The files and filesystems can be shared and accessed concurrently within the cluster. However, file sharing and access from outside the cluster will still require NFS - client systems which are not members of the CFS cluster will use NFS to access the shared filesystems.
Cross mounting (with the nfs_xmnt script) is not needed since you can use CFS to share files and filesystems within the cluster.
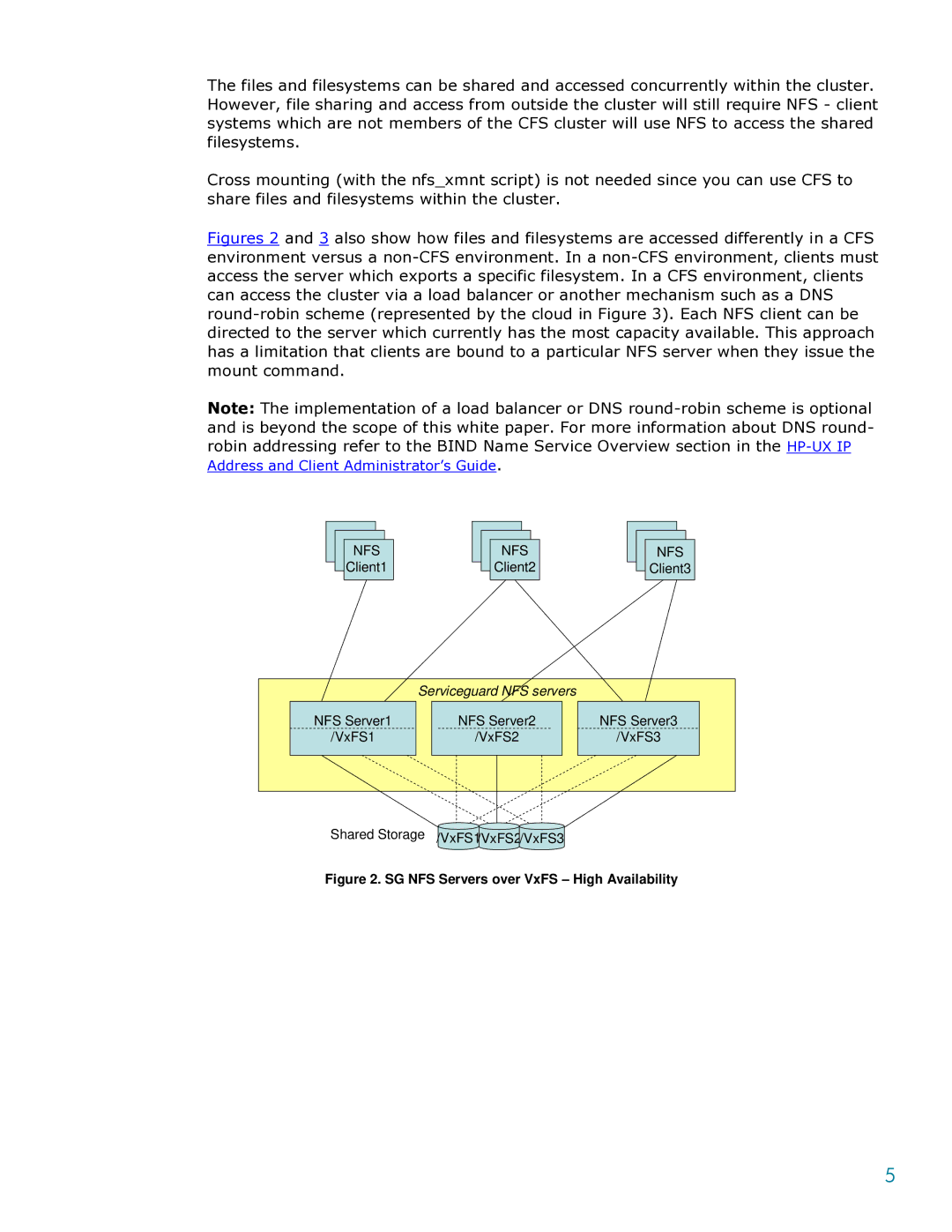
Figures 2 and 3 also show how files and filesystems are accessed differently in a CFS environment versus a non-CFS environment. In a non-CFS environment, clients must access the server which exports a specific filesystem. In a CFS environment, clients can access the cluster via a load balancer or another mechanism such as a DNS round-robin scheme (represented by the cloud in Figure 3). Each NFS client can be directed to the server which currently has the most capacity available. This approach has a limitation that clients are bound to a particular NFS server when they issue the mount command.
Note: The implementation of a load balancer or DNS
NFS
![]() Client1
Client1
NFS
![]() Client2
Client2
NFS
![]() Client3
Client3
| Serviceguard NFS servers |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
NFS Server1 |
| NFS Server2 | NFS Server3 | |
/VxFS1 |
| /VxFS2 | /VxFS3 | |
Shared Storage | /VxFS1/VxFS2/VxFS3 |
Figure 2. SG NFS Servers over VxFS – High Availability
5