4 Using the Notebook PC
 Wireless LAN Connection
Wireless LAN Connection
The optional built-in wireless LAN is a compact easy-to-use wireless Ethernet adapter. Implementing the IEEE 802.11 standard for wireless LAN (WLAN), the optional built-in wireless LAN is capable of fast data transmission rates using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) and Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) technologies on 2.4GHz/5GHz frequencies. The optional built-in wireless LAN is backward compatible with the earlier IEEE 802.11 standards allowing seamless interfacing of wireless LAN standards.
The optional built-in wireless LAN is a client adapter that supports Infrastructure and Ad-hoc modes giving you flexibility on your existing or future wireless network configurations for distances up to 40 meters between the client and the access point.
To provide efficient security to your wireless communication, the optional built-in wireless LAN comes with a 64-bit/128-bit Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) features.
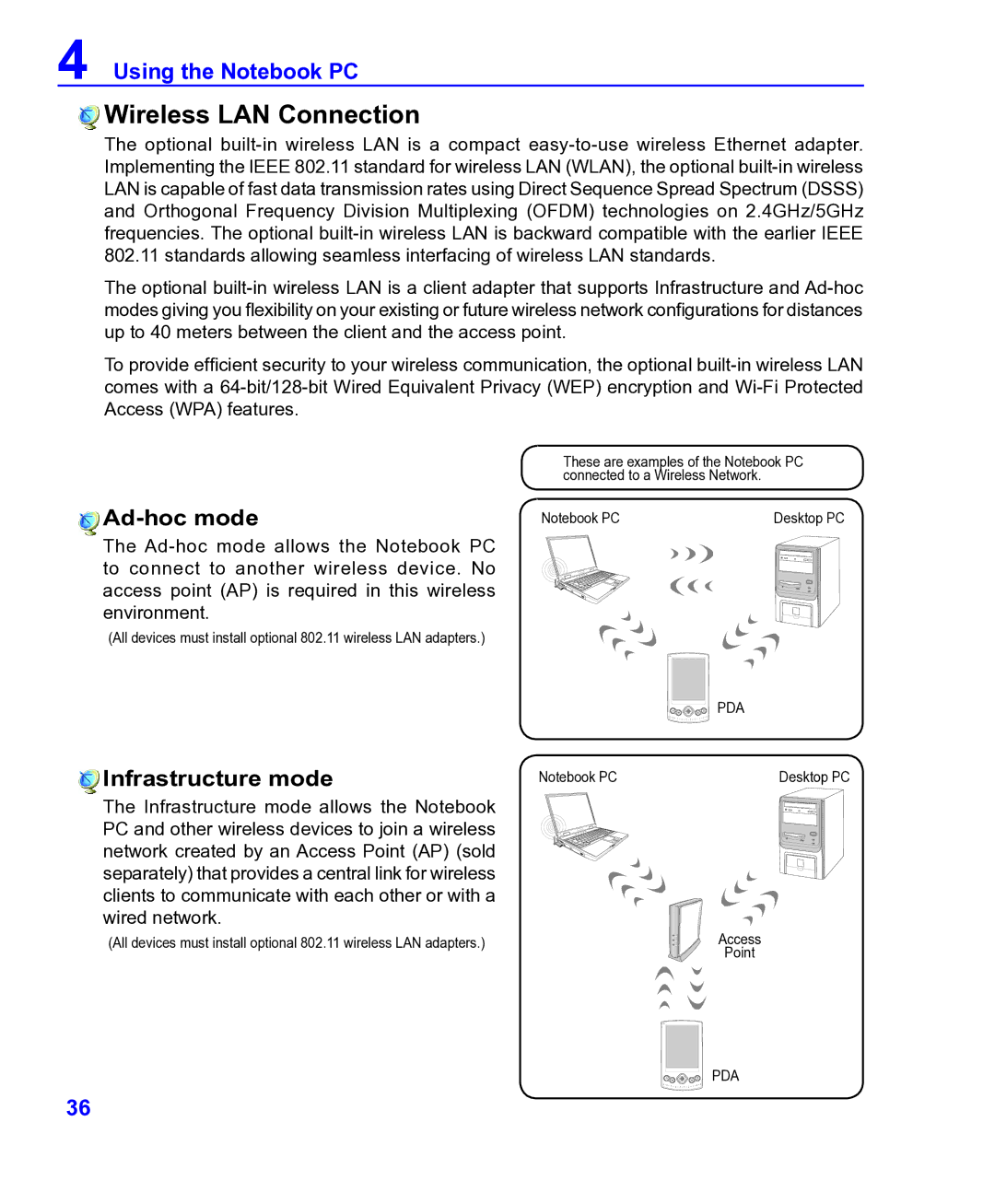
Ad-hoc mode
The Ad-hoc mode allows the Notebook PC to connect to another wireless device. No access point (AP) is required in this wireless environment.
(All devices must install optional 802.11 wireless LAN adapters.)
These are examples of the Notebook PC connected to a Wireless Network.
| | PDA |
Infrastructure mode | Notebook PC | Desktop PC |
The Infrastructure mode allows the Notebook PC and other wireless devices to join a wireless network created by an Access Point (AP) (sold separately) that provides a central link for wireless clients to communicate with each other or with a wired network.
(All devices must install optional 802.11 wireless LAN adapters.) | Access |
| Point |
PDA

 Wireless LAN Connection
Wireless LAN Connection