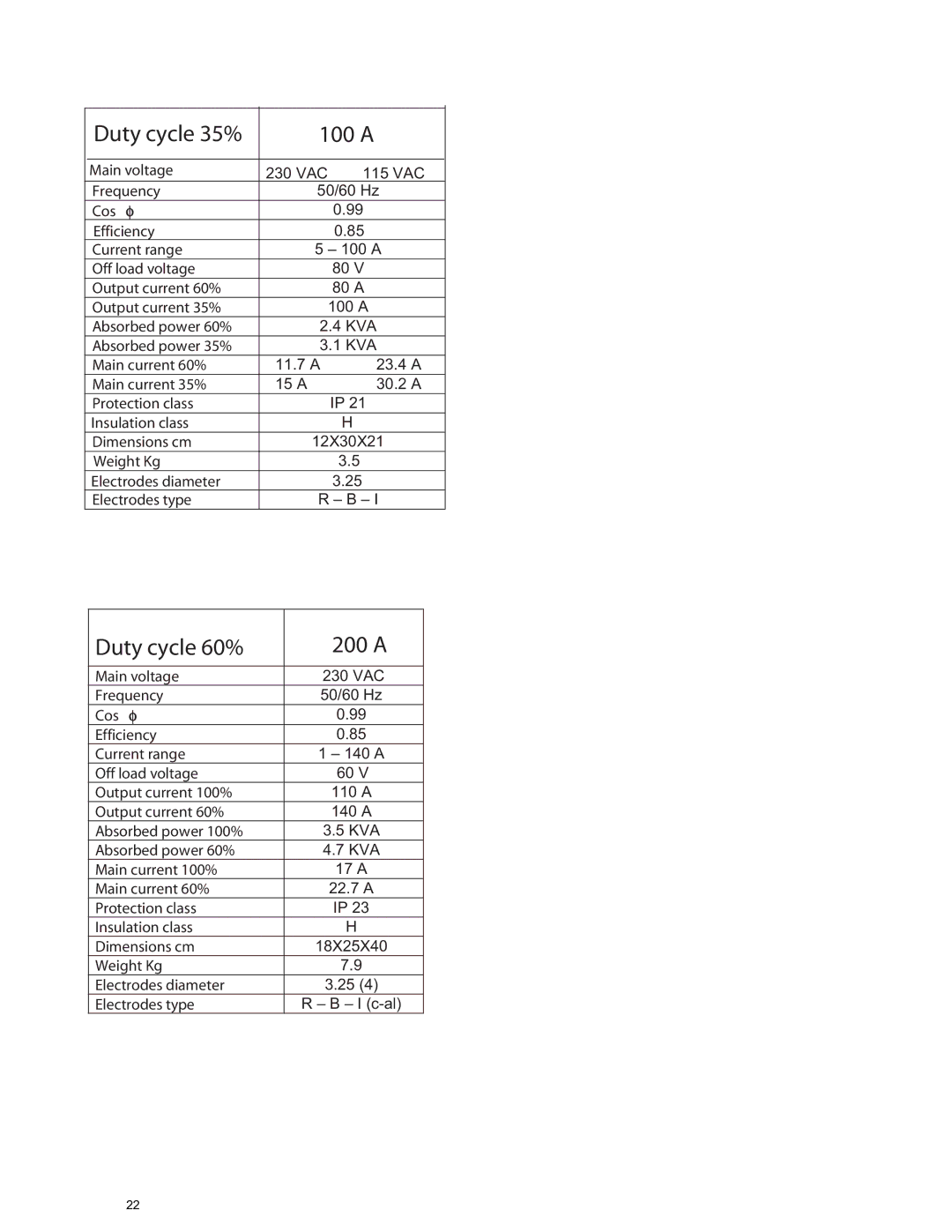
Inverter Power Sources specifications
ARC inverter power sources are essential tools in the field of welding, known for their efficiency, versatility, and advanced technological features. These devices convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC), which allows operators to produce high-quality welds with greater control and stability. The evolution of inverter technology has significantly improved the performance of welding equipment, making ARC inverter power sources a popular choice among professionals in various industries.One of the main features of ARC inverter power sources is their lightweight and compact design. Compared to traditional transformer-based welders, inverter models are significantly smaller and easier to transport, which is particularly beneficial for mobile welding applications. Their portability does not compromise their power output; in fact, many modern inverter welders can deliver high amperage while remaining energy-efficient.
A notable technological advancement in ARC inverter power sources is their use of high-frequency inverter circuits. These circuits enhance the welding process by providing a more stable and consistent arc, reducing the likelihood of defects such as undercutting or spatter. Additionally, the high-frequency operation allows for better control over the heat input, making it easier to weld thin materials without causing warping or burn-through.
Another characteristic of these power sources is their user-friendly interface and adjustable settings. Many models come equipped with digital displays, allowing welders to monitor parameters such as voltage, amperage, and duty cycle in real time. This adaptability ensures that operators can tailor the welding process to suit various materials and thicknesses, improving overall weld quality.
ARC inverter power sources are also designed with built-in safety features, including thermal overload protection and automatic shutdown functions. These safety measures help prevent equipment damage and enhance operator safety, making them suitable for both novice and experienced welders.
Overall, ARC inverter power sources combine advanced technology, ease of use, and robust performance, making them an indispensable asset in the welding industry. As manufacturers continue to innovate, these devices are likely to become even more efficient and versatile, solidifying their place in modern fabrication and construction projects. With their growing range of applications, from automotive repair to heavy industrial work, ARC inverter power sources are revolutionizing the way welding is performed.