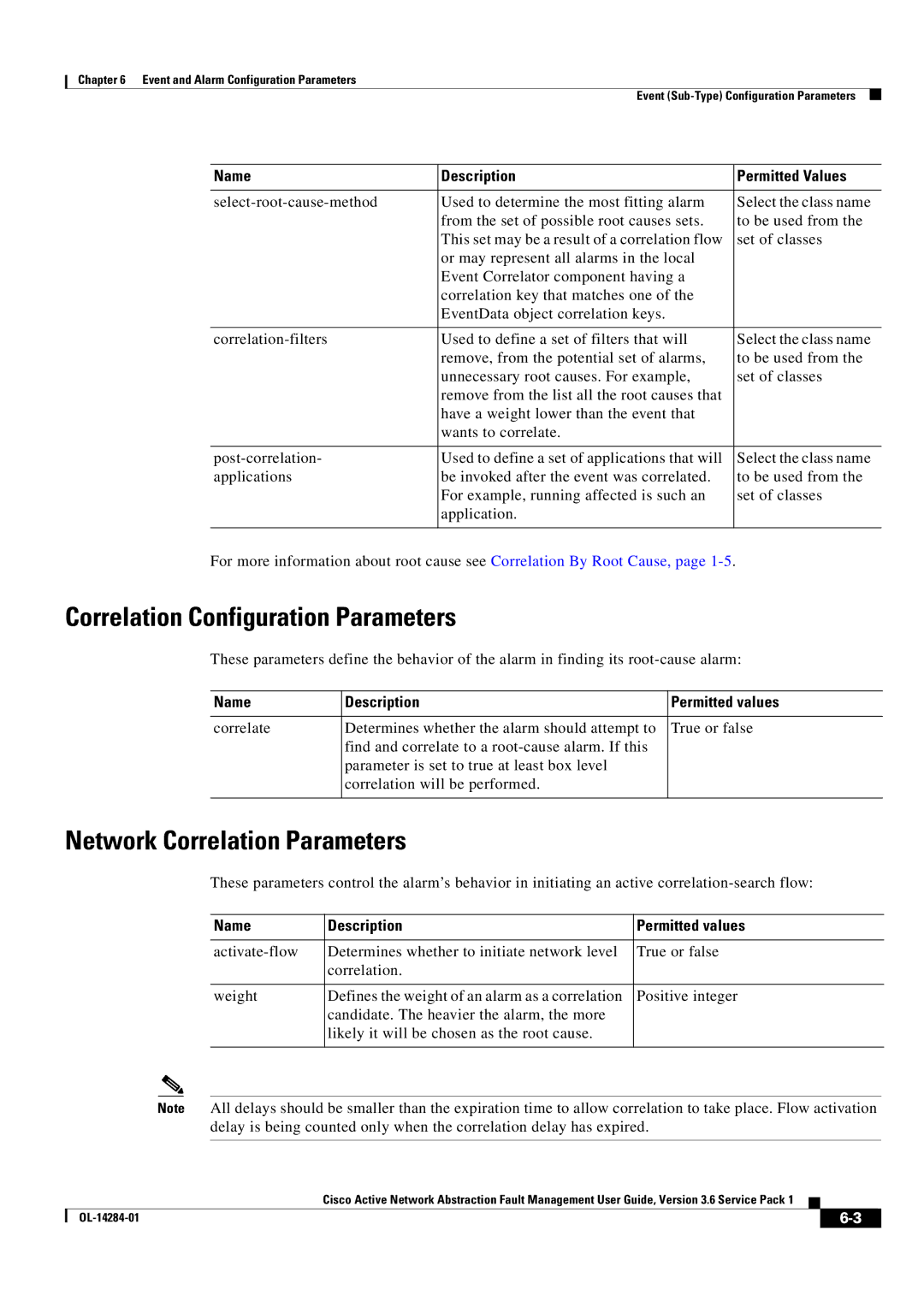
3.6 specifications
Cisco Systems 3.6 marks a significant advancement in network technology, presenting an innovative suite of features and capabilities designed to enhance performance, security, and flexibility for modern networks. As a leader in networking solutions, Cisco continues to evolve its offerings, ensuring they meet the demands of businesses operating in increasingly complex environments.One of the standout features of Cisco Systems 3.6 is the introduction of enhanced automation capabilities. Automation reduces the manual effort required for network management, allowing IT teams to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine maintenance. The system leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to analyze network behavior, detect anomalies, and suggest optimizations, which enhances operational efficiency and uptime.
In terms of security, Cisco Systems 3.6 integrates robust cybersecurity measures directly into its architecture. It incorporates Cisco's SecureX framework, which provides centralized visibility and control across the entire security stack. This feature allows organizations to respond rapidly to threats, leveraging threat intelligence and automated response mechanisms to mitigate risks effectively.
Another notable characteristic is improved compatibility with cloud environments. With the rise of hybrid cloud models, Cisco Systems 3.6 offers seamless integration capabilities that enable businesses to connect their on-premises networks with public and private cloud infrastructures. This ensures greater flexibility and enhanced performance for cloud-based applications.
Cisco also emphasizes software-defined networking (SDN) with its updated platform. This approach allows for greater agility, enabling network administrators to programmatically manage resources through a centralized interface. SDN facilitates rapid deployment of services and applications, optimizing the overall user experience.
Cisco Systems 3.6 also boasts enhanced collaboration tools, fostering improved communication across teams. Featuring advanced video conferencing and messaging capabilities, it enhances productivity and streamlines processes, regardless of employee location. These tools are designed to support remote work environments, which have become increasingly important in today's business landscape.
Furthermore, energy efficiency is a core aspect of Cisco Systems 3.6. The system is designed to optimize power consumption and reduce overall operating costs, aligning with global sustainability goals. The efficient design prioritizes environmentally friendly practices while still delivering high performance.
In conclusion, Cisco Systems 3.6 represents a comprehensive evolution in networking technology, focusing on automation, security, cloud integration, SDN, collaboration, and energy efficiency. These features position Cisco as a pivotal player in supporting organizations as they navigate the complexities of digital transformation and the future of networking.