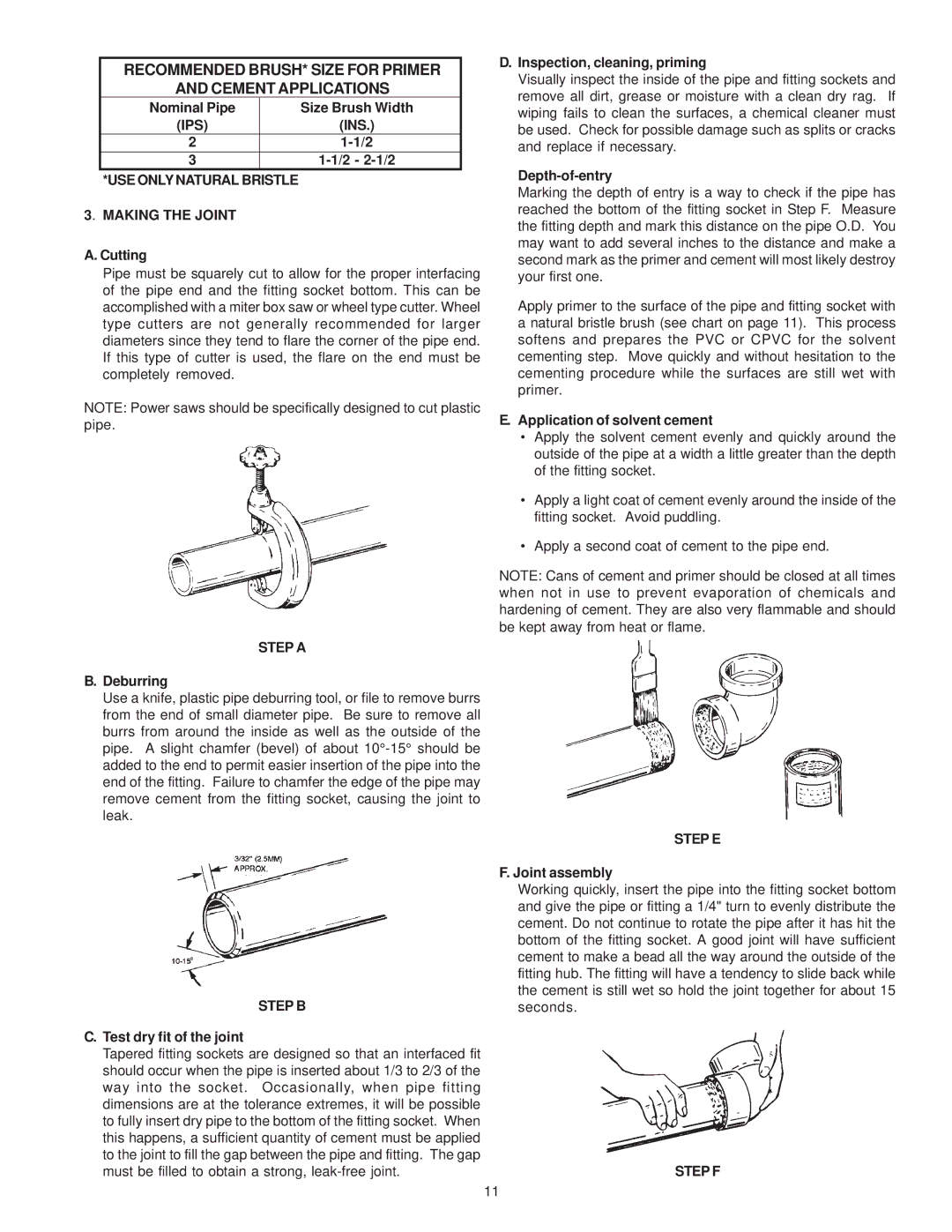
| RECOMMENDED BRUSH* SIZE FOR PRIMER | ||
| AND CEMENT APPLICATIONS | ||
| Nominal Pipe |
| Size Brush Width |
| (IPS) |
| (INS.) |
| 2 |
| |
| 3 |
| |
| *USE ONLY NATURAL BRISTLE |
| |
3. MAKING THE JOINT |
| ||
A. Cutting
Pipe must be squarely cut to allow for the proper interfacing of the pipe end and the fitting socket bottom. This can be accomplished with a miter box saw or wheel type cutter. Wheel type cutters are not generally recommended for larger diameters since they tend to flare the corner of the pipe end. If this type of cutter is used, the flare on the end must be completely removed.
NOTE: Power saws should be specifically designed to cut plastic pipe.
STEP A
B.Deburring
Use a knife, plastic pipe deburring tool, or file to remove burrs from the end of small diameter pipe. Be sure to remove all burrs from around the inside as well as the outside of the pipe. A slight chamfer (bevel) of about
STEP B
C.Test dry fit of the joint
Tapered fitting sockets are designed so that an interfaced fit should occur when the pipe is inserted about 1/3 to 2/3 of the way into the socket. Occasionally, when pipe fitting dimensions are at the tolerance extremes, it will be possible to fully insert dry pipe to the bottom of the fitting socket. When this happens, a sufficient quantity of cement must be applied to the joint to fill the gap between the pipe and fitting. The gap must be filled to obtain a strong,
D.Inspection, cleaning, priming
Visually inspect the inside of the pipe and fitting sockets and remove all dirt, grease or moisture with a clean dry rag. If wiping fails to clean the surfaces, a chemical cleaner must be used. Check for possible damage such as splits or cracks and replace if necessary.
Depth-of-entry
Marking the depth of entry is a way to check if the pipe has reached the bottom of the fitting socket in Step F. Measure the fitting depth and mark this distance on the pipe O.D. You may want to add several inches to the distance and make a second mark as the primer and cement will most likely destroy your first one.
Apply primer to the surface of the pipe and fitting socket with a natural bristle brush (see chart on page 11). This process softens and prepares the PVC or CPVC for the solvent cementing step. Move quickly and without hesitation to the cementing procedure while the surfaces are still wet with primer.
E.Application of solvent cement
•Apply the solvent cement evenly and quickly around the outside of the pipe at a width a little greater than the depth of the fitting socket.
•Apply a light coat of cement evenly around the inside of the fitting socket. Avoid puddling.
•Apply a second coat of cement to the pipe end.
NOTE: Cans of cement and primer should be closed at all times when not in use to prevent evaporation of chemicals and hardening of cement. They are also very flammable and should be kept away from heat or flame.
STEP E
F. Joint assembly
Working quickly, insert the pipe into the fitting socket bottom and give the pipe or fitting a 1/4" turn to evenly distribute the cement. Do not continue to rotate the pipe after it has hit the bottom of the fitting socket. A good joint will have sufficient cement to make a bead all the way around the outside of the fitting hub. The fitting will have a tendency to slide back while the cement is still wet so hold the joint together for about 15 seconds.
STEP F
11