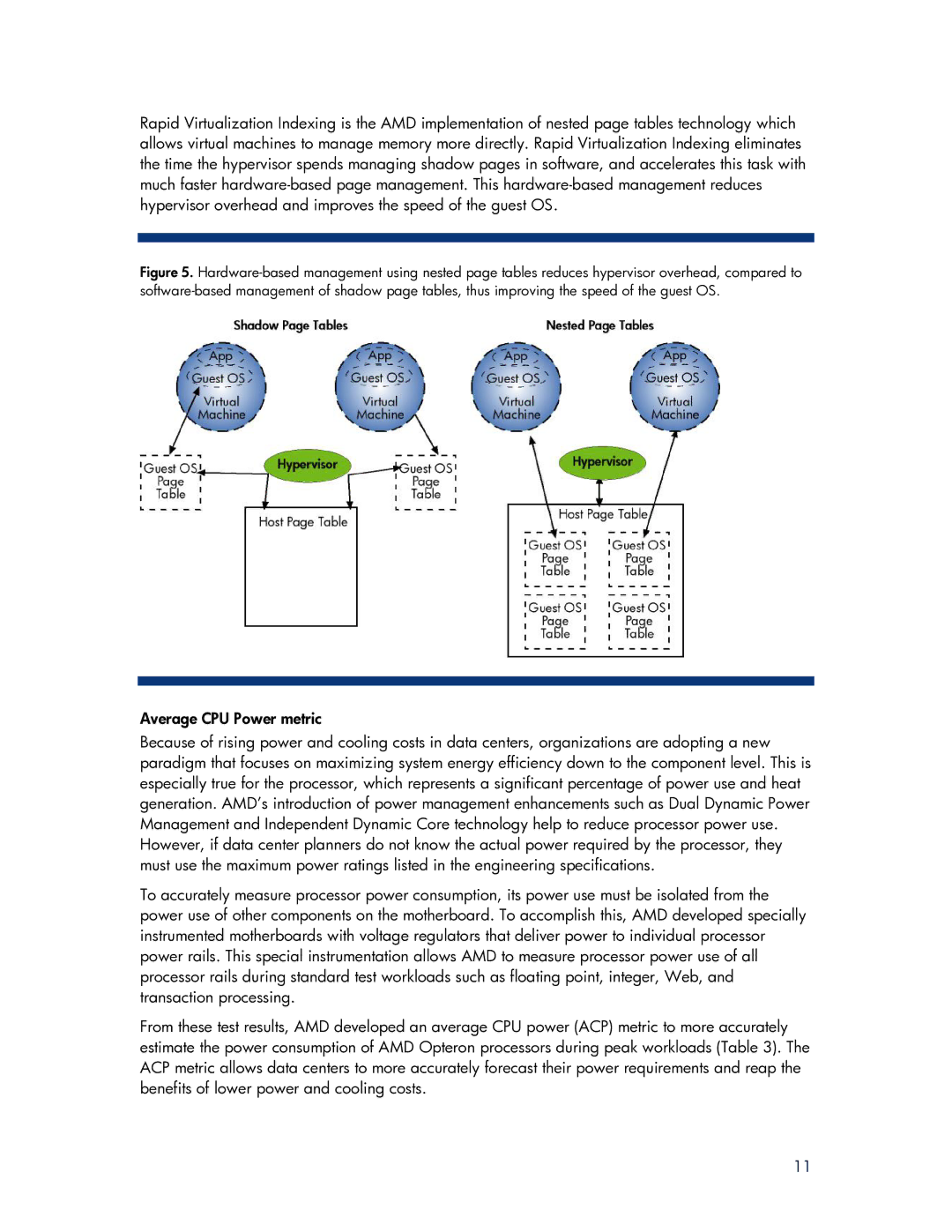
Rapid Virtualization Indexing is the AMD implementation of nested page tables technology which allows virtual machines to manage memory more directly. Rapid Virtualization Indexing eliminates the time the hypervisor spends managing shadow pages in software, and accelerates this task with much faster
Figure 5. Hardware-based management using nested page tables reduces hypervisor overhead, compared to software-based management of shadow page tables, thus improving the speed of the guest OS.
Average CPU Power metric
Because of rising power and cooling costs in data centers, organizations are adopting a new paradigm that focuses on maximizing system energy efficiency down to the component level. This is especially true for the processor, which represents a significant percentage of power use and heat generation. AMD’s introduction of power management enhancements such as Dual Dynamic Power Management and Independent Dynamic Core technology help to reduce processor power use. However, if data center planners do not know the actual power required by the processor, they must use the maximum power ratings listed in the engineering specifications.
To accurately measure processor power consumption, its power use must be isolated from the power use of other components on the motherboard. To accomplish this, AMD developed specially instrumented motherboards with voltage regulators that deliver power to individual processor power rails. This special instrumentation allows AMD to measure processor power use of all processor rails during standard test workloads such as floating point, integer, Web, and transaction processing.
From these test results, AMD developed an average CPU power (ACP) metric to more accurately estimate the power consumption of AMD Opteron processors during peak workloads (Table 3). The ACP metric allows data centers to more accurately forecast their power requirements and reap the benefits of lower power and cooling costs.
11