Dell PowerVault MD3000 RAID Enclosure
W . d e l l . c o m s u p p o r t . d e l l . c o m
February
Contents
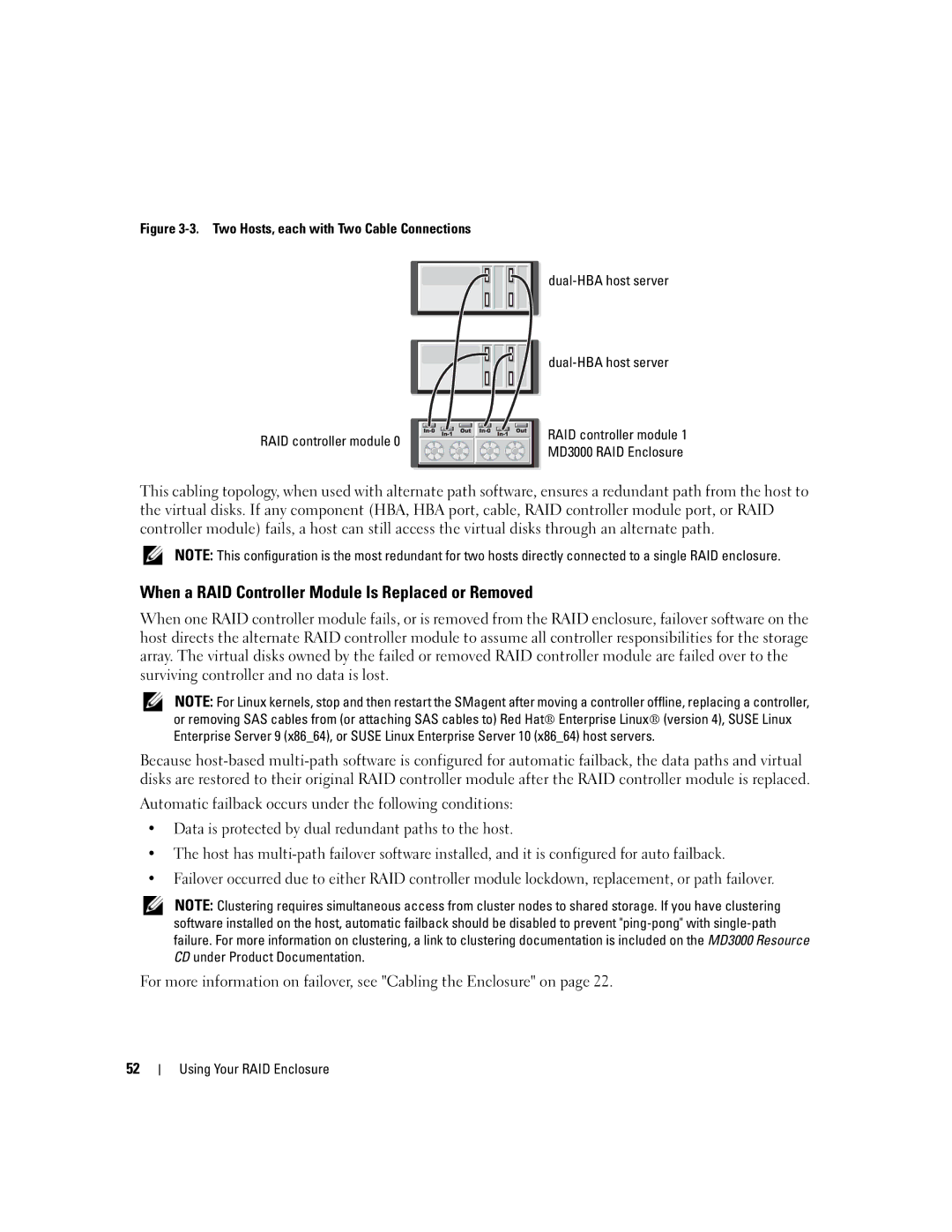
When a RAID Controller Module Is Replaced or Removed
Using Snapshot and Disk Copy Together
Virtual Disk Migration and Disk Roaming
Safety First-For You and Your Enclosure
Troubleshooting Enclosure Cooling Problems
Returning Items for Warranty Repair or Credit
103
111
Overview
Enclosure Features
About Your System
Other Information You May Need
Modular Disk Storage Manager
Hardware Features
Indicators on the Enclosure Bezel
Front-Panel Indicators and Features
Power green
Should always be unlit
Enclosure
Power LED green
Enclosure mode switch
Split mode LED green
Steady green
Back-Panel Indicators and Features
RAID Controller Modules
Off Battery backup unit and battery is operating
Green All links in port connected
Each SAS port
Off All links in port disconnected or cable
RAID Controller Module Battery backup unit BBU tray
Cache Functions and Features
Battery Backup Unit
AC power LED
Power Supply and Cooling Fan Features
Cooling fans On/off switch
Page
About Your System
Before You Begin
About the Enclosure Connections
Rail kit Any relevant documentation, including
Cabling Your RAID Enclosure
Cabling the Enclosure
Single SAS In-Port Configurations
Redundancy vs. Nonredundancy
MD1000 Expansion Enclosure Single-HBA host server
MD1000 Expansion Enclosure Cabling Your RAID Enclosure
MD3000 RAID Enclosure
Dual SAS In-Port Configurations
RAID controller module Single-HBA host server
MD1000 Expansion Enclosure
Page
Page
Page
Expanding with Previously Configured MD1000 Enclosures
Attaching MD1000 Expansion Enclosures
Expanding with New MD1000 Enclosures
Cabling Your RAID Enclosure
Physical Disks, Virtual Disks, and Disk Groups
Using Your RAID Enclosure
Physical Disks
Physical Disk States
Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology Smart
Supported RAID Levels
Virtual Disks and Disk Groups
Disk failures may result in data loss
Offline
RAID
RAID Level Usage
Hot Spares and Rebuild
Segment Size
Media Errors and Unreadable Sectors
Global Hot Spares
Hot Spare Operation
Rebuild
RAID Operations and Features
Virtual Disk Operations
Background Initialization
Foreground Initialization
RAID Level Migration
Disk Group Operations
Cycle Time
Page
RAID Background Operations Priority
Virtual Disk Migration and Disk Roaming
Using Your RAID Enclosure
Advanced Features
Storage Partitions
Host Types
Snapshot Virtual Disks
Virtual Disk Service
Snapshot Repository Virtual Disk
Volume Shadow-Copy Service
Virtual Disk Copy
