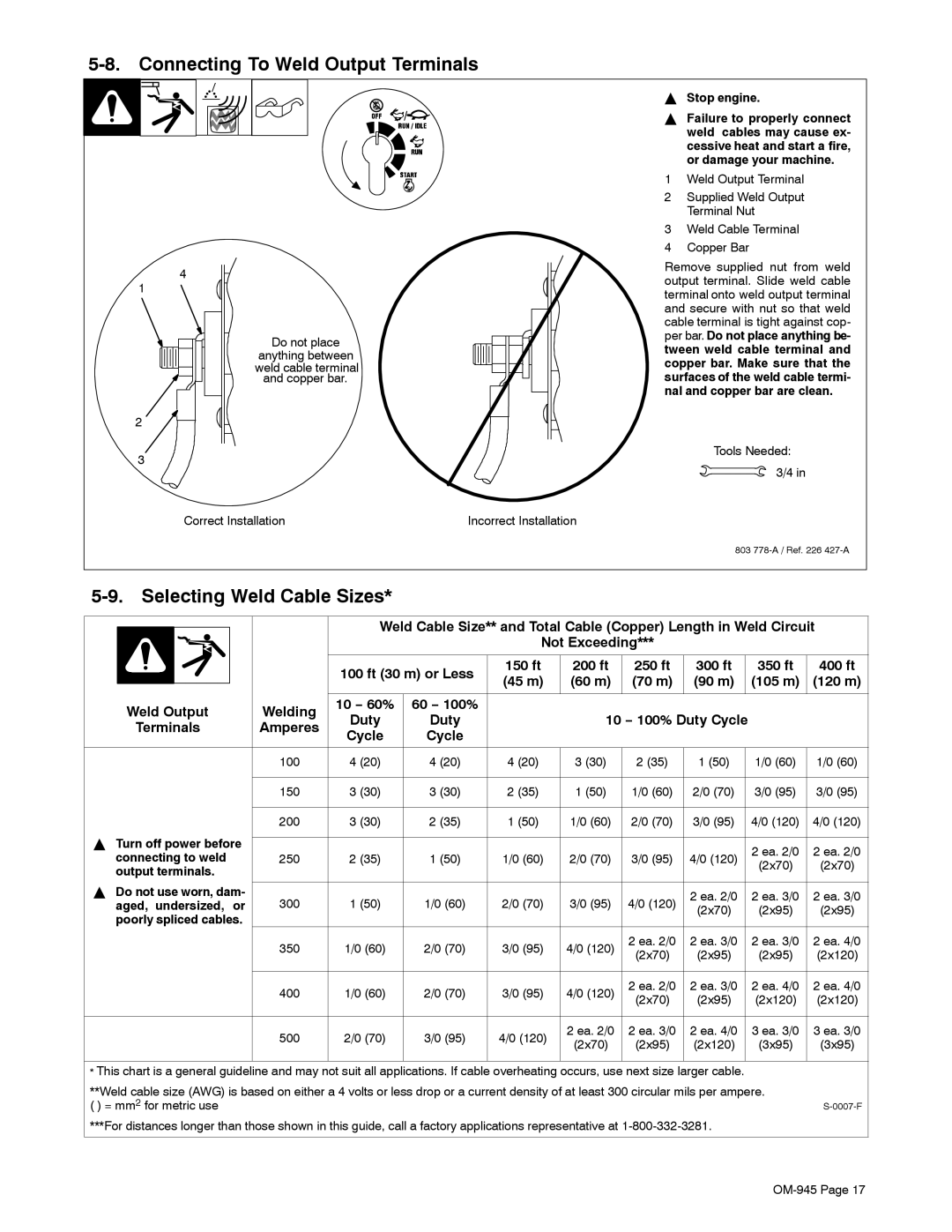
5-8. Connecting To Weld Output Terminals
4
1
Do not place anything between weld cable terminal and copper bar.
