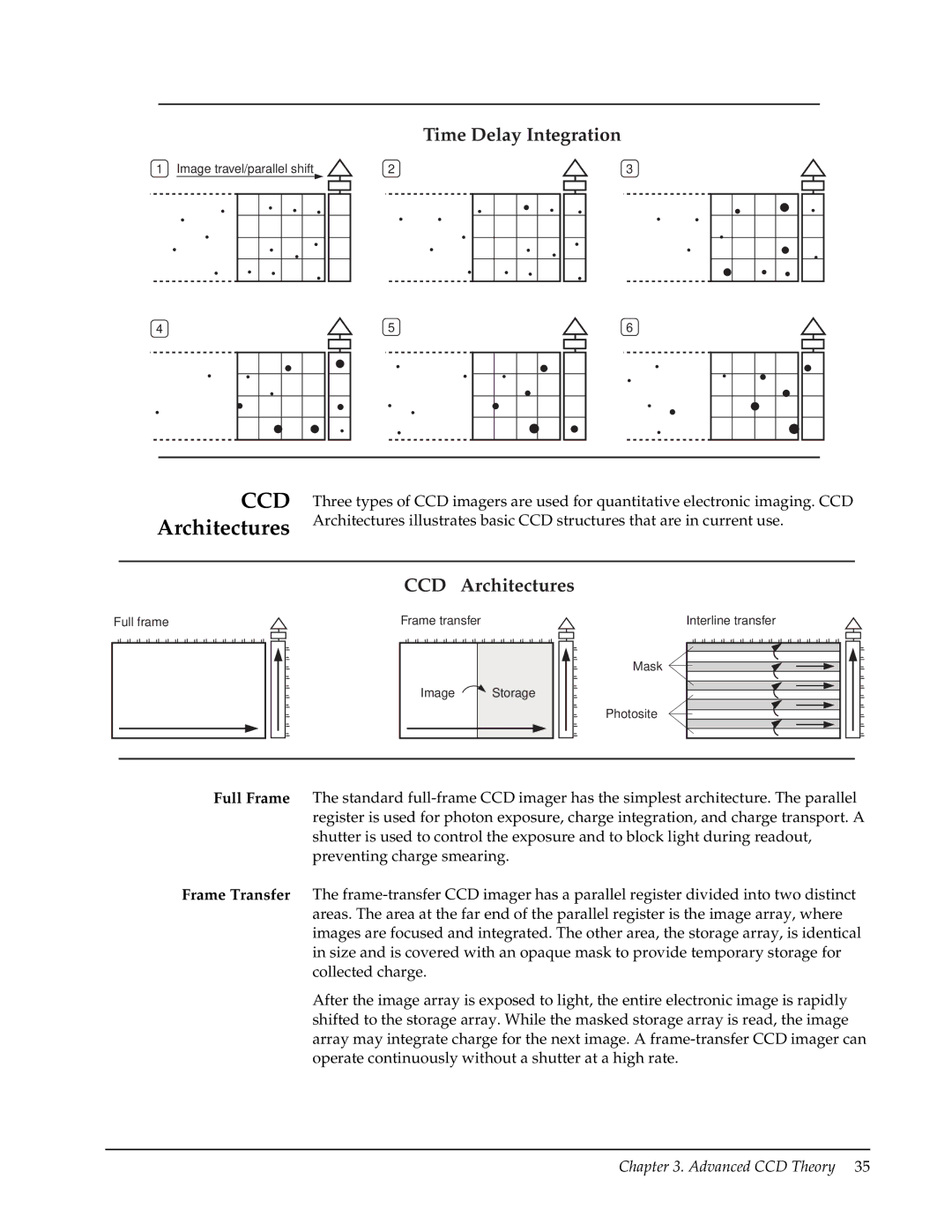
Time Delay Integration
1 Image travel/parallel shift | 2 | 3 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
CCD Architectures
Three types of CCD imagers are used for quantitative electronic imaging. CCD Architectures illustrates basic CCD structures that are in current use.
CCD Architectures
Full frame | | Frame transfer |
| | |
| | |
Interline transfer
Mask
Photosite
Full Frame The standard full-frame CCD imager has the simplest architecture. The parallel register is used for photon exposure, charge integration, and charge transport. A shutter is used to control the exposure and to block light during readout, preventing charge smearing.
Frame Transfer The frame-transfer CCD imager has a parallel register divided into two distinct areas. The area at the far end of the parallel register is the image array, where images are focused and integrated. The other area, the storage array, is identical in size and is covered with an opaque mask to provide temporary storage for collected charge.
After the image array is exposed to light, the entire electronic image is rapidly shifted to the storage array. While the masked storage array is read, the image array may integrate charge for the next image. A frame-transfer CCD imager can operate continuously without a shutter at a high rate.
Chapter 3. Advanced CCD Theory 35