Using Snapshot and Disk Copy Together
Redundancy and Non-Redundancy
Hardware Redundancy and Failover
Multi-Path Software
Host Bus Adapters
Host Cabling for Redundancy
Using Your RAID Enclosure
When a RAID Controller Module Is Replaced or Removed
RAID Enclosure Thermal Shutdown
RAID Controller Failover Modes
Updating Enclosure Firmware
RAID Controller Module Firmware
Physical Disk Firmware
Expansion Enclosure Firmware
Recommended Tools
Installing Enclosure Components
Removing and Replacing the Front Bezel
Removing and Installing Physical Disks
Removing Physical Disks from the Enclosure
Installing SAS Physical Disks in the Enclosure
Physical disk
Removing and Installing a RAID Controller Module
Removing a RAID Controller Module
Installing a RAID Controller Module
Removing and Installing a RAID Controller Module Release tab
Battery unit
Removing and Installing the Power Supply/Cooling Fan Module
Removing a Power Supply/Cooling Fan Module
Installing a Power Supply/Cooling Fan Module
Removing and Installing the Control Panel
Removing the Control Panel
Installing the Control Panel
Removing and Installing the Midplane
Removing and Replacing the Controller/Power Supply Cage
Controller/power supply cage
Page
Safety First-For You and Your Enclosure
Troubleshooting External Connections
Troubleshooting Your Enclosure
Start-Up Routine
Troubleshooting a Wet Enclosure
Troubleshooting a Damaged Enclosure
Problem
Liquid spilled on the enclosure Excessive humidity
Troubleshooting Power Supplies
Troubleshooting SAS Physical Disks
Troubleshooting Enclosure Cooling Problems
Troubleshooting a Fan
Physical disk status LED is flashing amber
Single physical disk is not seen in MD Storage Manager
Multiple physical disks are not seen in MD Storage Manager
Troubleshooting Enclosure Connections
ECC Errors
PCI Errors
Hard Controller Failures and Lockdown Conditions
Critical Conditions
Noncritical Conditions
Troubleshooting Your Enclosure
Obtaining Assistance
Online Services
Getting Help
AutoTech Service
Automated Order-Status Service
Dell Enterprise Training Problems With Your Order
Support Service
Before You Call
Contacting Dell
Technical Support Dell Dimension, Dell
Technical Support Services
Technical Support
Sales
Switchboard
International Access Code Tech Support for XPS
City Code Home/Small Business Fax
Home/Small Business Customer Care
Support Customer Service Home/Home Office
Customer Service small/med./large business
Hardware Warranty Phone Support Home/Home
Office Hardware Warranty Phone Support
Technical Support Dimension and Inspiron
Technical Support projectors, PDAs, switches
