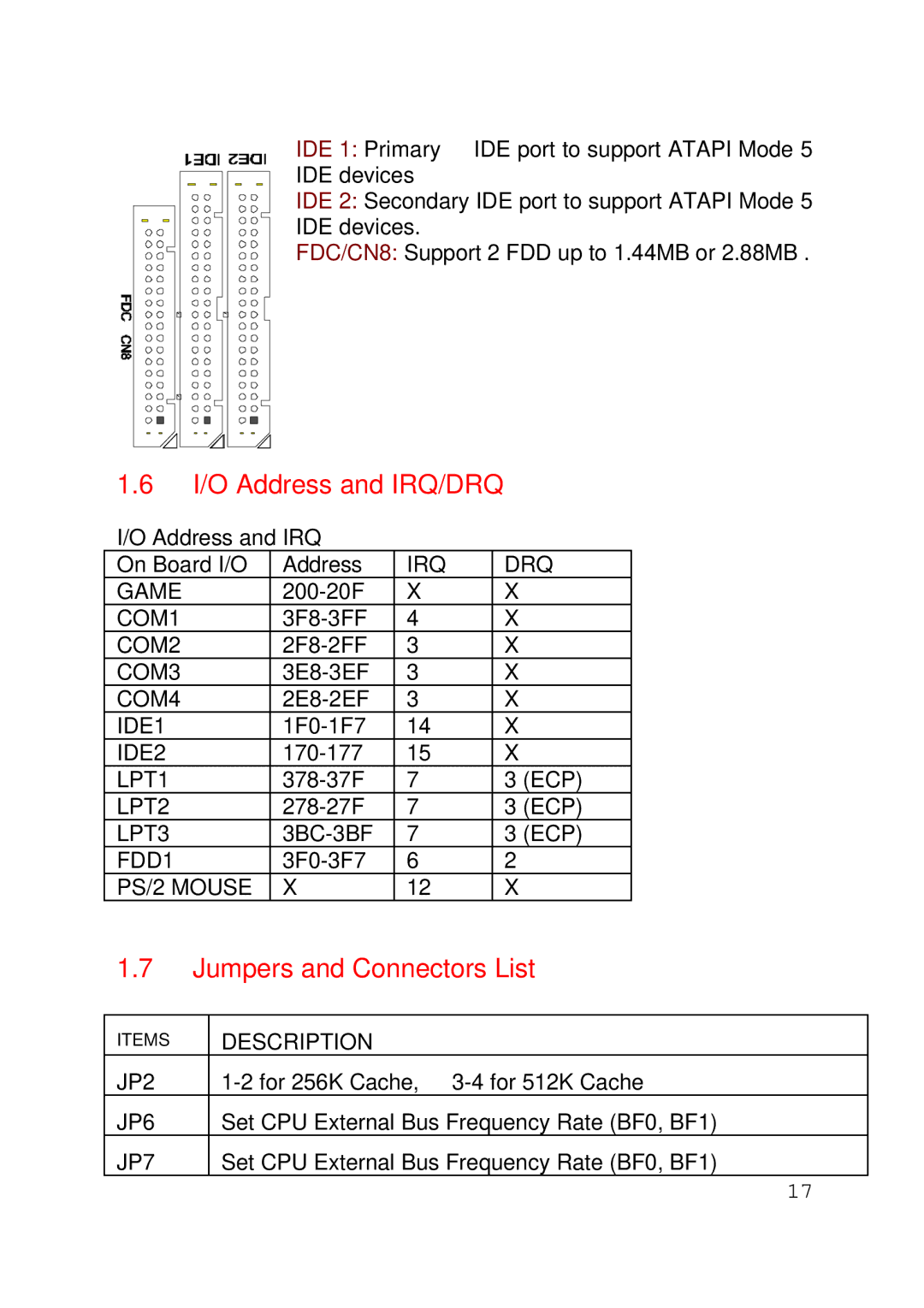
430TX specifications
The Intel 430TX chipset, introduced in the mid-1990s, was a significant advancement in computer technology, primarily designed to support Intel's Pentium processors. This chipset catered to the growing demand for improved multimedia performance, better system stability, and expanded features to accommodate developing applications.One of the main features of the Intel 430TX was its support for Dual Independent Bus architecture. This allowed for simultaneous data transfers between the CPU and the memory, significantly improving system performance. The chipset supported up to 512 MB of EDO (Extended Data Out) RAM and featured a memory bus that could handle speeds of up to 66 MHz, making it suitable for a variety of applications ranging from home computing to business use.
Another significant characteristic of the 430TX was its integration of a PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) bus, which allowed for higher bandwidth compared to the older ISA (Industry Standard Architecture) connections. The chipset provided up to five PCI slots, facilitating the addition of modern peripherals like graphics cards, sound cards, and network interfaces without compromising system performance. This flexibility was vital as multimedia applications became increasingly common during that era.
The Intel 430TX also incorporated support for the newer ATA/33 standard for hard drives, allowing for faster data transfer rates compared to previous standards. This enhancement contributed to improved overall system responsiveness. Moreover, the chipset partially supported USB (Universal Serial Bus) devices, paving the way for the increasingly popular external peripherals that were emerging at the time.
In terms of power management, the 430TX featured advanced management capabilities, allowing the system to achieve better energy efficiency through features such as ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface) support. This was particularly important as users began to prioritize environmental concerns alongside performance.
Overall, the Intel 430TX chipset represented a balance of performance, compatibility, and innovative feature integration. Its legacy is evident in the foundational technologies it helped propel, influencing the design and features of future chipsets. Today, revisiting the Intel 430TX illustrates the rapid technological evolution that has occurred since its introduction, underscoring its importance in the development of modern computer systems. The 430TX was pivotal in bridging the gap between early PC architectures and the advanced systems we utilize today.