Iolan DS1/TS2
EN 55022 1998, Class A, Note
Table of Contents
Configuration Methods
DHCP/BOOTP
Getting Started
Configuring Serial Ports
Console Management Profile
Configuring Users
Configuring Security
UDP
Configuring the System
Controlling the I/O Channels
Appendix a Virtual Modem AT Commands
Appendix D I/O Wiring Diagrams
Appendix G Troubleshooting
Documentation
Preface
About This Book
Intended Audience
Online Help
Typeface Conventions
About the Iolan
Introduction
Iolan Family Models
Hardware
Iolan Features
Security
Software
Iolan Features
Introduction
Connectivity
Iolan Components
Overview
Power Supply Specifications
Getting to Know Your Iolan
Desktop Models
Serial Activity
DS1
End View
Top View
Console Mode
Console/Serial Switch
Serial Mode
Serial Only Models
Powering Up the Iolan
Models
Configuration Methods Chapter
Configures an IP Address
Configuration Methods Overview
Requires a Configured IP Address
Easy Config Wizard
DeviceManager
Access Platforms
Unique Features
Connecting to the Iolan Using DeviceManager
DeviceManager
Using DeviceManager
WebManager
Connecting to the Iolan Using WebManager
Using WebManager
Connecting to the Iolan Using the CLI
Command Line Interface
Through the Network
Through the Serial Port
Using the CLI
Connecting to the Iolan Using the Menu
Menu
Using the Menu
Using DHCP/BOOTP
Connecting to the Iolan Using DHCP/BOOTP
DHCP/BOOTP Parameters
Snmp
Connecting to the Iolan Using Snmp
Using the Snmp MIB
Snmp
Getting Started
Easy Configuration Wizard
Setting Up the Network
Using a Direct Serial Connection to Enable BOOTP/DHCP
Using a Direct Serial Connection to Specify an IP Address
Set server internet dhcp/bootp on
For an IPv6 Network
Using ARP-Ping
Setting Up the Serial Ports
Setting Up the Serial Ports
Setting Up Users
Using DeviceManager WebManager
DeviceManager
Navigating DeviceManager/WebManager
WebManager
Starting a New Session
Using DeviceManager to Connect to the Iolan
Assigning a Temporary IP Address to a New Iolan
Logging in to the Iolan
Adding/Deleting Manual IOLANs
Logging into the Iolan
Using WebManager to Connect to the Iolan
Configuration Files
Creating a New Iolan Configuration in DeviceManager
Importing an Existing Configuration File
Opening an Existing Configuration File
Managing the Iolan
Network Settings
Field Descriptions
IP Settings
IP Settings
Overview
Advanced
Automatically server Default Enabled
Host Table
Advanced
Functionality
Route List
Adding/Editing a Host
Adding/Editing Routes
Functionality
Serial Ports
Editing a Serial Port
Resetting a Serial Port
Common Tabs
Serial Port Profiles
Hardware Tab Field Descriptions
Enable Inbound
Default None
Default Full
Default Auto Flow Control
Packet Forwarding Tab Field Descriptions
Packet Size
Enable Trigger1
Enable Trigger2
Packet Definition
Console Management Profile
Data Options IPv4 Address
Default Telnet
General Tab Field Descriptions
Protocol Listen for Connections on TCP Port
Advanced Tab Field Descriptions
Dial Out
Dial Timeout
Break Handling
Dial
TruePort Profile
Connect to
System Default Enabled Host Name
Connect to remote
TCP Port
Define a primary
Host and backup
Adding/Editing Additional TruePort Hosts
Hosts to connect to
Adding/Editing a Multihost Entry
Backup Host
Primary Host
When
Signals high
Day Motd Default Disabled Idle Timeout
Session Timeout
TCP Sockets Profile
General Tab Field Descriptions
