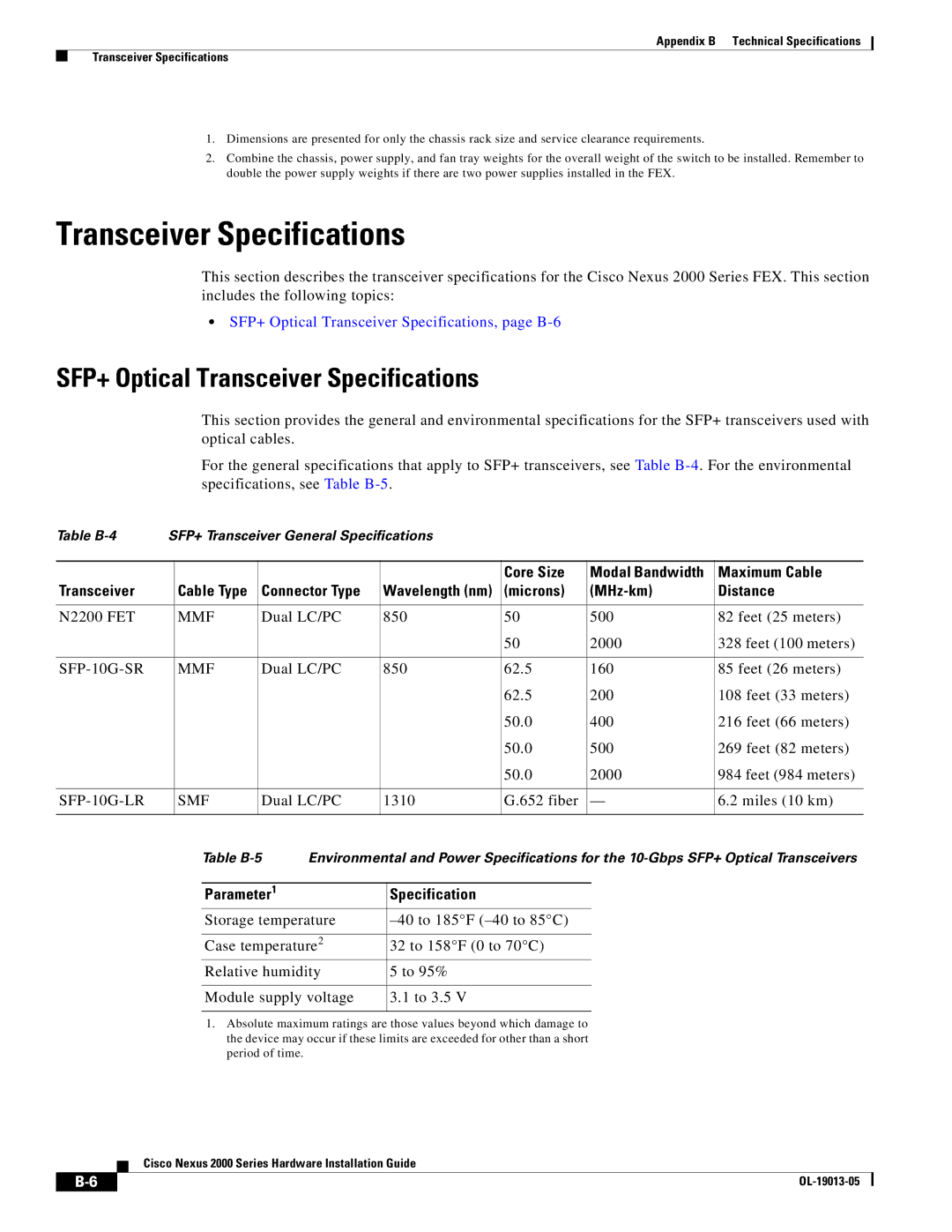
2000 specifications
In the year 2000, Cisco Systems, a leading technology company, was at the forefront of networking and communication solutions. With a rich history of innovation, Cisco solidified its position as a global leader in providing advanced networking technologies, hardware, and software.One of the most significant features of Cisco in 2000 was its comprehensive portfolio of routers and switches. The company was known for its powerful routers, which were essential for managing internet traffic efficiently. Cisco’s Catalyst series of switches provided high levels of performance and scalability, enabling companies to build robust local area networks (LANs). These devices supported Ethernet technologies and catered to the growing demands of businesses for faster and more reliable connectivity.
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, the internet was experiencing rapid growth, and Cisco capitalized on this surge by introducing technologies that facilitated internet protocol (IP) networking. Its focus on developing IP-based solutions allowed businesses to integrate voice, video, and data services seamlessly over a single network. This was a significant advancement known as convergence, fundamentally changing how organizations approached communication.
Another characteristic of Cisco in 2000 was its commitment to security. As businesses began to increase their reliance on the internet, the risks associated with cyber threats also grew. Cisco developed security solutions such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems to help protect networks from potential attacks. The introduction of the Cisco Secure Network Architecture laid the foundation for comprehensive network security strategies.
Cisco also emphasized research and development, consistently investing in new technologies and innovations. The company was a pioneer in developing optical networking solutions, which enabled faster data transmission over long distances. This was crucial for supporting the growing bandwidth demands of the era.
Furthermore, Cisco’s collaboration with various technology partners and its global presence allowed it to provide customers with tailored solutions to meet diverse needs across different industries. The introduction of certification programs, like the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA), helped create a skilled workforce equipped to deploy and manage Cisco technologies effectively.
In summary, Cisco Systems in 2000 showcased a blend of powerful routing and switching capabilities, a commitment to internet security, and innovative solutions that paved the way for future networking technologies. Its focus on convergence and relentless drive for high-performance networking made it a vital player in the evolving landscape of technology during this period.