12
For detailed information on CS 1000 components and operation please refer to Communication Server 1000 Release 6.0 user guides.
SSM Operation
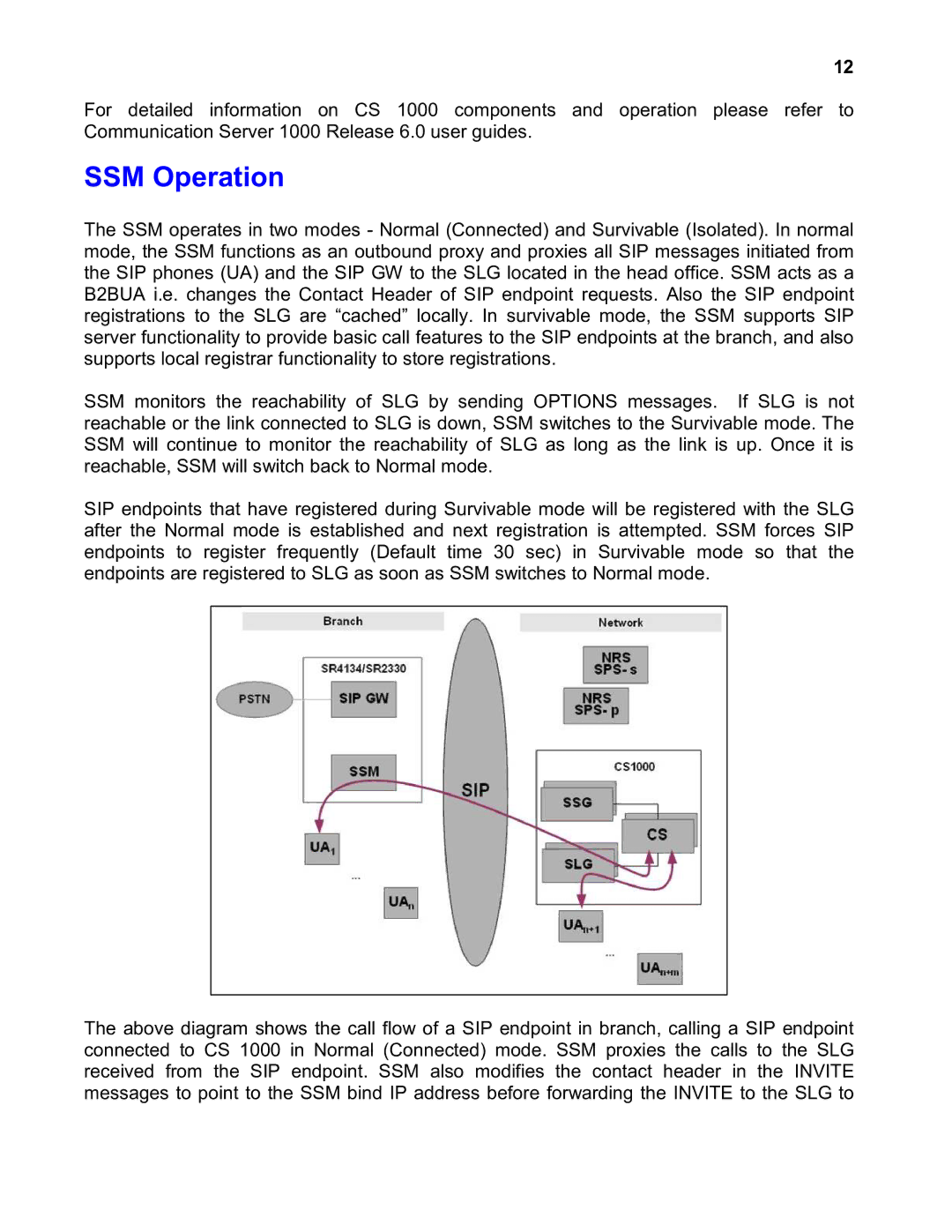
The SSM operates in two modes - Normal (Connected) and Survivable (Isolated). In normal mode, the SSM functions as an outbound proxy and proxies all SIP messages initiated from the SIP phones (UA) and the SIP GW to the SLG located in the head office. SSM acts as a B2BUA i.e. changes the Contact Header of SIP endpoint requests. Also the SIP endpoint registrations to the SLG are “cached” locally. In survivable mode, the SSM supports SIP server functionality to provide basic call features to the SIP endpoints at the branch, and also supports local registrar functionality to store registrations.
SSM monitors the reachability of SLG by sending OPTIONS messages. If SLG is not reachable or the link connected to SLG is down, SSM switches to the Survivable mode. The SSM will continue to monitor the reachability of SLG as long as the link is up. Once it is reachable, SSM will switch back to Normal mode.
SIP endpoints that have registered during Survivable mode will be registered with the SLG after the Normal mode is established and next registration is attempted. SSM forces SIP endpoints to register frequently (Default time 30 sec) in Survivable mode so that the endpoints are registered to SLG as soon as SSM switches to Normal mode.
The above diagram shows the call flow of a SIP endpoint in branch, calling a SIP endpoint connected to CS 1000 in Normal (Connected) mode. SSM proxies the calls to the SLG received from the SIP endpoint. SSM also modifies the contact header in the INVITE messages to point to the SSM bind IP address before forwarding the INVITE to the SLG to