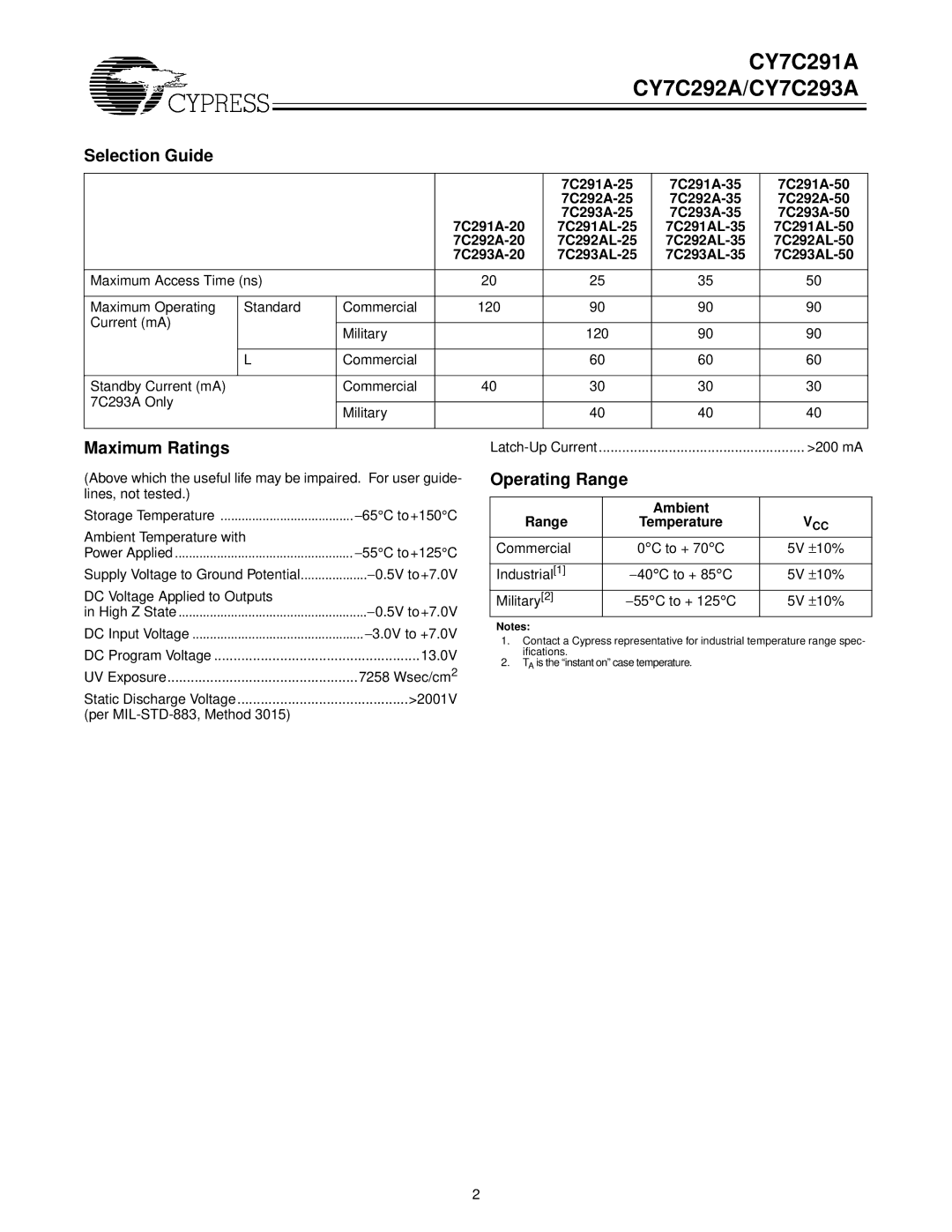
CY7C291A, CY7C292A, CY7C293A specifications
The Cypress CY7C293A, CY7C292A, and CY7C291A are high-performance static random-access memory (SRAM) devices designed for various applications requiring fast access and low power consumption. These memory chips are particularly suitable for use in telecommunications, networking, industrial, automotive, and consumer electronics.One key feature of the CY7C293A model is its 2 megabit capacity, which offers a vast storage solution for applications needing quick read and write capabilities. The CY7C292A and CY7C291A, on the other hand, provide 1 megabit and 256 kilobits, respectively, catering to a range of memory needs. The devices utilize a 16-bit organization, optimally balancing capacity and access speed.
A standout technology is the use of a fast access time, with the CY7C293A achieving speeds of up to 12 nanoseconds. This rapid access capability significantly enhances the performance of systems that depend on swift data retrieval. The SRAM devices are built using Cypress’s unique CMOS technology, which not only supports a dense manufacturing process but also ensures low power consumption. The standby current is minimal, making these chips suitable for battery-powered applications where energy efficiency is critical.
The packaging options available for the CY7C293A, CY7C292A, and CY7C291A include various forms such as 28-pin DIP and 32-pin TSOP, allowing for ease of integration into different circuit layouts. The devices feature an asynchronous operation, providing straightforward interfacing with no need for external clocks, which simplifies system design.
In terms of reliability, these SRAMs are equipped with robust features that ensure data integrity and stability. They offer a wide operating voltage range, typically from 4.5V to 5.5V, accommodating different power supply configurations. Furthermore, the chips are designed to withstand multiple read/write cycles, making them ideal for applications that demand frequent data manipulation.
Overall, the Cypress CY7C293A, CY7C292A, and CY7C291A SRAM devices represent a versatile memory solution that combines speed, efficiency, and reliability, making them a favored choice for engineers and designers working across various technological domains. Their adaptability to different applications ensures that they remain relevant in the rapidly evolving landscape of electronics and memory technology.