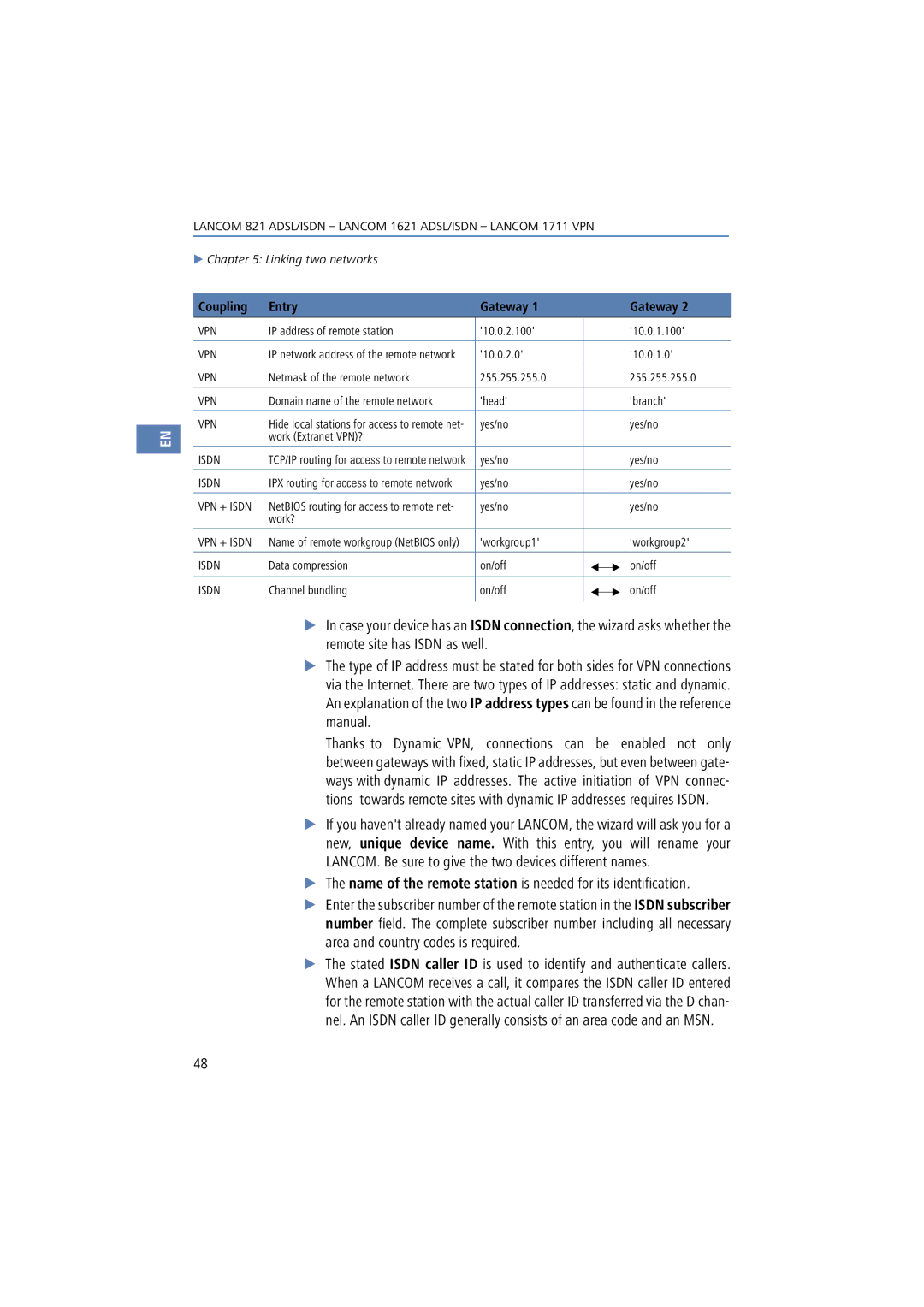
1621, 1711, 821 specifications
Lancom Systems is a notable player in the networking solutions market, and its range of routers, specifically the 821, 1621, and 1711 models, showcases the company's commitment to delivering robust, high-quality products for various enterprise needs. Each model brings distinct features, making them suitable for different environments and operational demands.The Lancom 821 is particularly designed for small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) requiring reliable internet connectivity and secure networking. This router supports various VPN technologies, ensuring secure data transmission across the organization. Equipped with advanced firewall capabilities, the 821 can handle multiple connections while protecting against potential cyber threats. Its support for IPv6 enhances compatibility with future networks, making it a long-term investment. The device’s manageable architecture allows for remote access and troubleshooting, reducing the need for on-site IT interventions.
On the other hand, the Lancom 1621 is tailored for larger organizations or those with more extensive networking demands. This model offers enhanced throughput and is capable of managing large volumes of traffic without compromising performance. It features a variety of WAN connection options, including DSL, LTE, and fiber, allowing businesses to choose the best solution for their requirements. The 1621 also incorporates sophisticated Quality of Service (QoS) settings, which prioritize critical applications to ensure optimal performance during peak times. Built-in redundancy features enhance reliability, making it an excellent choice for mission-critical applications.
The Lancom 1711 takes networking capabilities a step further, targeting enterprises with even more complex needs. It boasts advanced routing and switching features, making it suitable for enterprise-grade deployments. The 1711 supports enterprise WLAN management, allowing seamless integration with wireless access points. Its robust performance over WAN connections enables the deployment of various real-time applications, such as voice over IP (VoIP) and video conferencing, without latency issues. Security is a top priority, with features including an IPSec VPN and integrated threat detection to safeguard organizational data.
In summary, the Lancom 821, 1621, and 1711 routers serve as versatile tools for businesses, each designed with distinct capabilities to meet specific networking needs. Their strengths lie in their security features, support for various connection types, and reliable performance under heavy loads. With these devices, organizations can ensure that their network infrastructure not only meets current demands but is also poised for future growth.