Introduction
Increasing demand for portable DC power has risen from improvements in battery and motor design technol- ogy. More than ever before, portable DC powered products have become available in many diverse applications. Rechargeable batteries appear in all types of products from analytical electronic equipment to power tools and toys. In some instances, these diverse applications pose different requirements on the source of DC Power. Fortunately, availability of many types of battery chemistries yield unique characteristics. Table 1 contains just some of the different battery types and their advantages.
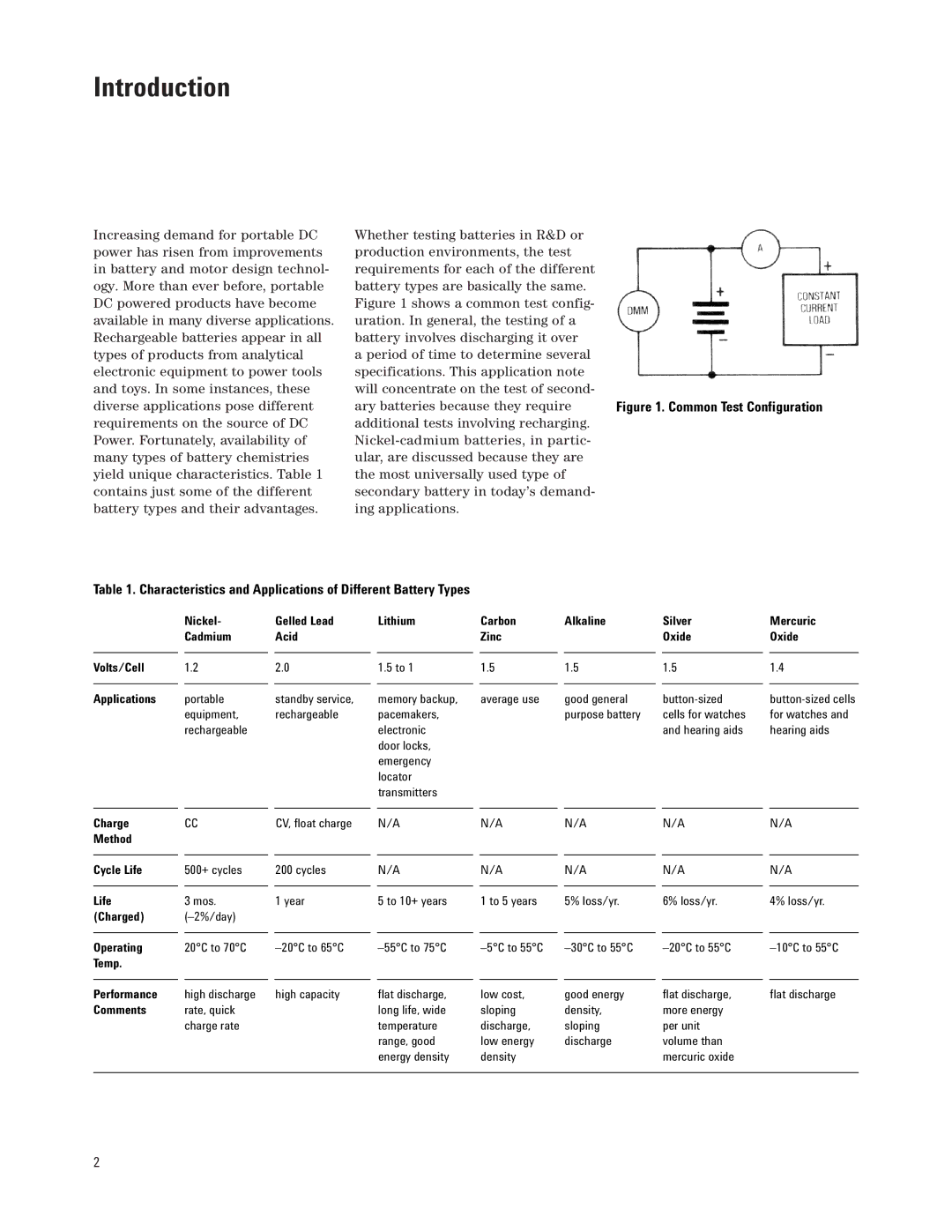
Whether testing batteries in R&D or production environments, the test requirements for each of the different battery types are basically the same. Figure 1 shows a common test config- uration. In general, the testing of a battery involves discharging it over
a period of time to determine several specifications. This application note will concentrate on the test of second-
ary batteries because they require Figure 1. Common Test Configuration additional tests involving recharging.
Table 1. Characteristics and Applications of Different Battery Types
| Nickel- | Gelled Lead | Lithium | Carbon | Alkaline | Silver | Mercuric |
| Cadmium | Acid |
| Zinc |
| Oxide | Oxide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Volts/Cell | 1.2 | 2.0 | 1.5 to 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Applications | portable | standby service, | memory backup, | average use | good general | ||
| equipment, | rechargeable | pacemakers, |
| purpose battery | cells for watches | for watches and |
| rechargeable |
| electronic |
|
| and hearing aids | hearing aids |
|
|
| door locks, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| emergency |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| locator |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| transmitters |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Charge | CC | CV, float charge | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
Method |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cycle Life | 500+ cycles | 200 cycles | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Life | 3 mos. | 1 year | 5 to 10+ years | 1 to 5 years | 5% loss/yr. | 6% loss/yr. | 4% loss/yr. |
(Charged) |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Operating | 20°C to 70°C | ||||||
Temp. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Performance | high discharge | high capacity | flat discharge, | low cost, | good energy | flat discharge, | flat discharge |
Comments | rate, quick |
| long life, wide | sloping | density, | more energy |
|
| charge rate |
| temperature | discharge, | sloping | per unit |
|
|
|
| range, good | low energy | discharge | volume than |
|
|
|
| energy density | density |
| mercuric oxide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2