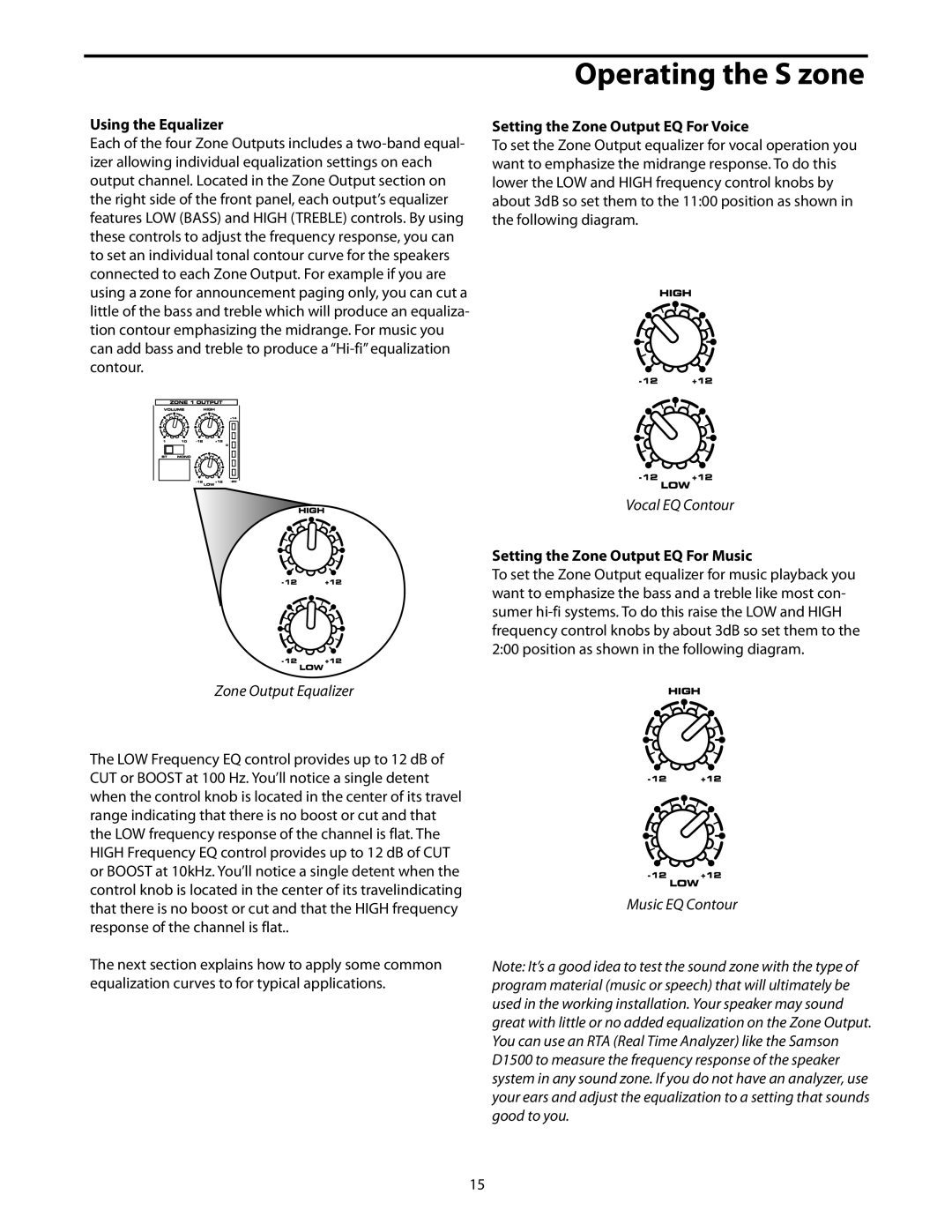
Using the Equalizer
Each of the four Zone Outputs includes a
Operating the S zone
Setting the Zone Output EQ For Voice
To set the Zone Output equalizer for vocal operation you want to emphasize the midrange response. To do this lower the LOW and HIGH frequency control knobs by about 3dB so set them to the 11:00 position as shown in the following diagram.
Zone Output Equalizer
The LOW Frequency EQ control provides up to 12 dB of CUT or BOOST at 100 Hz. You’ll notice a single detent when the control knob is located in the center of its travel range indicating that there is no boost or cut and that the LOW frequency response of the channel is flat. The HIGH Frequency EQ control provides up to 12 dB of CUT or BOOST at 10kHz. You’ll notice a single detent when the control knob is located in the center of its travel indicating that there is no boost or cut and that the HIGH frequency response of the channel is flat.
The next section explains how to apply some common equalization curves to for typical applications.
Vocal EQ Contour
Setting the Zone Output EQ For Music
To set the Zone Output equalizer for music playback you want to emphasize the bass and a treble like most con- sumer
Music EQ Contour
Note: It’s a good idea to test the sound zone with the type of program material (music or speech) that will ultimately be used in the working installation. Your speaker may sound great with little or no added equalization on the Zone Output. You can use an RTA (Real Time Analyzer) like the Samson D1500 to measure the frequency response of the speaker system in any sound zone. If you do not have an analyzer, use your ears and adjust the equalization to a setting that sounds good to you.
15