Service and Appearance Care
Seats and Restraint Systems
Customer Assistance and Information
How to Use This Manual
Canadian Owners
About Driving Your Vehicle
Safety Warnings and Symbols
Index
Vehicle Symbols
Vehicle Damage Warnings
Page
Page
Seats and Restraint Systems
Section Seats and Restraint Systems
Front Seats
Manual Passenger Seat
Four-Way Manual Driver Seat
Six-Way Power Seats
Manual Lumbar Heated Seats
Reclining Seatbacks
Head Restraints
Split Bench Seats
Rear Seats
Rear Seat Operation
Folding or Reclining the Seatbacks
Removing the Split Bench Seat
Up-Level
Base-Level
Replacing the Split Bench Seat
Page
Adjusting the Captain’s Chairs Second Row
Captain Chairs
Removing the Captain’s Chairs
Replacing the Captain’s Chairs
Page
Stowable Seat
Folding the Seatback
Removing the Stowable Seat
Replacing the Stowable Seat
Page
Safety Belts
Safety Belts They Are for Everyone
Why Safety Belts Work
Page
Person keeps going until stopped by something.
Questions and Answers About Safety Belts
How to Wear Safety Belts Properly
Driver Position
Lap-Shoulder Belt
Page
Page
What is wrong with this?
Belt is buckled in the wrong place
Belt is over an armrest
What is wrong with this?
Belt is twisted across the body
Shoulder Belt Height Adjustment
Rear Seat Passengers
Safety Belt Use During Pregnancy
Right Front Passenger Position
Rear Seat Outside Passenger Positions
Lap-Shoulder Belt
Page
To unlatch the belt, just push the button on the buckle
Center Rear Passenger Position
Page
Page
Second Row Center Position
For second row center position do the following
Safety Belt Pretensioners
Safety Belt Extender
What is the proper way to wear safety belts?
Child Restraints
Older Children
Page
Infants and Young Children
Page
What are the different types of add-on child restraints?
Child Restraint Systems
Page
How do child restraints work?
Page
Where to Put the Restraint
Top Strap
Top Strap Anchor Location
Captain’s Chairs
Page
Second Row Center Position Bench Seat with Third Row Seat
Third Row Passenger’s Side Outside Position
Lower Anchorages and Top Tethers for Children Latch System
Page
Securing a Child Restraint Designed for the Latch System
Securing a Child Restraint in a Rear Outside Seat Position
Page
Securing a Child Restraint in a Center Rear Seat Position
Page
Securing a Child Restraint in the Right Front Seat Position
Page
Page
Airbag System
Page
Page
Where Are the Airbags?
Page
Page
When Should an Airbag Inflate?
Page
What Makes an Airbag Inflate?
How Does an Airbag Restrain?
What Will You See After an Airbag Inflates?