Technical Support OptiPlex, Latitude, and Dell
Precision Technical Support servers and storage
International Access Code Technical Support for XPS
Switchboard Relational
Switchboard Fax Relational
Switchboard Home/Small Business
General Support calling from Guayaquil
Mail fisupport@dell.com Country Code Technical Support
City Code Customer Care
Sales under 500 employees
Switchboard calls from outside of France
Country Code Technical Support for XPS
City Codes 1 Technical Support for all other Dell computers
Fax calls from outside of France
International Access Code Technical Support
Country Code Gold Service Technical Support
Gold Service Switchboard
Routers, and so on Customer Care
Technical Support portables, desktops, servers,
Storage Sales Large Corporate Accounts
Sales Home and Small Business
City Code Ireland Sales
Country Code Technical Support
Technical Support outside of Japan Dimension
Inspiron Technical Support Dell Precision, OptiPlex,
Latitude Technical Support outside of Japan Dell Precision
Routers Technical Support outside of Japan projectors
City Code Support Dimension, PDA, Electronics,
Accessories Sales
Customer Service Austin, Texas, U.S.A
Fax Technical Support and Customer Service
International Access Code Technical Support XPS
City Code Latitude Technical Support Dimension, Inspiron,
Customer Service
Country Code Technical Support Dell Precision, OptiPlex,
Switchboard Fax
Fax Switchboard
Relational Customer Care
Relational Sales
Reception Desk Fax
Customer Service Fax
Country Code Customer Care
Precision Technical Support PowerApp, PowerEdge
Switchboard Sales
International Access Code Mail dellzasupport@dell.com
Technical Support, Customer Service, and Sales
City Code Relational Customer Care
Employee Purchase Program EPP Support
City Code Technical Support Home and Small Business for
All other Dell products Technical Support Corporate
PowerConnect, and PowerVault Customer Care
Technical Support OptiPlex, Latitude, Inspiron
International Access Code Country Code City Code
Mail delldirectsupport@dell.com Customer Care website
Home and Small Business Sales
Corporate/Public Sector Sales
100
101
102
BTU British thermal unit
Amperes AC Alternating current
Celsius
104
Cm Centimeters Cmos Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor
105
Fahrenheit
106
LVD Low voltage differential Meters MA Milliamperes
107
108
System diskette See bootable diskette
TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
109
Volts VAC Volts alternating current VDC Volts direct current
110
Redundancy consistency check
Safety Segment size migration
Index
Index