1 Overview
CAUTION: Data Protector Express security is disabled at installation to simplify the evaluation process. When installing the product in a production environment HP recommends, at a minimum, that you set a user password for the Admin user. Doing so will result in the Administrator prompting the user for a password before starting. See “Setting a User Password” for details.
Concepts
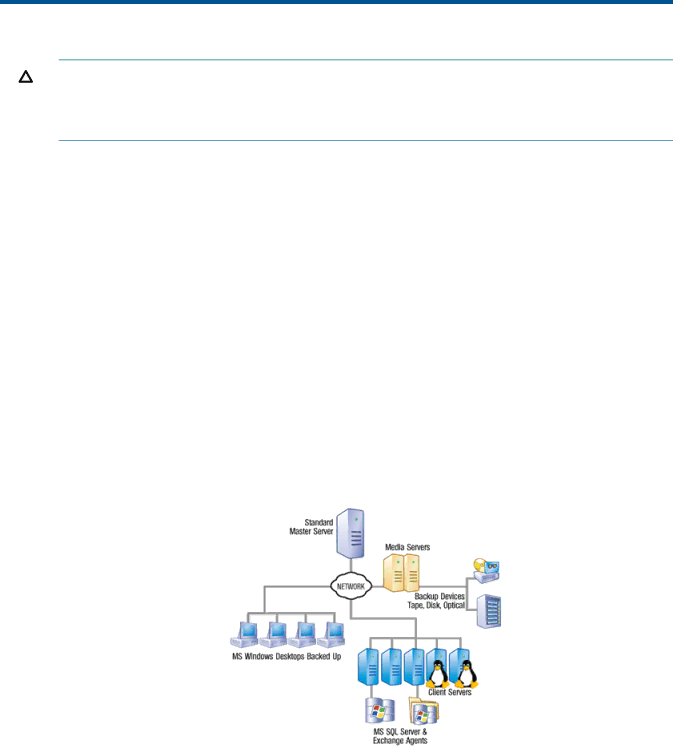
Data Protector Express is designed to operate within your existing network to protect your vital data. Each machine that will be protected must have Data Protector Express installed. One machine acts as the Domain Server which houses the catalog and establishes a Backup Domain. Other machines become clients of the Backup Domain by identifying themselves as clients of the Domain Server during installation.
Data Protector Express can back up data from clients over a network to a backup device attached to a remove machine. A client with an attached device acts as a Media Server.
When a machine is being backed up or restored it is operating the client role. When it is providing access to a backup device it is operating as a Media Server. And when a machine is hosting the catalog it is operating as the Domain Server. A single machine can operate in one or more roles at the same time.
Data on client machines is read and written with agents such as the File System, Windows System State, Microsoft SQL, and Microsoft Exchange agents. The configuration of agents is done on a client by client basis.
A typical installation of Data Protector Express is shown in Figure 1 (page 5).
Figure 1 Basic Architecture
Terminology
The following terms are used throughout this document ...
•Clients— A client is any computer (or Machine) in the Backup Domain other than the Domain Server. This includes file servers, application servers, and user PCs (desktops and laptops). All client computers must have Data Protector Express installed. For licensing purposes, clients are classified as being server or workstation class machines. All clients are considered to be server class clients unless they are running Windows XP, Vista, or Windows 7.
•Backup Domain— A Backup Domain is a collection of computers and backup devices that is managed together as a group. A Backup Domain can encompass an entire company or each
Concepts 5