Passenger Sensing System
Page
Seat Position on
Page
Page
Servicing Your Airbag-Equipped Vehicle
Adding Equipment to Your Airbag-Equipped Vehicle
Restraint System Check
Checking Your Restraint Systems
Replacing Restraint System Parts After a Crash
Page
Features and Controls
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle
Section Features and Controls
Keys
Be sure you have spare keys
Remote Keyless Entry System
Remote Keyless Entry System Operation
Battery Replacement
Matching Transmitters to Your Vehicle
United States Canada
Doors and Locks
Door Locks
Power Door Locks
Delayed Locking
Programmable Automatic Door Locks
Rear Door Security Locks
Canceling the Rear Door Security Locks
Lockout Protection
Liftgate
Liftgate Release
Liftgate Handle
Windows
Power Windows
Express-Down Window
Content Theft-Deterrent
Theft-Deterrent Systems
Sun Visors
Arming with the Power Lock Switch
Arming with the Remote Keyless Entry Transmitter
PASS-KeyIII
Disarming with Your Key
Disarming with the Remote Keyless Entry Transmitter
PASS-KeyIII Operation
Starting and Operating Your Vehicle
New Vehicle Break-In
Ignition Positions
Retained Accessory Power RAP
Starting Your Engine
Engine Coolant Heater
To Use the Engine Coolant Heater
Automatic Transaxle Operation
Reverse R Use this gear to back up
Warm-Up Shift
Automatic Overdrive D
All-Wheel Drive
Parking Brake
Shifting Into Park P
Leaving Your Vehicle With the Engine Running
Shifting Out of Park P
Torque Lock
Parking Over Things That Burn
Engine Exhaust
Running Your Engine While You Are Parked
Outside Power Mirror
Mirrors
Manual Rearview Mirror
Outside Curb View Assist Mirror
Outside Convex Mirror
Outside Heated Mirrors
Safe and Sound Plan
OnStar Services
OnStar System
Directions and Connections Plan
HomeLink Transmitter
OnStar Personal Calling
OnStar Virtual Advisor
Programming the HomeLink Transmitter
Programming HomeLink
Using HomeLink
Gate Operator and Canadian Programming
Glove Box
Resetting Defaults
Storage Areas
Erasing HomeLink Buttons
Overhead Console
Cupholders
Cell Phone Storage Area
Floor Console Storage Area
Front Armrest Storage Area
Rear Storage Area
Roof Rack System
Rails, making sure to fasten it securely
Page
Convenience Net
Cargo Cover
Rear Convenience Center
Removing the Extended Rear Convenience Center
Reinstalling the Extended Rear Convenience Center
Page
Sunroof
Vehicle Personalization
Memory Seat
Page
Instrument Panel
Driver Information Center DIC
Page
Instrument Panel Overview
Shift Lever. See Automatic Transaxle Operation on
Horn
Hazard Warning Flashers
Other Warning Devices
Tilt Wheel
Turn Signal/Multifunction Lever
Turn and Lane-Change Signals
Turn Signal On Chime
Headlamp High/Low-Beam Changer
Flash-to-Pass
Windshield Wipers
Windshield Washer
Cruise Control
Rear Window Washer/Wiper
Page
Setting Cruise Control
Increasing Speed While Using Cruise Control
Resuming a Set Speed
Using Cruise Control on Hills
Reducing Speed While Using Cruise Control
Passing Another Vehicle While Using Cruise Control
Ending Cruise Control
Exterior Lamps
Daytime Running Lamps DRL
Lamps on Reminder
Automatic Headlamp System
Fog Lamps
Interior Lamps
Instrument Panel Brightness
Interior Lamps Control
Headlamp Exit Delay
Entry Lighting
Delayed Lighting
Exit Lighting
Rear Reading Lamps
Perimeter Lighting
Front Reading Lamps
Cargo Lamp
Battery Run-Down Protection
Instrument Panel Switchbank
Head-Up Display HUD
Low Oil Pressure. See Low Oil Pressure Message on
Page
Fuse is blown. See Fuses and Circuit Breakers on
Ultrasonic Rear Parking Assist Urpa
How the System Works
Description English Metric
Accessory Power Outlets
When the System Does Not Seem to Work Properly
Ashtrays and Cigarette Lighter
Climate Controls
Climate Control System
Operation
Defogging and Defrosting
Dual Climate Control System
Rear Window Defogger
Page
To the defogger grid
Dual Automatic Climate Control System
Automatic Operation
Manual Operation
Defogging and Defrosting
Outlet Adjustment
Operation Tips
Page
Instrument Panel Cluster
Speedometer and Odometer Trip Odometer
Retro-Active Reset
Tachometer
Safety Belt Reminder Light
Airbag Readiness Light
