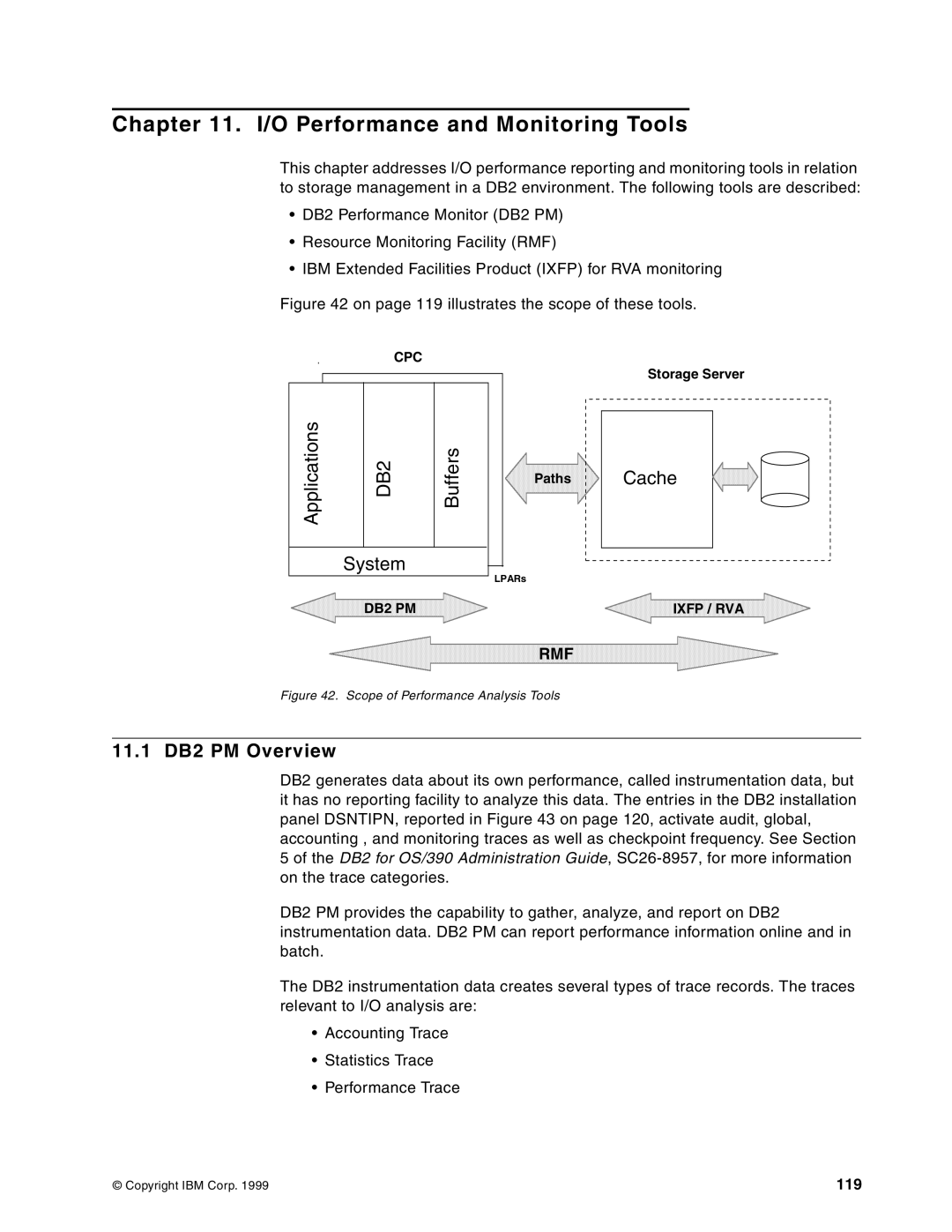
5695-DF1, 5655-DB2 specifications
IBM 5655-DB2 and 5695-DF1 are significant components within the IBM software ecosystem, predominantly focusing on data management and integration solutions. These offerings cater primarily to enterprise environments that require robust database management systems and associated frameworks to maintain and manipulate data efficiently.IBM 5655-DB2 is a well-known relational database management system (RDBMS) that excels in managing large volumes of structured data. Its architecture is designed to support high availability, scalability, and performance, crucial for businesses operating in today’s data-driven world. Some of its main features include advanced indexing capabilities, support for complex queries, and dynamic workload management. Additionally, it provides strong concurrency controls, which enable multiple users to access and manipulate data simultaneously without compromising data integrity.
One of the key characteristics of DB2 is its support for various data types, including JSON and XML, making it versatile for modern applications that generate data in diverse formats. It also features robust security mechanisms to protect sensitive data, aligning with compliance standards across industries. Integration with analytics tools further allows businesses to derive insights from their data, enhancing decision-making processes.
On the other hand, IBM 5695-DF1, also known as the InfoSphere DataStage, is a powerful data integration tool that facilitates the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) of data from various sources to target systems. It empowers organizations to streamline their data flows, ensuring that clean, consistent information is available for analysis and operational use. Key features of 5695-DF1 include a user-friendly graphical interface that enhances developer productivity and a rich set of connectors for numerous data sources, enabling seamless data integration.
DataStage also supports real-time data integration, allowing businesses to keep their data synchronized across multiple platforms. Its parallel processing capabilities dedicatedly optimize performance, enabling organizations to handle vast datasets efficiently. It incorporates data quality tools that help in validating and cleansing data before it is used for decision-making processes.
Both IBM 5655-DB2 and 5695-DF1 are part of a broader strategy to accommodate the evolving landscape of data management. Businesses leverage these technologies to enhance their data architectures, fostering agility and competitive advantage in their respective markets. Their integration capabilities, along with a focus on security and scalability, position them as vital assets in modern enterprise environments. Whether managing critical data within a database or ensuring seamless data flow across systems, these IBM offerings provide a comprehensive approach to handling complex data challenges.