Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Many router hardware components are sensitive to damage from static electricity. Some components can be impaired by voltages as low as 30 V. You can easily generate potentially damaging static voltages whenever you handle plastic or foam packing material or if you move components across plastic or carpets. Observe the following guidelines to minimize the potential for electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can cause intermittent or complete component failures:
■Always use an ESD wrist strap or ankle strap, and make sure that it is in direct contact with your skin.
CAUTION: For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the ESD strap. The measurement should be in the range of 1 to 10 Mohms.
■When handling any component that is removed from the chassis, make sure the equipment end of your ESD strap is attached to one of the ESD points on the chassis, which are shown in Figure 11 on page 8 and Figure 12 on page 8.
■Avoid contact between the component and your clothing. ESD voltages emitted from clothing can still damage components.
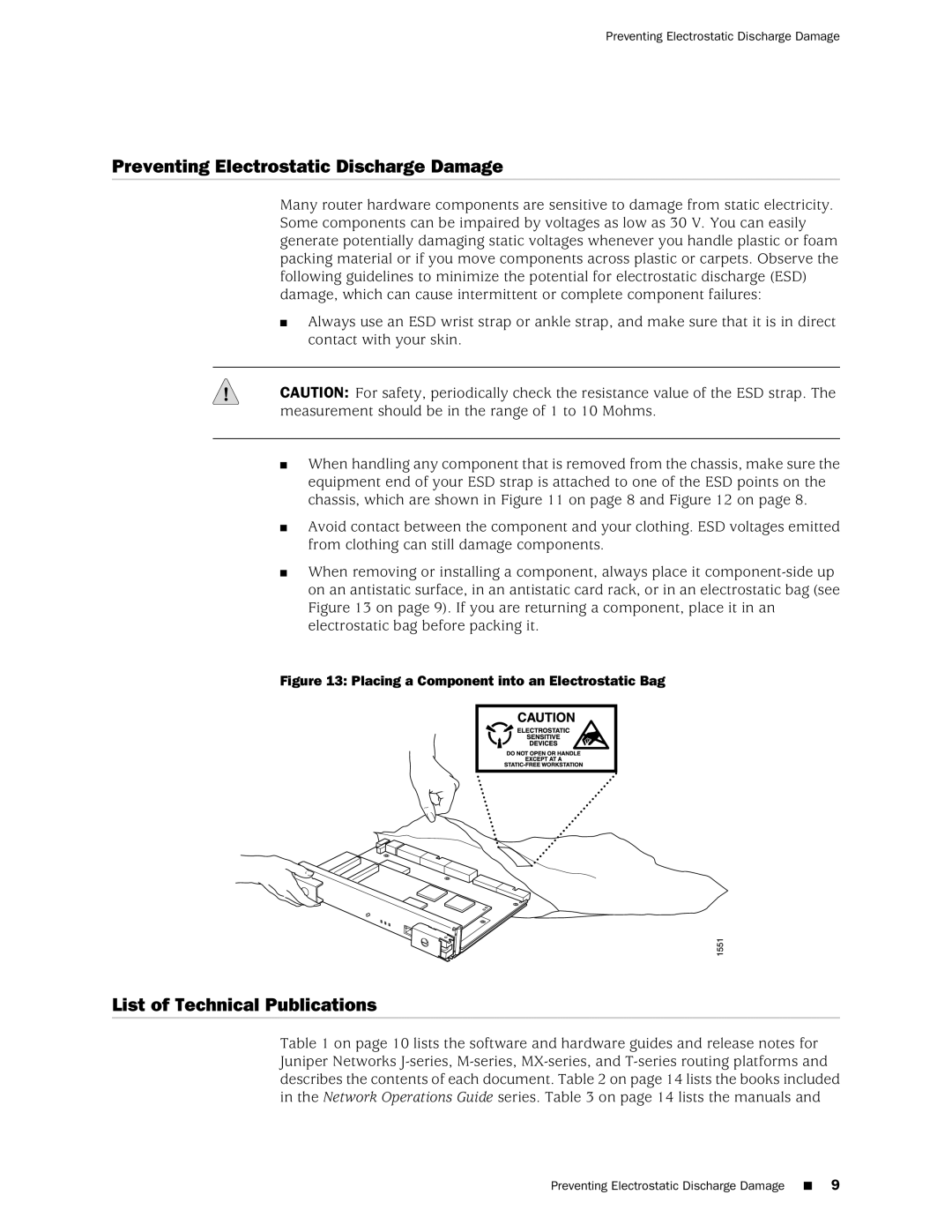
■When removing or installing a component, always place it
Figure 13: Placing a Component into an Electrostatic Bag
List of Technical Publications
Table 1 on page 10 lists the software and hardware guides and release notes for Juniper Networks
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage ■ 9