Passenger Airbag Status Indicator
Page
Brake System Warning Light
United States Canada
Engine Coolant Temperature Gage
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
If the Light Is Flashing
If the Light Is On Steady
Emissions Inspection and Maintenance Programs
Highbeam On Light
Fuel Gage
Service Traction System Warning Message
Message Center
Passenger Seatbelt Reminder Message
Traction Active Message Engine Coolant Temperature
If this message comes on and stays on, see your dealer
Low Oil Pressure Message
Low Engine Oil Level Message Change Engine Oil Message
Low Tire Message Door Ajar Warning Message
Rear Hatch Ajar Warning Message
All-Wheel Drive Disable Warning Message
Check Gas Cap Message
PASS-KeyIII Security Message
Low Washer Fluid Warning Message Low Fuel Warning Message
Low Brake Fluid Warning Message Service Vehicle Soon Message
United States Canada
Parking Lamp Warning Message Highbeam Out Warning Message
Compass Calibration
Driver Information Center DIC
Compass Variance
United States shown, Canada similar
Press SET to Calibrate Compass
DIC Controls and Displays
Oil Life System on page 5-19 for more information
Entering Programming Mode
DIC Vehicle Personalization
Headlamp Exit Delay
Interior Lighting Delay
Interior Lighting On
Auto Door Lock/Unlock
Delayed Locking
Remote Door Unlock
Unlock Feedback
Lock Feedback
Seat Recall
Tilt Mirror
Exiting Programming Mode
Audio Systems
Setting the Time
Radio with CD
Radio Data System RDS
XM Satellite Radio Service Playing the Radio
Finding a Station
Setting Preset Stations
Setting the Tone Bass/Treble
Adjusting the Speakers Balance/Fade
Finding a Program Type PTY Station RDS and XM
RDS Messages
Radio Messages
XM Radio Messages
Radio Display Condition Action Required Message
XM Radio Messages cont’d
Playing a CD
CD Messages
Radio with Cassette and CD
Listening to a DVD
XM Satellite Radio Service Playing the Radio
Finding a Station
Setting Preset Stations
Finding a Program Type PTY Station
RDS Messages
Radio Messages
Audio system is acquiring and processing audio and text
XM Radio Messages cont’d
Playing a Cassette Tape
Cassette Tape Messages
CD Adapter Kits
Playing a CD
CD Messages
Radio with Six-Disc CD
XM Satellite Radio Service Playing the Radio
Finding a Station
Setting Preset Stations
Adjusting the Speakers Balance/Fade
Setting Preset PTYs RDS Only
RDS Messages
Radio Messages
XM Radio Messages
XM Radio Messages cont’d
Playing a CD
Playing a Specific Loaded CD
Page
Using Song List Mode
CD Messages
Rear Seat Entertainment System
Parental Control
Headphones
Before You Drive
Battery Replacement
Stereo RCA Jacks
Audio Output
Video Screen
DVD Player
DVD Player Buttons
Ejecting a Disc
Playing a Disc
Stopping and Resuming Playback
Q t, p r, o Directional Control
Remote Control
Remote Control Buttons
Remote control stored in a cool, dry place
Page
Setup Menu
Tips and Troubleshooting Chart
Problem Recommended Action
Quickly press and release
Player to get to auxiliary
Problem Recommended Action
DVD Messages
Cleaning the DVD Player
Cleaning the Video Screen
DVD Distortion
Navigation/Radio System
Rear Seat Audio RSA
Primary Radio Controls
Rear Seat Audio RSA Controls
Theft-Deterrent Feature
Audio Steering Wheel Controls
Care of Your Cassette Tape Player
XM Satellite Radio Service
Radio Reception
FM Stereo
Integrated Windshield Antenna
Care of Your CDs and DVDs
Care of Your CD and DVD Player
XM Satellite Radio Antenna System
136
Section Driving Your Vehicle
Your Driving, the Road, and Your Vehicle
Driving Environment
Your Driving, the Road, and Your Vehicle
Driver Behavior
Vehicle Design
Defensive Driving
Drunken Driving
Page
Page
Control of a Vehicle
Braking
Anti-Lock Brake System ABS
Page
Using Anti-Lock
Braking in Emergencies
Traction Control System TCS
All-Wheel Drive AWD System
Steering Tips
Power Steering
Steering
Driving on Curves
Steering in Emergencies
Off-Road Recovery
Passing
Loss of Control
Skidding
Driving at Night
Driving in Rain and on Wet Roads
Page
Hydroplaning
Some Other Rainy Weather Tips
City Driving
Freeway Driving
Before Leaving on a Long Trip
Fuel, Engine Oil, Other Fluids Have you checked all levels?