2 ![]()
3
Correct Installation | Incorrect Installation |
YStop engine.
YFailure to properly connect weld cables may cause ex- cessive heat and start a fire, or damage your machine.
1Weld Output Terminal
2Supplied Weld Output Terminal Nut
3Weld Cable Terminal
4Copper Bar
Remove supplied nut from weld output terminal. Slide weld cable terminal onto weld output terminal and secure with nut so that weld cable terminal is tight against cop- per bar. Do not place anything be- tween weld cable terminal and copper bar. Make sure that the surfaces of the weld cable termi- nal and copper bar are clean.
Tools Needed: 3/4 in
803
5-9. Selecting Weld Cable Sizes*
|
|
|
|
| Weld Cable Size** and Total Cable (Copper) Length in Weld Circuit | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
| |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Not Exceeding*** |
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 100 ft (30 m) or Less | 150 ft | 200 ft | 250 ft | 300 ft |
| 350 ft | 400 ft | |
|
|
|
|
| (45 m) | (60 m) | (70 m) | (90 m) |
| (105 m) | (120 m) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Weld Output | Welding | 10 − 60% | 60 − 100% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| Duty | Duty |
| 10 − 100% Duty Cycle |
|
| |||||||
| Terminals | Amperes |
|
|
| ||||||||
| Cycle | Cycle |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 100 | 4 (20) | 4 (20) | 4 (20) | 3 (30) | 2 (35) | 1 (50) |
| 1/0 (60) | 1/0 (60) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 150 | 3 (30) | 3 (30) | 2 (35) | 1 (50) | 1/0 (60) | 2/0 (70) |
| 3/0 (95) | 3/0 (95) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 200 | 3 (30) | 2 (35) | 1 (50) | 1/0 (60) | 2/0 (70) | 3/0 (95) |
| 4/0 (120) | 4/0 (120) |
Y Turn off power before |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 2 ea. 2/0 | 2 ea. 2/0 | ||||
connecting to weld | 250 | 2 (35) | 1 (50) | 1/0 (60) | 2/0 (70) | 3/0 (95) | 4/0 (120) |
| |||||
| (2x70) | (2x70) | |||||||||||
output terminals. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
Y Do not use worn, dam- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
300 | 1 (50) | 1/0 (60) | 2/0 (70) | 3/0 (95) | 4/0 (120) | 2 ea. 2/0 |
| 2 ea. 3/0 | 2 ea. 3/0 | ||||
aged, undersized, or |
| ||||||||||||
(2x70) |
| (2x95) | (2x95) | ||||||||||
poorly spliced cables. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| 350 | 1/0 (60) | 2/0 (70) | 3/0 (95) | 4/0 (120) | 2 ea. 2/0 | 2 ea. 3/0 |
| 2 ea. 3/0 | 2 ea. 4/0 |
|
|
|
| (2x70) | (2x95) |
| (2x95) | (2x120) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 400 | 1/0 (60) | 2/0 (70) | 3/0 (95) | 4/0 (120) | 2 ea. 2/0 | 2 ea. 3/0 |
| 2 ea. 4/0 | 2 ea. 4/0 |
|
|
|
| (2x70) | (2x95) |
| (2x120) | (2x120) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 500 | 2/0 (70) | 3/0 (95) | 4/0 (120) | 2 ea. 2/0 | 2 ea. 3/0 | 2 ea. 4/0 |
| 3 ea. 3/0 | 3 ea. 3/0 |
|
|
|
| (2x70) | (2x95) | (2x120) |
| (3x95) | (3x95) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*This chart is a general guideline and may not suit all applications. If cable overheating occurs, use next size larger cable.
**Weld cable size (AWG) is based on either a 4 volts or less drop or a current density of at least 300 circular mils per ampere. |
|
( ) = mm2 for metric use |
***For distances longer than those shown in this guide, call a factory applications representative at