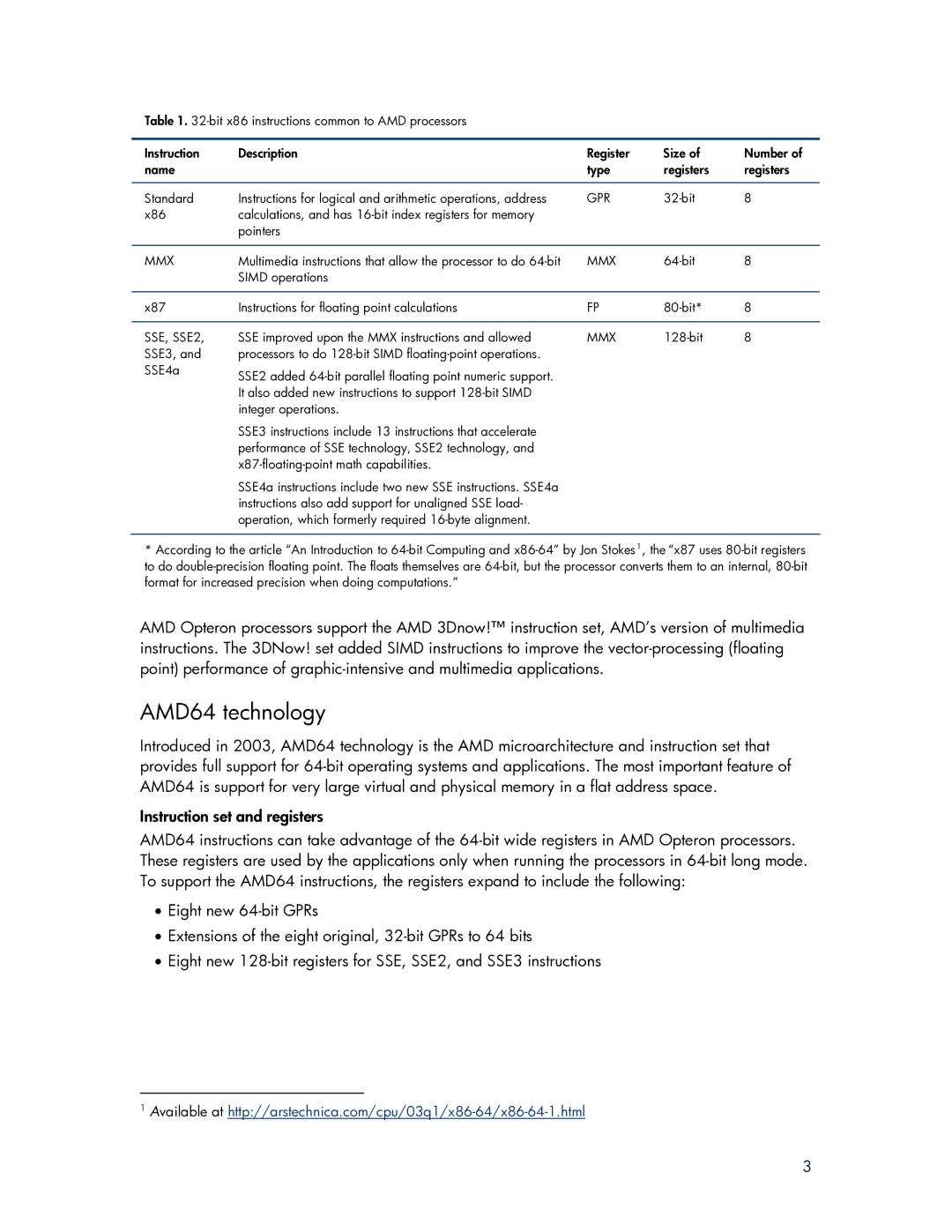
Table 1.
Instruction | Description | Register | Size of | Number of |
name |
| type | registers | registers |
|
|
|
|
|
Standard | Instructions for logical and arithmetic operations, address | GPR | 8 | |
x86 | calculations, and has |
|
|
|
| pointers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
MMX | Multimedia instructions that allow the processor to do | MMX | 8 | |
| SIMD operations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
x87 | Instructions for floating point calculations | FP | 8 | |
|
|
|
|
|
SSE, SSE2, | SSE improved upon the MMX instructions and allowed | MMX | 8 | |
SSE3, and | processors to do |
|
|
|
SSE4a | SSE2 added |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
It also added new instructions to support
SSE3 instructions include 13 instructions that accelerate performance of SSE technology, SSE2 technology, and
SSE4a instructions include two new SSE instructions. SSE4a instructions also add support for unaligned SSE load- operation, which formerly required
*According to the article “An Introduction to
AMD Opteron processors support the AMD 3Dnow!™ instruction set, AMD’s version of multimedia instructions. The 3DNow! set added SIMD instructions to improve the
AMD64 technology
Introduced in 2003, AMD64 technology is the AMD microarchitecture and instruction set that provides full support for
Instruction set and registers
AMD64 instructions can take advantage of the
•Eight new
•Extensions of the eight original,
•Eight new
1Available at
3