Highway Hypnosis
Hill and Mountain Roads
Page
Winter Driving
Driving on Snow or Ice
Page
If You Are Caught in a Blizzard
Page
If You Are Stuck In Sand, Mud, Ice or Snow
Rocking Your Vehicle to Get It Out
Loading Your Vehicle
Tire and Loading Information Label
Steps for Determining Correct Load Limit
Example Label
Example Description Total
Example Description Total
Certification/Tire Label
United States version shown, Canada similar
Towing
Towing Your Vehicle
Recreational Vehicle Towing
Dinghy Towing
Dolly Towing Two-Wheel-Drive Vehicles
Level Control
Towing a Trailer
If You Do Decide To Pull a Trailer
Weight of the Trailer
Weight of the Trailer Tongue
Total Weight on Your Vehicle’s Tires
Hitches
Safety Chains
Trailer Brakes
Driving with a Trailer
Backing Up
Following Distance
Passing
Making Turns
Turn Signals When Towing a Trailer
Driving On Grades
Parking on Hills
When You Are Ready to Leave After Parking on a Hill
Maintenance When Trailer Towing
Trailer Wiring Harness
Page
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
Checking Things Under the Hood
Capacities and Specifications
Service
California Proposition 65 Warning
Doing Your Own Service Work
Gasoline Octane
Fuel
Adding Equipment to the Outside of Your Vehicle
Gasoline Specifications
California Fuel
Additives
Fuels in Foreign Countries
Filling Your Tank
Page
Checking Things Under the Hood
Filling a Portable Fuel Container
Hood Release
To open the hood, do the following
Engine Compartment Overview
Battery. See Battery on
Page
Battery. See Battery on
Engine Oil
Checking Engine Oil
3400 V6 Engine 6L V6 Engine
When to Add Engine Oil
What Kind of Engine Oil to Use
Page
When to Change Engine Oil
Engine Oil Life System
Engine Oil Additives
How to Reset the Engine Oil Life System
What to Do with Used Oil
How to Inspect the Engine Air Cleaner/Filter
Engine Air Cleaner/Filter
When to Inspect the Engine Air Cleaner/Filter
3400 V6 engine shown, 3.6 L V6 engine similar
When to Check and Change Automatic Transaxle Fluid
Automatic Transaxle Fluid
How to Check Automatic Transaxle Fluid
Checking the Fluid Level
Then, without shutting off the engine, do the following
How to Add Automatic Transaxle Fluid
Engine Coolant
What Coolant to Use
Checking Coolant
Adding Coolant
Radiator Pressure Cap
Engine Overheating
If Steam Is Coming From Your Engine
If No Steam Is Coming From Your Engine
Overheated Engine Protection Operating Mode
Cooling System
3400 V6 engine
L V6 engine
How to Add Coolant to the Coolant Recovery Tank
Page
How to Add Coolant to the Radiator
Housing Bypass Tube
Page
Power Steering Fluid
When to Check Power Steering Fluid
