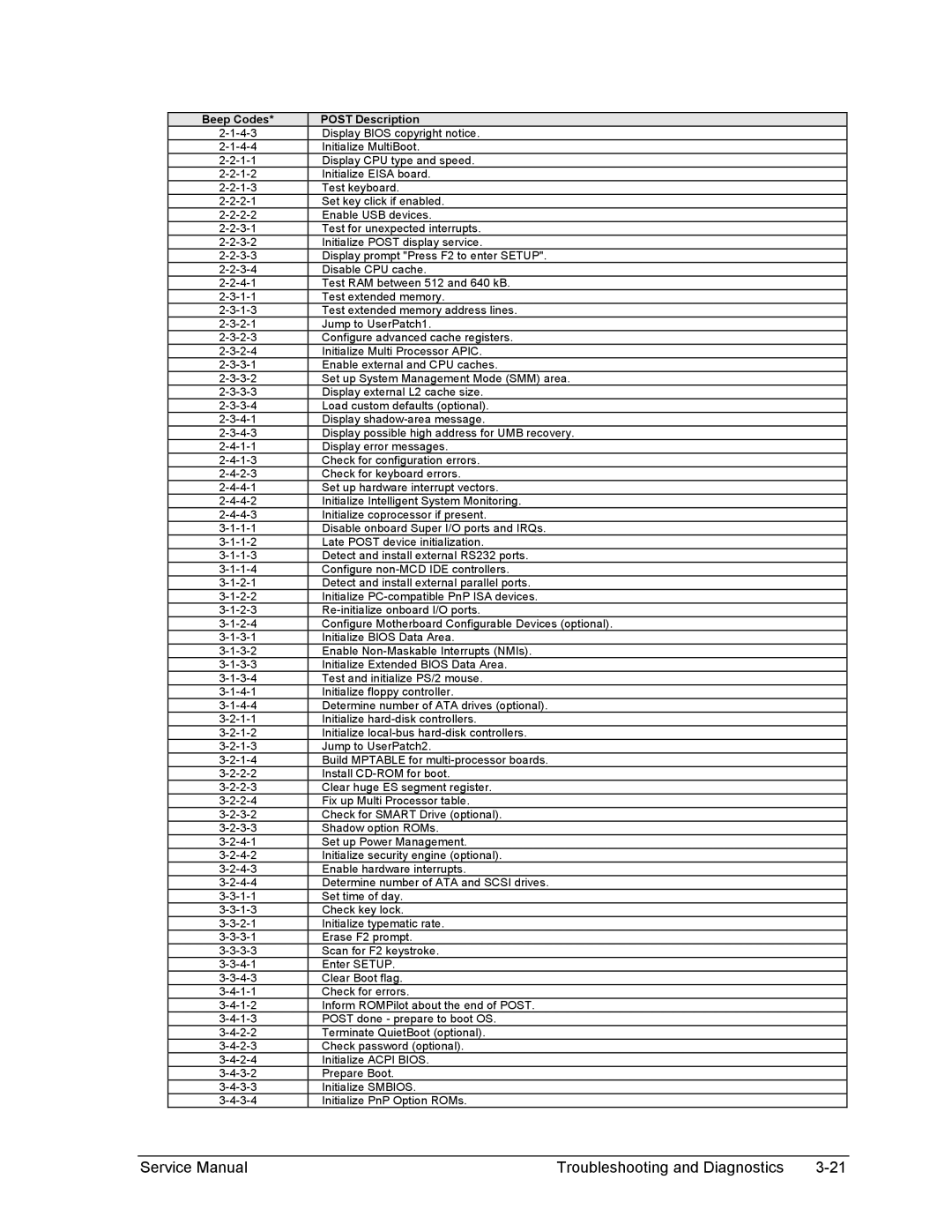
2500, 2100, 1100 specifications
The HP 1100 and 1100A are pivotal laser printers developed by Hewlett-Packard in the early 1990s, marking significant advancements in printing technology of their time. Since their introduction, these models have garnered a reputation for reliability and efficiency, making them a staple in many offices.One of the standout features of the HP 1100 series is its fast printing speed. The printers can produce up to 12 pages per minute, which was an impressive feat at the time of their release. This speed significantly reduced waiting times, allowing users to handle large-volume printing jobs with ease. Furthermore, the printers support a variety of media types, including letterhead, envelopes, and labels, enhancing versatility in print applications.
The HP 1100 and 1100A utilize laser technology, which ensures sharp and high-quality prints. The printers have a native resolution of 600 x 600 dots per inch (DPI), enabling crisp text and detailed graphics. This high-resolution output made the models particularly favored for producing professional documents and presentations.
Another key characteristic is the generous memory capacity. The HP 1100 typically comes with 2 MB of standard RAM, which is expandable, allowing for improved performance in handling complex print jobs. Users can adjust the memory according to their requirements, resulting in better efficiency, particularly in environments that demand high-volume printing.
The HP 1100 series also showcases a straightforward and user-friendly operation. The built-in control panel simplifies the printing process, allowing users to manage jobs intuitively. Additionally, with the inclusion of parallel and later USB connectivity options, integration with various computer systems was seamless, ensuring compatibility with existing office infrastructure.
Energy efficiency is another aspect worth noting, as the printers are designed to consume minimal power when idle, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly solutions.
Overall, the HP 1100 and 1100A stand out for their robust construction, high-speed performance, exceptional print quality, and user-friendly features, making them a trusted choice for small to medium-sized businesses in need of dependable printing solutions. Their impact on the printing landscape during the 1990s continues to be felt today, as they paved the way for subsequent generations of laser printers.