Parts and features
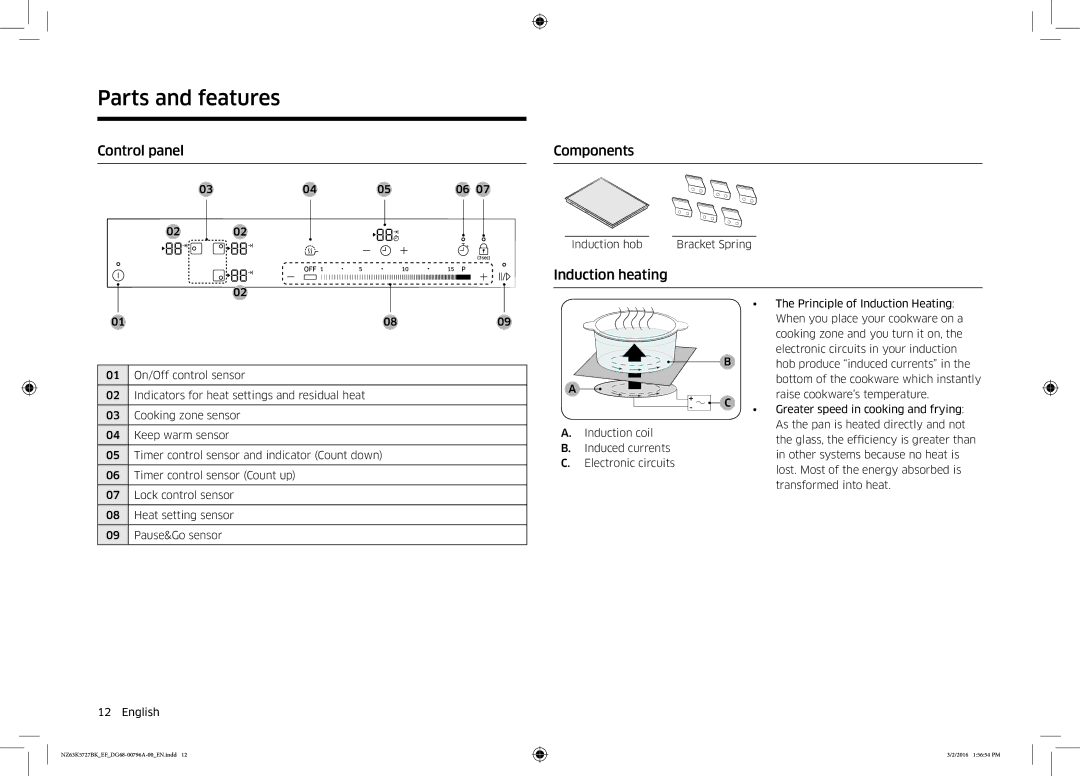
Control panel
03 | 04 | 05 | 06 07 |
02 | 02 |
|
|
| 02 |
|
|
Components
Induction hob |
| Bracket Spring |
Induction heating
| 01 | 08 | 09 |
Parts |
|
|
|
01 | On/Off control sensor |
| |
and |
|
|
|
02 | Indicators for heat settings and residual heat |
| |
|
|
| |
features | 03 | Cooking zone sensor |
|
|
|
| |
04 | Keep warm sensor |
| |
|
|
| |
05 | Timer control sensor and indicator (Count down) |
| |
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| 06 | Timer control sensor (Count up) |
|
|
|
|
|
| 07 | Lock control sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
| 08 | Heat setting sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
| 09 | Pause&Go sensor |
|
|
|
|
|
12 English
A![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
A.Induction coil
B.Induced currents
C.Electronic circuits
•The Principle of Induction Heating: When you place your cookware on a cooking zone and you turn it on, the
electronic circuits in your induction
Bhob produce “induced currents” in the bottom of the cookware which instantly
C |
| raise cookware’s temperature. | |
• | Greater speed in cooking and frying: | ||
| |||
|
| As the pan is heated directly and not | |
|
| the glass, the efficiency is greater than | |
|
| in other systems because no heat is | |
|
| lost. Most of the energy absorbed is | |
|
| transformed into heat. |
3/2/2016 1:56:54 PM