Operation - Continued
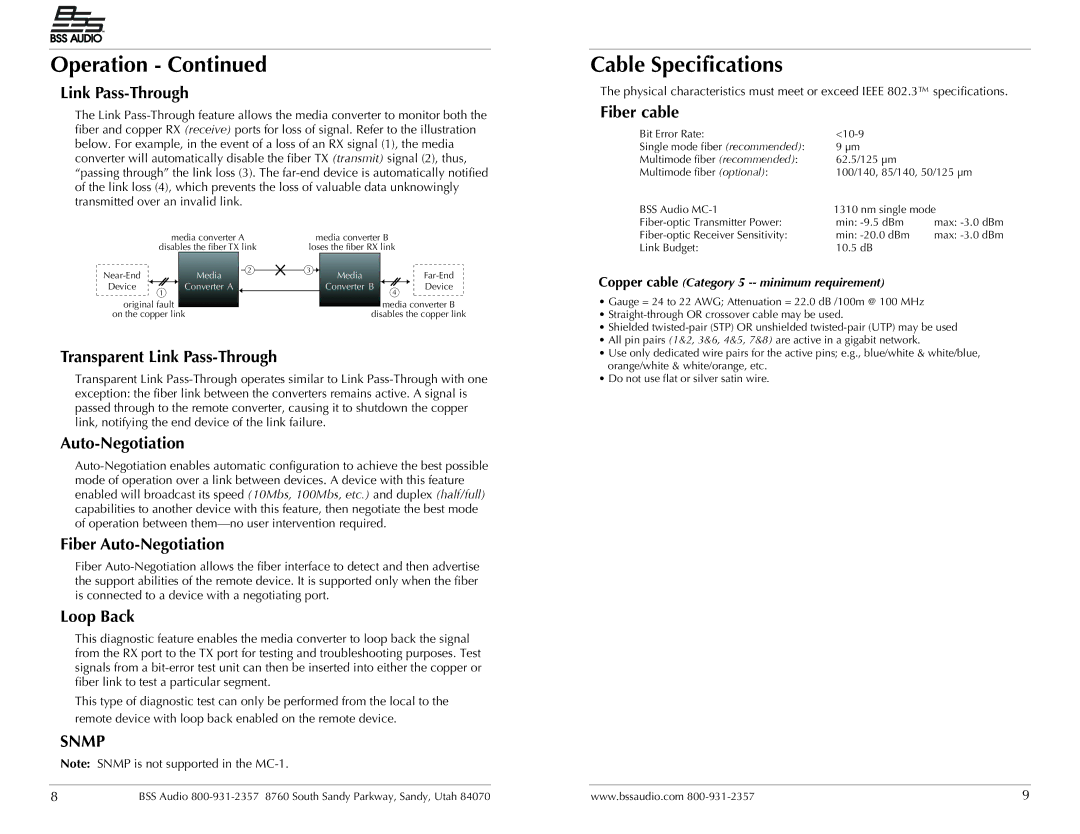
Link Pass-Through
The Link
|
|
| media converter A |
|
| media converter B |
|
| ||||||
|
| disables the fiber TX link | loses the fiber RX link |
|
| |||||||||
|
|
| Media |
|
| 2 | 3 |
| Media |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
| Device | 1 |
| Converter A |
|
|
|
|
| Converter B | 4 |
| Device |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
| original fault |
|
|
|
|
|
| media converter B | ||||||
| on the copper link |
|
|
| disables the copper link | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transparent Link Pass-Through
Transparent Link
Auto-Negotiation
Fiber Auto-Negotiation
Fiber
Loop Back
This diagnostic feature enables the media converter to loop back the signal from the RX port to the TX port for testing and troubleshooting purposes. Test signals from a
This type of diagnostic test can only be performed from the local to the remote device with loop back enabled on the remote device.
SNMP
Note: SNMP is not supported in the
Cable Specifications
The physical characteristics must meet or exceed IEEE 802.3™ specifications.
Fiber cable
Bit Error Rate: |
| |
Single mode fiber (recommended): | 9 µm |
|
Multimode fiber (recommended): | 62.5/125 µm |
|
Multimode fiber (optional): | 100/140, 85/140, 50/125 µm | |
BSS Audio | 1310 nm single mode | |
min: | max: | |
min: | max: | |
Link Budget: | 10.5 dB |
|
Copper cable (Category 5 -- minimum requirement)
•Gauge = 24 to 22 AWG; Attenuation = 22.0 dB /100m @ 100 MHz
•
•Shielded
•All pin pairs (1&2, 3&6, 4&5, 7&8) are active in a gigabit network.
•Use only dedicated wire pairs for the active pins; e.g., blue/white & white/blue, orange/white & white/orange, etc.
•Do not use flat or silver satin wire.
8 | BSS Audio | www.bssaudio.com | 9 |