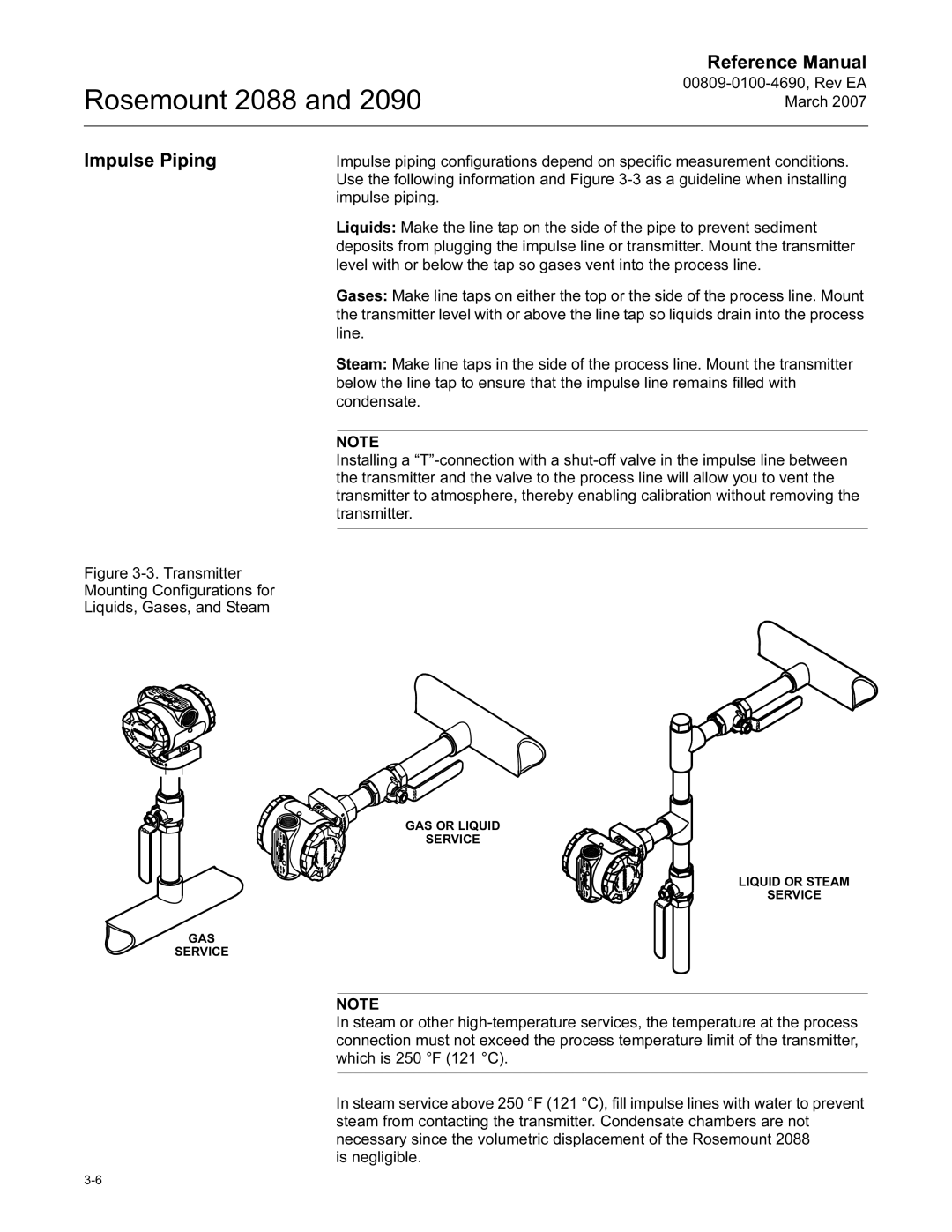
2088, 2090 specifications
Emerson Process Management, a global leader in process automation and control solutions, has developed a series of advanced controllers including the 2090 and 2088 models. These controllers are integral to modern industrial applications, enhancing operational efficiencies and ensuring precise control over processes.The Emerson 2090 controller is renowned for its high performance and reliability. It supports both continuous and batch processes, making it versatile for various industrial environments. One of its main features is its modular architecture, which allows for easy scalability and customization according to specific operational needs. The controller is equipped with advanced communication capabilities, supporting multiple protocols such as Modbus, Ethernet/IP, and Profibus, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems.
The 2090 also boasts sophisticated data processing abilities. It employs predictive analytics, enabling users to forecast potential issues and optimize process performance before disturbances occur. With its intuitive user interface and graphical programming environment, operators can design control strategies easily, significantly reducing programming time and enhancing user experience.
On the other hand, the Emerson 2088 controller offers a powerful yet cost-effective solution for smaller-scale applications. Designed for simplicity and ease of use, it contains essential control features while maintaining flexibility. It supports a variety of input and output modules, allowing for extensive configuration options to meet specific requirements. The 2088 is particularly noted for its reliability in extreme conditions, making it an ideal choice for demanding environments.
Both the 2090 and 2088 controllers utilize Emerson’s latest technologies, including advanced algorithms for PID control, and they support redundancy options for critical applications. The emphasis on cybersecurity in both models further ensures safe operation, protecting sensitive data and control systems from potential threats.
These controllers exemplify Emerson's commitment to innovation, efficiency, and reliability in process management. Their robust design and advanced features cater to a wide range of industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, and water treatment. As industry standards evolve, Emerson continues to lead the charge by integrating cutting-edge technologies into their controller solutions to meet the ever-changing demands of process automation.