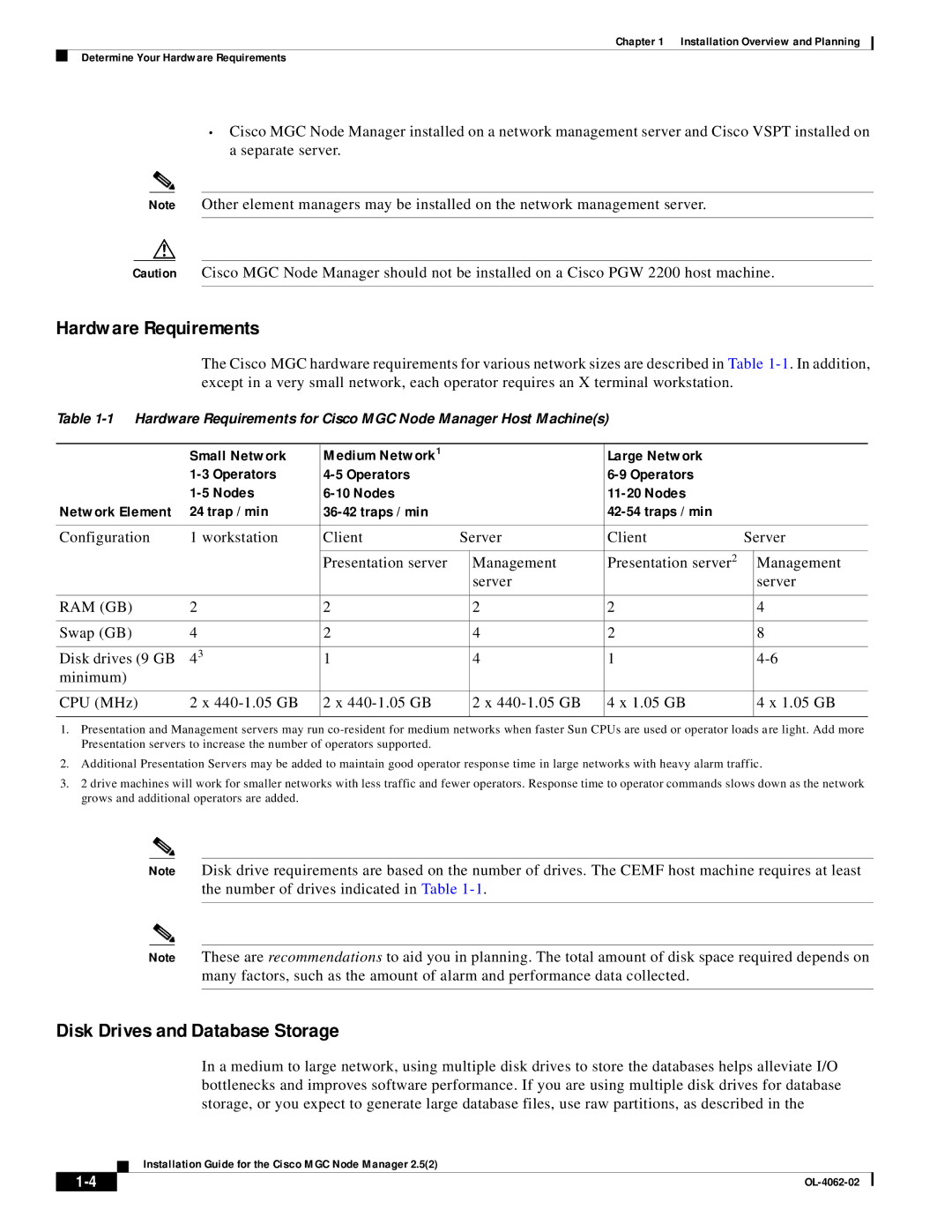
MGC Node Manager specifications
Cisco Systems MGC (Media Gateway Controller) Node Manager is a vital component in the realm of telecommunications, particularly in the development and management of Voice over IP (VoIP) networks. As a software-based solution, it plays a crucial role in integrating and controlling various media gateways, ensuring efficient handling of voice and multimedia traffic.One of the main features of the Cisco MGC Node Manager is its ability to provide centralized control and management of media gateways. This centralized approach enables network operators to have a single point of management for multiple gateways, simplifying configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting processes. The manager can handle thousands of calls simultaneously, making it suitable for both small and large enterprise environments.
In terms of technology, Cisco MGC Node Manager is built on robust protocols like H.323 and SIP (Session Initiation Protocol). These protocols are essential for establishing, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions in VoIP systems. The flexibility to support multiple protocols ensures interoperability among various network components and third-party devices. This cross-compatibility is vital for organizations that use diverse hardware and software solutions.
Another noteworthy characteristic of the MGC Node Manager is its scalability. As business needs grow, the Node Manager can easily scale to accommodate increased traffic and additional gateways. This feature is particularly important for enterprises that experience fluctuating demand, allowing them to adapt to changing usage patterns without investing in significant new infrastructure.
Security is also a prominent focus within the MGC Node Manager’s architecture. By utilizing advanced encryption techniques and implementing robust authentication protocols, it ensures that sensitive voice data remains protected from potential threats. This is critical in maintaining regulatory compliance and safeguarding user privacy.
Furthermore, it offers detailed analytics and reporting capabilities, providing insights into call quality, traffic patterns, and system performance. This data assists network operators in optimizing the network for improved performance and user experience, ultimately supporting business continuity.
In summary, Cisco Systems MGC Node Manager provides a powerful, centralized solution for managing media gateways within VoIP networks. Its support for multiple protocols, scalability, robust security features, and detailed analytics make it an essential tool for organizations looking to enhance their telecommunications infrastructure and drive greater efficiency.