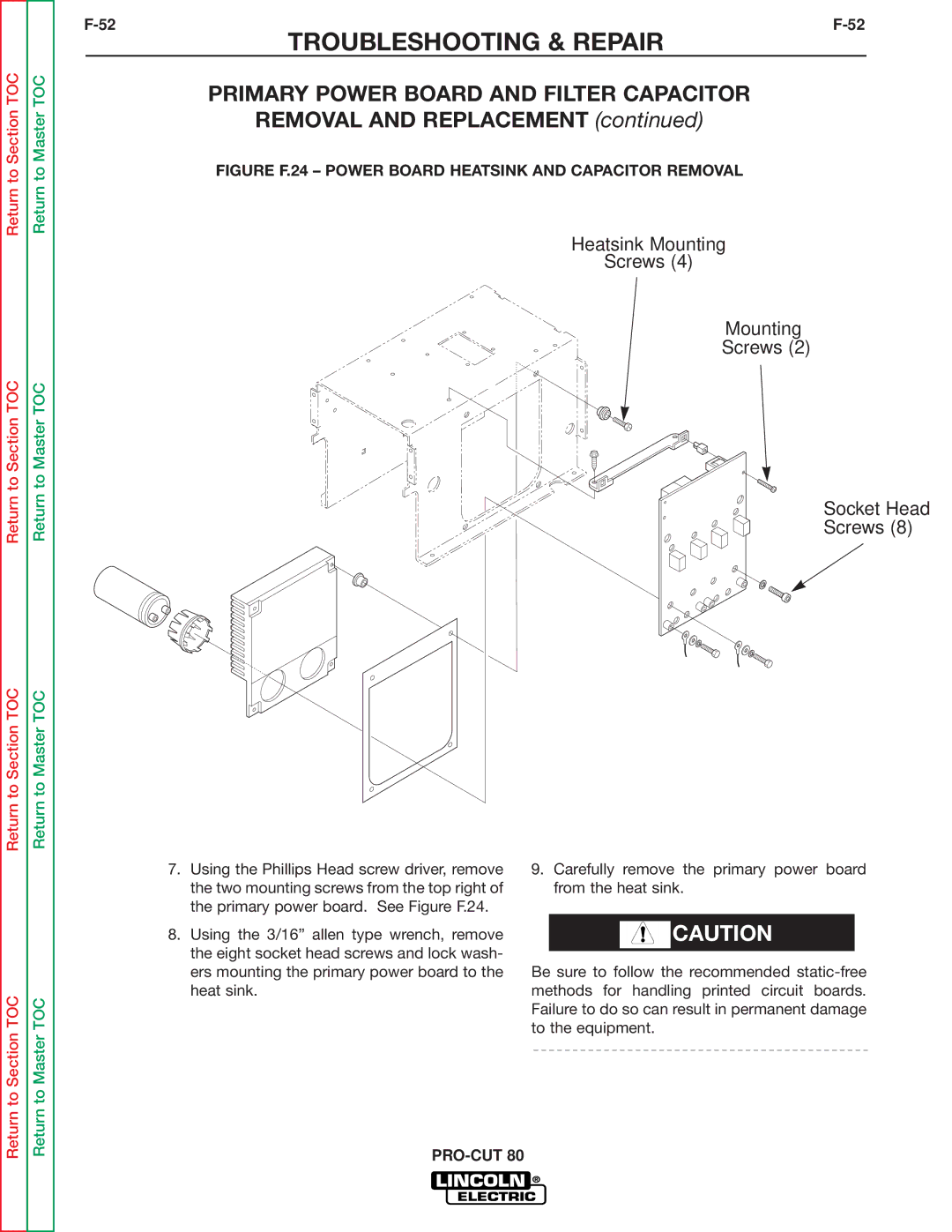
SVM146-A specifications
Lincoln Electric's SVM146-A is a versatile and powerful multi-process welding machine designed for professionals in various industries. Known for its robustness and reliability, this machine excels in both performance and user-friendly features, making it a popular choice among welders.One of the standout features of the SVM146-A is its multi-process capability, allowing users to perform MIG, TIG, and stick welding using a single unit. This versatility is enhanced by Lincoln Electric's innovative Auto-Set technology, which automatically adjusts the machine's settings based on the selected process and materials being welded. This feature significantly reduces the time spent on setup and helps ensure optimal weld quality, even for less experienced operators.
The SVM146-A is powered by a reliable inverter design, which provides greater efficiency compared to traditional transformer-based machines. This compact and lightweight design allows for easy transport, making it ideal for job sites or remote locations. The inverter technology also contributes to enhanced arc stability and better overall performance, providing high-quality welds in less time.
Another key characteristic of this welding machine is its robust construction, designed to withstand the rigors of heavy industrial use. The SVM146-A features a durable chassis and control panel, ensuring longevity and reliability under challenging working conditions. Additionally, its intuitive interface allows users to easily navigate settings and make adjustments as needed.
Safety is a paramount concern in welding applications, and the SVM146-A is equipped with several safety features, including over-temperature and over-voltage protection, ensuring that the machine operates safely even in demanding environments. It also features a start inhibit system, preventing the machine from being started under unsafe conditions.
The SVM146-A is compatible with a variety of welding accessories and consumables, enhancing its flexibility and usability across different applications. Whether it’s automotive repair, heavy fabrication, or maintenance work, this welding machine adapts to various tasks, making it a valuable addition to any professional's toolkit.
In conclusion, Lincoln Electric's SVM146-A stands out as a multi-process welding machine that combines advanced technology, robust design, and user-friendly features. It is engineered for performance and reliability, making it an excellent investment for professionals dedicated to achieving high-quality welds.