Adding/Editing Additional Hosts
Adding/Editing a Multihost Entry
Keepalive
Enable TCP
UDP Sockets Profile
This entry is disabled since Direction is set to Disabled
Autolearn
Listen for connections on UDP port Direction
Start IP Address
End IP Address
Port
Default 0 zero
Terminal Profile
Any Port
VT320 specifically supporting VT320-7
Default Dumb
VT100
TVI925
Automatically
When any data is
Day Motd Default Disabled
Protocol
Data Range
Disconnect User logs out Default Disabled
Login Settings
User Service Settings
Telnet Settings
Echo
Interrupt
Quit
Erase
Client Iolan Tunnel
Serial Tunneling Profile
Serial Server Tunnel
Serial
Act As Tunnel
Client Default Disabled Host Name
Server
Virtual Modem Profile
100 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
DTR Signal Acts as RTS Signal Always On RTS Signal Acts as
Phone Number to Host Mapping
Host IP Address
Control Signal I/O Profile
VModem Phone Number Entry
Phone Number
Latch
Input Signal Field Descriptions
Invert Signal
Description
Manual Clear
Output Signal Field Descriptions
Auto Clear Mode
Mode Default Disabled Syslog
Modbus Gateway Profile
IP Mappings
Settings Button Modbus/RTU
Mode
Destination Slave
Default 1000 ms
Default 30 ms
Advanced Field Descriptions
Adding/Editing Modbus Slave IP Settings
Modbus Slave IP Settings Field Descriptions
UID Start
Data Options TCP or UDP
Default Host
Default TCP
UID End
Modbus Slave Advanced Settings Field Descriptions
General Tab Field Description
Custom Application Profile
Monitor
Advanced Serial Settings Tab
Closing Serial Port Default Disabled Deny Multiple
Network
Adding/Editing a Modem
Modems Tab
Name Name of the modem
Field Definitions
TruePort Baud Rate Tab
116 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
Configuring Users
User Settings
General Tab
Adding/Editing Users
Level
Default Normal
Host IP
Services Tab
Service
Default DSPrompt
Advanced Tab
Default English
Language
Sessions Tab
Connect
Session 1, 2, 3
Serial Port Access Tab
126 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
Services
Configuring Security
Field Descriptions
Configuring I/O InterfacesChapter
Access Functionality
Settings
Advanced Slave Modbus Settings
Failsafe Action is triggered
Failsafe Timer Functionality
Timeout
Default 30 seconds
Broadcast of I/O Default Disabled Status
Enable UDP
UDP Functionality
UDP Entry
Temperature Functionality
UDP Settings
Default Celsius
Analog
Channels
Alarm Settings
Default Current
Digital I/O
Digital Input
Input Mode
139
Digital Output
Output
Output Mode
Default Sink
Default Manual
Pulse Count
Pulse Mode
Inactive Signal Width Active Signal Width
Delay
Application Industrial Freezers
Relay
Relay I/O
Monitoring Device Server
Width
Inactive Signal
Active Signal
Temperature
Default RTD
Basic Analog Alarm Settings
Alarm Settings
Clear
Advanced Analog Alarm Settings
Clear Mode
Trigger Type
Analog Data
UDP Unicast Format
Total Data Length Exists
Length Data
Serial Pin Signal Data
UDP Unicast Example
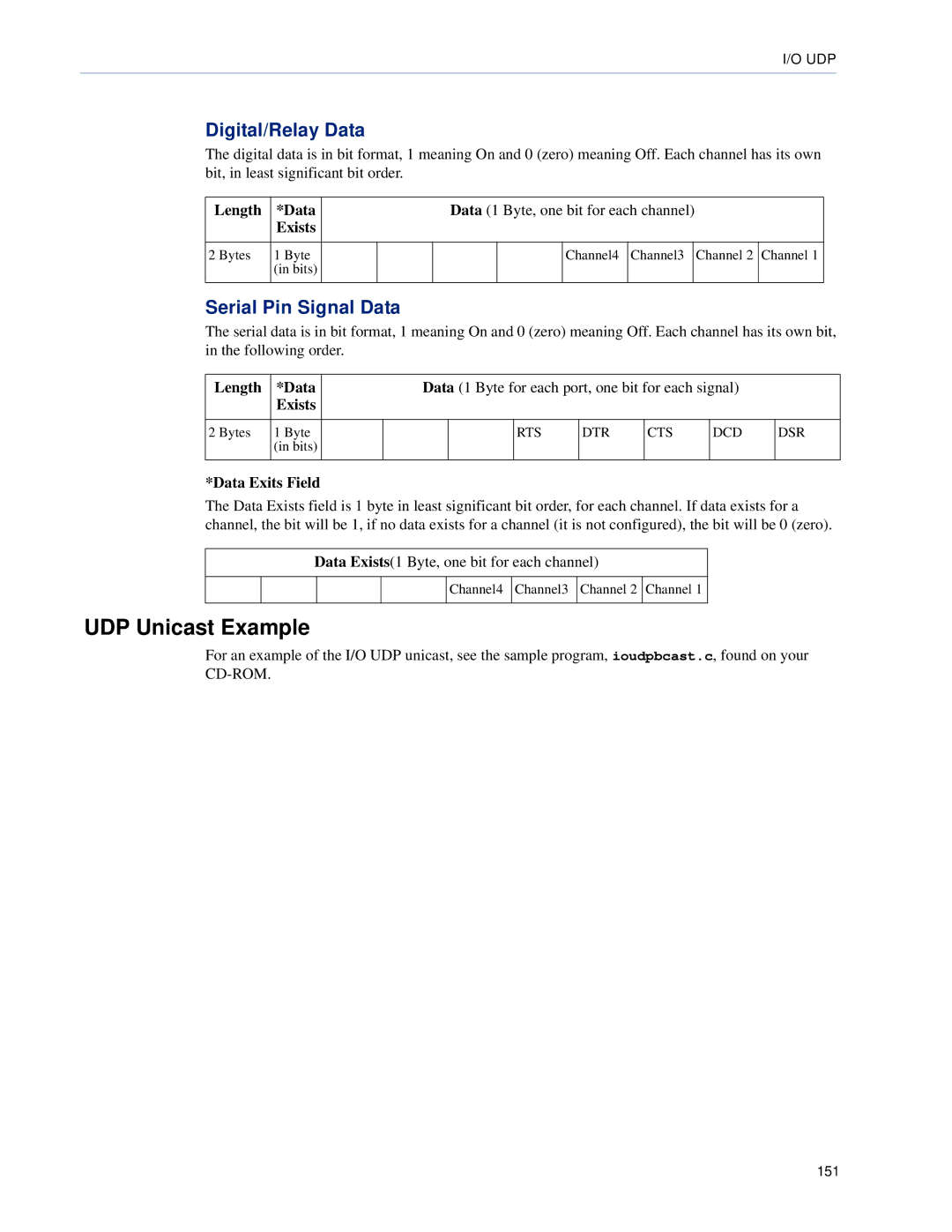
Digital/Relay Data
Modbus Serial Application Connected to the Serial Port
Modbus Slave
Modbus Serial Application Connected to the Network
Modbus TCP Application
Modbus I/O Access
Function Codes
Coil/Register Descriptions
Input Registers
Serial Port Coil/Register Descriptions
A4/T4 Registers
Data Model A1/T1 A2/T2 A3/T3 A4/T4 Holding Registers
Data Model D1/R1 D2/R2 Coils