Windshield Washer Fluid
How to Check Power Steering Fluid
What Power Steering Fluid to Use
What Washer Fluid to Use
Brakes
Adding Washer Fluid
Brake Fluid
What to Add
Brake Adjustment
Brake Wear
Brake Pedal Travel
Battery
Replacing Brake System Parts
Vehicle Storage
Jump Starting
Page
Page
Page
Jumper Cable Removal
How to Check Lubricant
Transfer Case Power Transfer Unit
When to Check Lubricant
All-Wheel Drive
Carrier Assembly-Differential Rear Drive Module
When to Check and Change Lubricant
Bulb Replacement
Headlamps, Front Turn Signal, Sidemarker, and Parking Lamps
Halogen Bulbs
Page
Front Turn Signal, Sidemarker and Parking Lamps
Taillamps, Turn Signal, and Stoplamps
Taillamps and Back-Up Lamps
Windshield Wiper Blade Replacement
Replacement Bulbs
Exterior Lamp Bulb Number
Page
Tires
Tire Sidewall Labelling
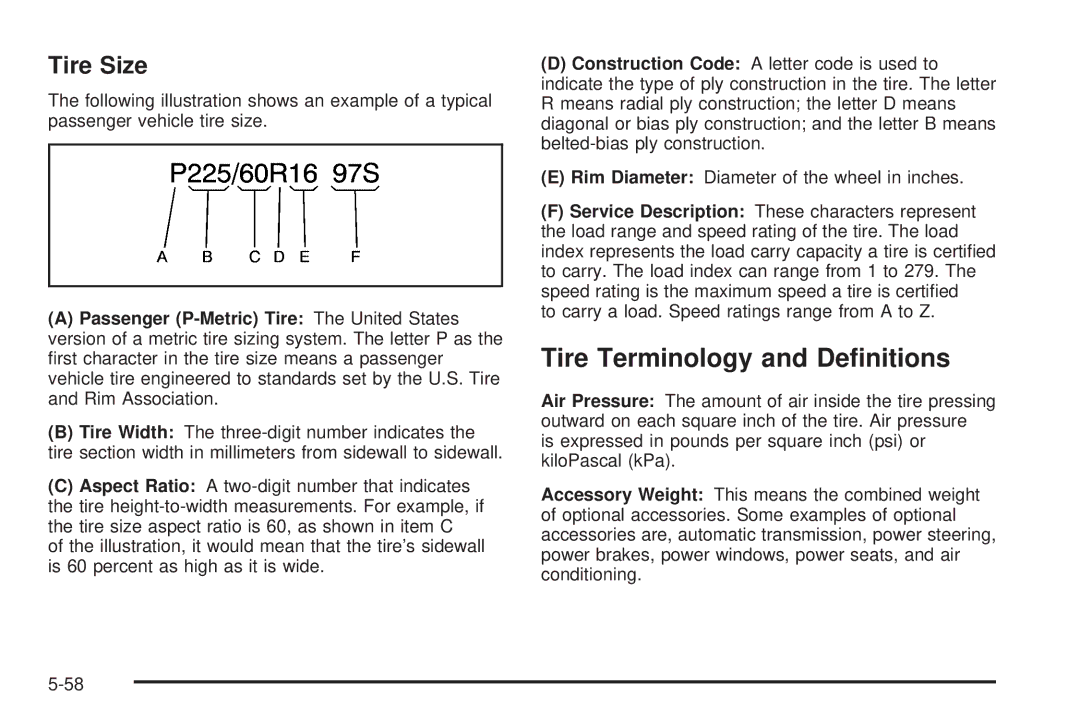
Passenger P-Metric Tire Example
Compact Spare Tire Example
If a Tire Goes Flat on
Tire Terminology and Definitions
Tire Size
From driving. See Inflation Tire Pressure on
Page
When to Check
Inflation Tire Pressure
How to Check
Check Tire Pressure System
Page
Tire Inspection and Rotation
When It Is Time for New Tires
Buying New Tires
Treadwear
Treadwear 200 Traction AA Temperature a
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
Traction AA, A, B, C
Wheel Replacement
Temperature A, B, C
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
Used Replacement Wheels
Accessory Inflator
Tire Chains
Time only
If a Tire Goes Flat
Changing a Flat Tire
Page
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools
Compact Spare Tire
Page
Page
Flat Tire and Installing the Spare Tire on
Page
Removing the Flat Tire and Installing the Spare Tire
Page
Page
Page
Secondary Latch System
All-wheel-drive Vehicle shown
Front-wheel-drive Vehicle shown
Page
Storing a Flat or Spare Tire and Tools
Page
Storing the Flat Tire Vehicles with a Stowable Seat
Hook
Storing the Spare Tire and Tools
Page
Compact Spare Tire
All-Wheel Drive
Appearance Care
Fabric/Carpet
Using Cleaner on Fabric
Special Fabric Cleaning Problems
Instrument Panel
Vinyl
Leather
Interior Plastic Components
Weatherstrips
Care of Safety Belts
Glass Surfaces
Washing Your Vehicle
Cleaning Exterior Lamps/Lenses
Finish Care
Windshield, Backglass, and Wiper Blades
Aluminum or Chrome-Plated Wheels
Tires
Finish Damage
Underbody Maintenance
Sheet Metal Damage
Chemical Paint Spotting
Vehicle Care/Appearance Materials
Description Usage
Vehicle Identification Number VIN
Service Parts Identification Label
Vehicle Identification
Engine Identification
Electrical System
Headlamp Wiring
Power Windows and Other Power Options
