VERTICAL VENT THROUGH ROOF
This unit is approved for venting through the roof with the type vent terminal that is included with the unit. A proper flashing or “BOOT” should be used to seal the pipe where it exits the roof.
The total vent system should not exceed that which is specified in the table on page 9.
All of the pipe should be secured as per the instructions in the “INSTALLATION OF VENT SYSTEM” on page 9.
VERTICAL VENT TERMINATION
RESTRICTIONS
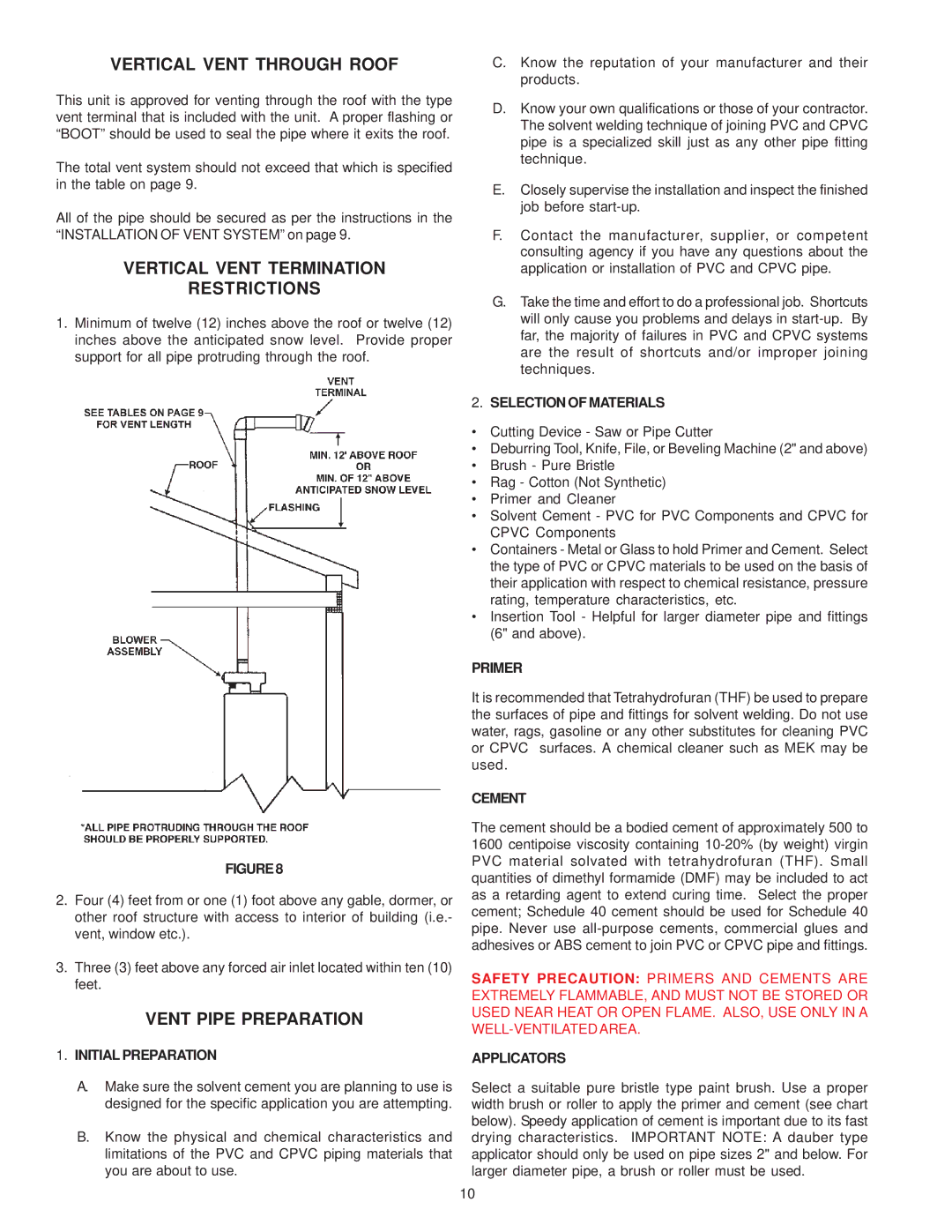
1.Minimum of twelve (12) inches above the roof or twelve (12) inches above the anticipated snow level. Provide proper support for all pipe protruding through the roof.
FIGURE8
2.Four (4) feet from or one (1) foot above any gable, dormer, or other roof structure with access to interior of building (i.e.- vent, window etc.).
3.Three (3) feet above any forced air inlet located within ten (10) feet.
VENT PIPE PREPARATION
1.INITIAL PREPARATION
C.Know the reputation of your manufacturer and their products.
D.Know your own qualifications or those of your contractor. The solvent welding technique of joining PVC and CPVC pipe is a specialized skill just as any other pipe fitting technique.
E.Closely supervise the installation and inspect the finished job before
F.Contact the manufacturer, supplier, or competent consulting agency if you have any questions about the application or installation of PVC and CPVC pipe.
G.Take the time and effort to do a professional job. Shortcuts will only cause you problems and delays in
2.SELECTION OF MATERIALS
•Cutting Device - Saw or Pipe Cutter
•Deburring Tool, Knife, File, or Beveling Machine (2" and above)
•Brush - Pure Bristle
•Rag - Cotton (Not Synthetic)
•Primer and Cleaner
•Solvent Cement - PVC for PVC Components and CPVC for CPVC Components
•Containers - Metal or Glass to hold Primer and Cement. Select the type of PVC or CPVC materials to be used on the basis of their application with respect to chemical resistance, pressure rating, temperature characteristics, etc.
•Insertion Tool - Helpful for larger diameter pipe and fittings (6" and above).
PRIMER
It is recommended that Tetrahydrofuran (THF) be used to prepare the surfaces of pipe and fittings for solvent welding. Do not use water, rags, gasoline or any other substitutes for cleaning PVC or CPVC surfaces. A chemical cleaner such as MEK may be used.
CEMENT
The cement should be a bodied cement of approximately 500 to 1600 centipoise viscosity containing
SAFETY PRECAUTION: PRIMERS AND CEMENTS ARE EXTREMELY FLAMMABLE, AND MUST NOT BE STORED OR USED NEAR HEAT OR OPEN FLAME. ALSO, USE ONLY IN A
APPLICATORS
A.Make sure the solvent cement you are planning to use is designed for the specific application you are attempting.
B.Know the physical and chemical characteristics and limitations of the PVC and CPVC piping materials that you are about to use.
Select a suitable pure bristle type paint brush. Use a proper width brush or roller to apply the primer and cement (see chart below). Speedy application of cement is important due to its fast drying characteristics. IMPORTANT NOTE: A dauber type applicator should only be used on pipe sizes 2" and below. For larger diameter pipe, a brush or roller must be used.
10