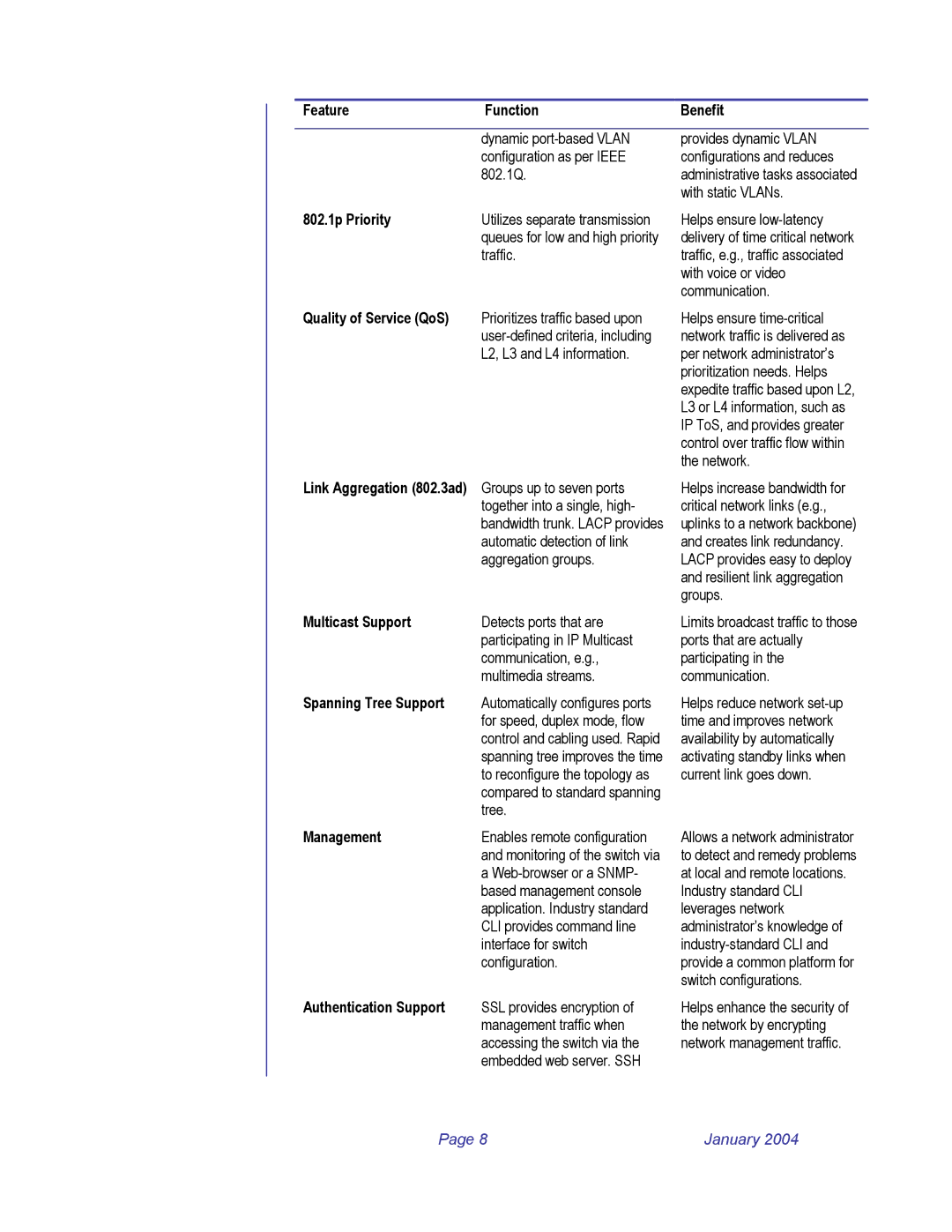
Feature | Function | Benefit |
| dynamic |
| configuration as per IEEE |
| 802.1Q. |
802.1p Priority | Utilizes separate transmission |
| queues for low and high priority |
| traffic. |
Quality of Service (QoS) | Prioritizes traffic based upon |
| |
| L2, L3 and L4 information. |
Link Aggregation (802.3ad) | Groups up to seven ports |
| together into a single, high- |
| bandwidth trunk. LACP provides |
| automatic detection of link |
| aggregation groups. |
Multicast Support | Detects ports that are |
| participating in IP Multicast |
| communication, e.g., |
| multimedia streams. |
Spanning Tree Support | Automatically configures ports |
| for speed, duplex mode, flow |
| control and cabling used. Rapid |
| spanning tree improves the time |
| to reconfigure the topology as |
| compared to standard spanning |
| tree. |
Management | Enables remote configuration |
| and monitoring of the switch via |
| a |
| based management console |
| application. Industry standard |
| CLI provides command line |
| interface for switch |
| configuration. |
Authentication Support | SSL provides encryption of |
| management traffic when |
| accessing the switch via the |
| embedded web server. SSH |
provides dynamic VLAN configurations and reduces administrative tasks associated with static VLANs.
Helps ensure
Helps ensure
Helps increase bandwidth for critical network links (e.g., uplinks to a network backbone) and creates link redundancy. LACP provides easy to deploy and resilient link aggregation groups.
Limits broadcast traffic to those ports that are actually participating in the communication.
Helps reduce network
Allows a network administrator to detect and remedy problems at local and remote locations.
Industry standard CLI leverages network administrator’s knowledge of
Helps enhance the security of the network by encrypting network management traffic.
Page 8 | January 2004 |