A4D2/A4R2 Registers
Data Model Pin Coils
Serial Pin Signals
D4/D2R2 Registers
Data Model D3/R1 D4/R2 Coils
PC running a
Modbus Serial Application TruePort Power Digital Output
TruePort I/O
TruePort/Modbus Combination
API Over TruePort Only
Power Digital Output
PC running Custom Application API TruePort
Setup
Accessing I/O Data Via TruePort
Introduction
Response Format
Format of API Commands
Get Commands
Command Format
Set Commands
Example 2 Turn on the first and second relay on a D2R2 unit
Successful Response Format
Unsuccessful Response Format
Example 1 Turn on the first relay on a D2R2 unit
Snmp Traps
Error Codes
Alerts
Configuring the System Chapter
Syslog
Management
Custom App/Plugin
Field Description
Login Tab Field Descriptions
Bootup Files Tab Field Descriptions
Tftp Tab Field Descriptions
Message of the Day Motd Tab Field Descriptions
Controlling the I/O Channels
Activate Output Manually activates the channel output
Downloading Configuration Files
System Administration Chapter
Managing Configuration Files
Saving Configuration Files
Reboot Server
Downloading Configuration Files to Multiple IOLANs
Server Name
Downloading Iolan Firmware
Uploading Configuration Files
Calibrating I/O
Calibrating Temperature Input
Calibrating Analog Input
Calibrating RTD
Calibrating Analog Channels
Rebooting the Iolan
Setting the IOLAN’s Date and Time
Resetting Calibration Data
Language Support
Resetting the Iolan to Factory Defaults
Loading a Supplied Language
Translation Guidance
Software Upgrades and Language Files
Creating Terminal Definition Files
Downloading Terminal Definitions
For example
Resetting Configuration Parameters
Lost Admin Password
184 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
Virtual Modem Initialization Commands
Commands
AT&Rn
AT&Sn
AT&Cn
Serial Pinouts
Pinouts and Cabling Diagrams
DB25 Male
DB25 Female
GND CTS
RJ45
DB9 Male I/O
DB9 Male Serial Only
DB25 Female
EIA-232 Cabling Diagrams
Terminal DB25 Connector
DB25 Male
DB9 Male
RJ45
10-pin Pin
Iolan RJ45 DCE
Modem DB25 Connector
RxD TxD DTR 20 DTR GND
Port Iolan
Setting Jumpers
Iolan DB25 Male/Female
Iolan RJ45
DIP
Digital I/O Module
Analog Input Module
200 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
Digital Input Dry Contact
Wiring I/O Diagrams
Digital I/O
Digital Input Wet Contact
Digital Output Source
Digital Output Sink
Voltage
Temperature Input
Analog Input
Current
Relay Output
RTD 2-Wire
RTD 3-Wire
RTD 4-Wire
Normally Closed Contact
206 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
TruePort
TruePort Utility
API Request Format
API I/O Access Over TruePort
API Response Format
Error Codes
210 Iolan DS1/TS2 User’s Guide, Version
Starter Kit Adapters/Cable
Accessories
RJ45F DB25M DTE
RJ45F to DB25M DTE Crossover Adapter
RJ45F to DB25M DCE Modem Adapter
RJ45F DB25F
RJ45F to DB25F DTE Crossover Adapter
RJ45F to DB9M DTE Crossover Adapter
RJ45F to DB9F DTE Crossover Adapter
Sun/Cisco RJ45M Connector Cable for Rack Mount Models
Power/Ready LED continues to flash green in Desktop models
Troubleshooting
Hardware Problems
Communication Issues
Host Problems
DeviceManager Problems
Login Problems
Unknown IP Address
Problems with Terminals
Models
DHCP/BOOTP Problems
Language Problems
Long Reboot Cycle
Glossary
RIP Routing
PAP Password
Authentication Protocol Radius Remote
Authentication Dial Users Services Reverse Connection
Index
Bootp
Snmp