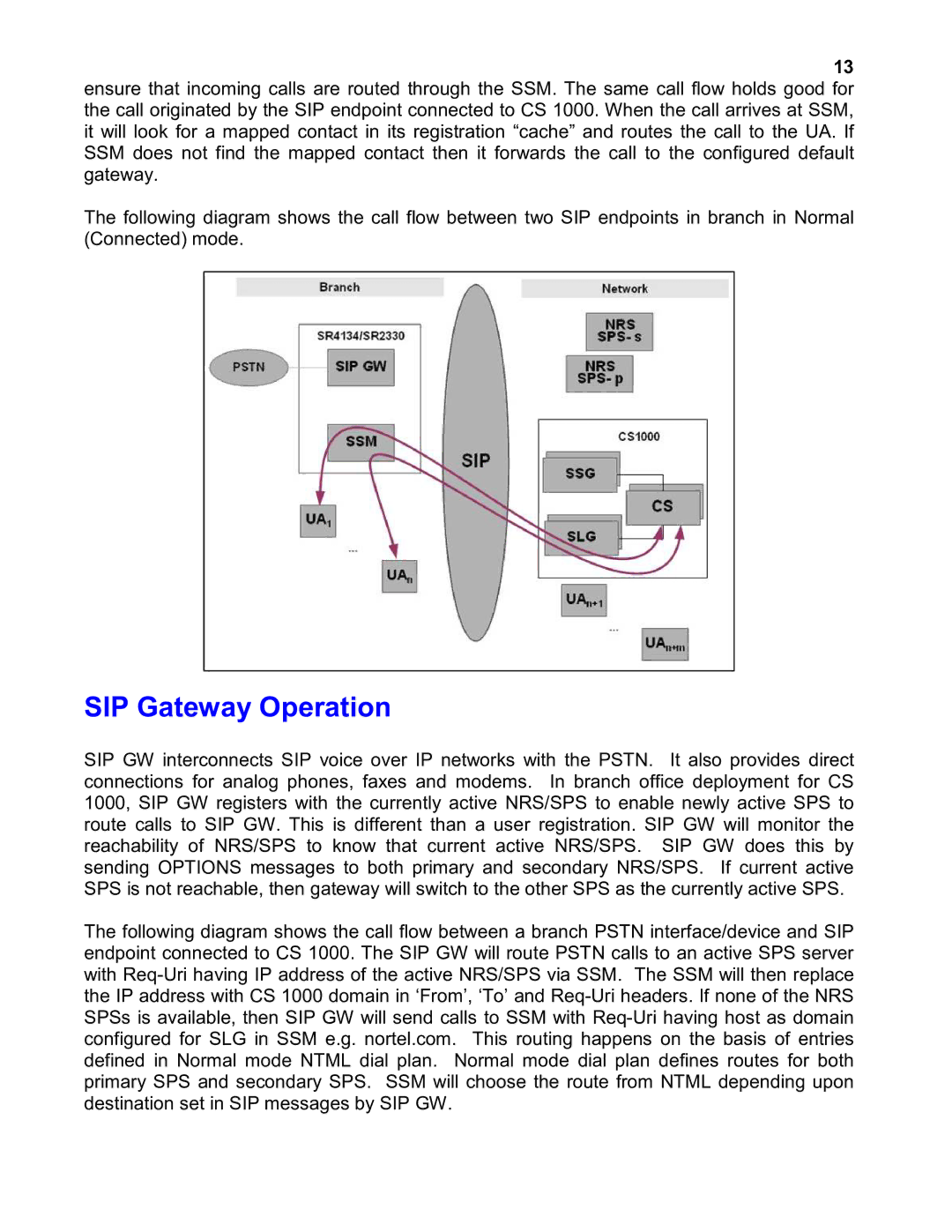
13 ensure that incoming calls are routed through the SSM. The same call flow holds good for the call originated by the SIP endpoint connected to CS 1000. When the call arrives at SSM, it will look for a mapped contact in its registration “cache” and routes the call to the UA. If SSM does not find the mapped contact then it forwards the call to the configured default gateway.
The following diagram shows the call flow between two SIP endpoints in branch in Normal (Connected) mode.
SIP Gateway Operation
SIP GW interconnects SIP voice over IP networks with the PSTN. It also provides direct connections for analog phones, faxes and modems. In branch office deployment for CS 1000, SIP GW registers with the currently active NRS/SPS to enable newly active SPS to route calls to SIP GW. This is different than a user registration. SIP GW will monitor the reachability of NRS/SPS to know that current active NRS/SPS. SIP GW does this by sending OPTIONS messages to both primary and secondary NRS/SPS. If current active SPS is not reachable, then gateway will switch to the other SPS as the currently active SPS.
The following diagram shows the call flow between a branch PSTN interface/device and SIP endpoint connected to CS 1000. The SIP GW will route PSTN calls to an active SPS server with