algorithm defined in the Internet Draft “GSS Algorithm for TSIG
•Establishing a security context by passing security tokens.
•Once a security context has been established, it has a finite lifetime during which it can be used to create and verify transaction signatures on messages between the two parties.
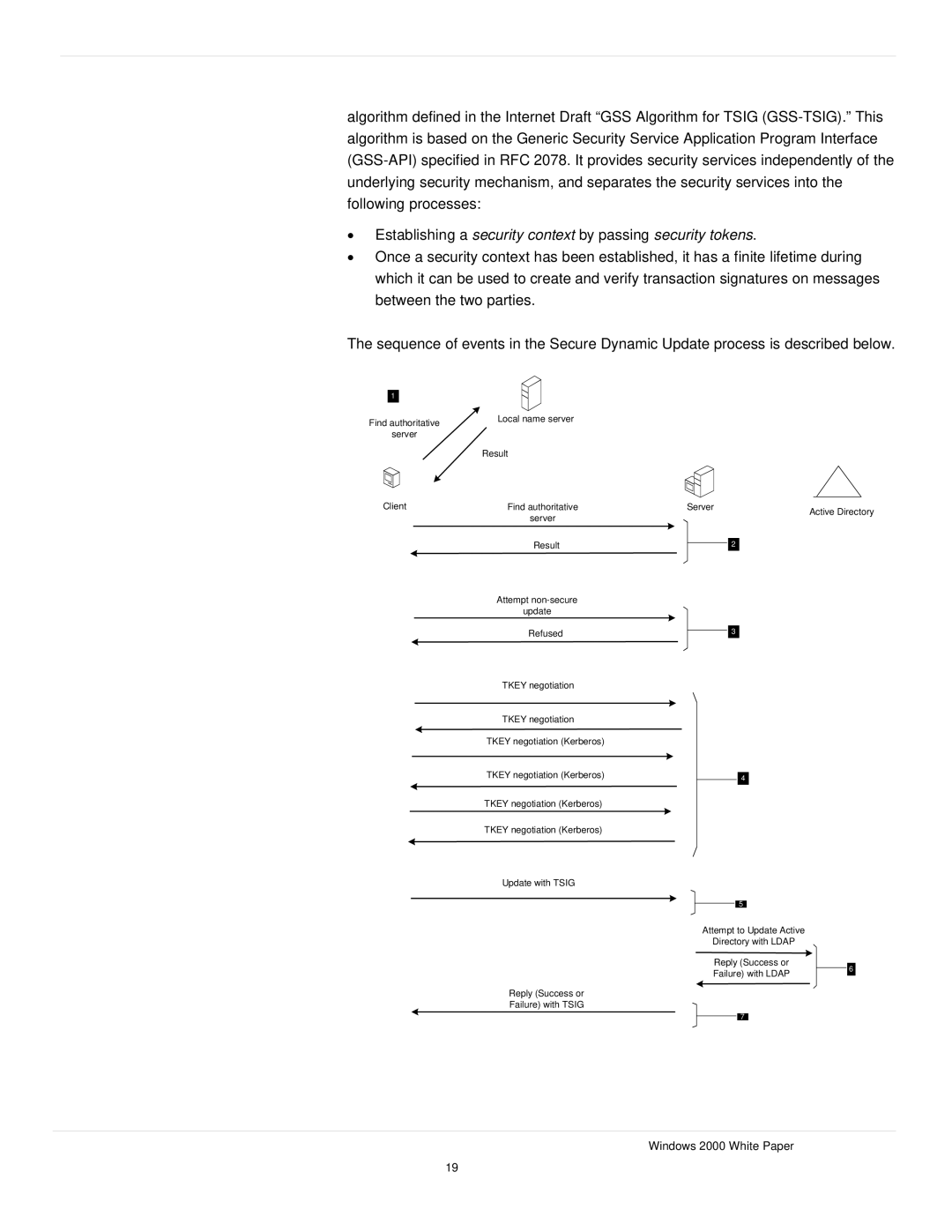
The sequence of events in the Secure Dynamic Update process is described below.
Find authoritative | Local name server |
| |||||
|
|
| |||||
server |
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
| Result |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Client | Find authoritative |
| |||||
|
|
|
|
| server |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Result |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Attempt |
| |
|
|
|
|
| update |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Refused |
| |
|
|
|
|
| TKEY negotiation |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TKEY negotiation |
| |
|
|
|
|
| TKEY negotiation (Kerberos) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TKEY negotiation (Kerberos) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| TKEY negotiation (Kerberos) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| TKEY negotiation (Kerberos) |
| |
|
|
|
|
| Update with TSIG |
| |
Reply (Success or
Failure) with TSIG
Server | Active Directory |
|
Attempt to Update Active
Directory with LDAP
Reply (Success or
Failure) with LDAP
Windows 2000 White Paper
19