Add-On Electrical Equipment
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
Floor Console Fuse Block
Fuse Usage
Underhood Fuse Block
Relay Usage
DVD
Automatic Transaxle Shift Lock
Engine Control Module ECM
Air Conditioning, Defogger
Capacities and Specifications
Engine Specifications
Engine Oil with Filter
Engine VIN Code Transaxle Spark Plug Gap
114
Section Maintenance Schedule
Using Your Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance Requirements Your Vehicle and the Environment
Introduction
Page
Scheduled Maintenance
Scheduled Maintenance
Service Maintenance
Additional Required Services
Additional Required Services
Maintenance Footnotes
At Each Fuel Fill
Owner Checks and Services
To your engine not covered by your warranty
Engine Oil Level Check
At Least Once a Month
At Least Once a Year
Automatic Transaxle Shift Lock Control System Check
Ignition Transaxle Lock Check
Underbody Flushing Service
Parking Brake and Automatic Transaxle Park P Mechanism Check
Recommended Fluids Lubricants
Usage Fluid/Lubricant
Engine Oil Filter
Normal Maintenance Replacement Parts
Part GM Part Number ACDelco Part Number
Spark Plugs
Maintenance Record
Maintenance Record
Maintenance Record cont’d
Maintenance Record cont’d
Section Customer Assistance and Information
Customer Satisfaction Procedure
Customer Assistance and Information
Online Owner Center
Online Owner Center allows you to
United States Customer Assistance
Customer Assistance for Text Telephone TTY Users
Customer Assistance Offices
Canada Customer Assistance
GM Mobility Reimbursement Program
Overseas Customer Assistance
Dealer Locator Service
Roadside Assistance Program
Courtesy Transportation
Canadian Roadside Assistance
Transportation Options
Scheduling Service Appointments
Shuttle Service
Public Transportation or Fuel Reimbursement
Additional Program Information
Courtesy Rental Vehicle
Vehicle Data Collection and Event Data Recorders
Reporting Safety Defects
Reporting Safety Defects to the United States Government
Service Publications Ordering Information
Reporting Safety Defects to the Canadian Government
Reporting Safety Defects to General Motors
Service Bulletins
Owner’s Information
Current and Past Model Order Forms
Order Toll Free Monday-Friday 800 AM 600 PM Eastern Time
Page
Antenna, XM Satellite Radio Antenna System
Setting the Time Theft-Deterrent Feature
Charging System Indicator Message
Cleaning Tires
Door Programmable Automatic Door Locks
Windshield Wiper
Hood Checking Things Under Release Horn
135
Page
130
Rear Seat Audio
Rear Seat Entertainment System
101
Specifications, Capacities
Understanding Radio Reception
DIC